PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
REV.-A
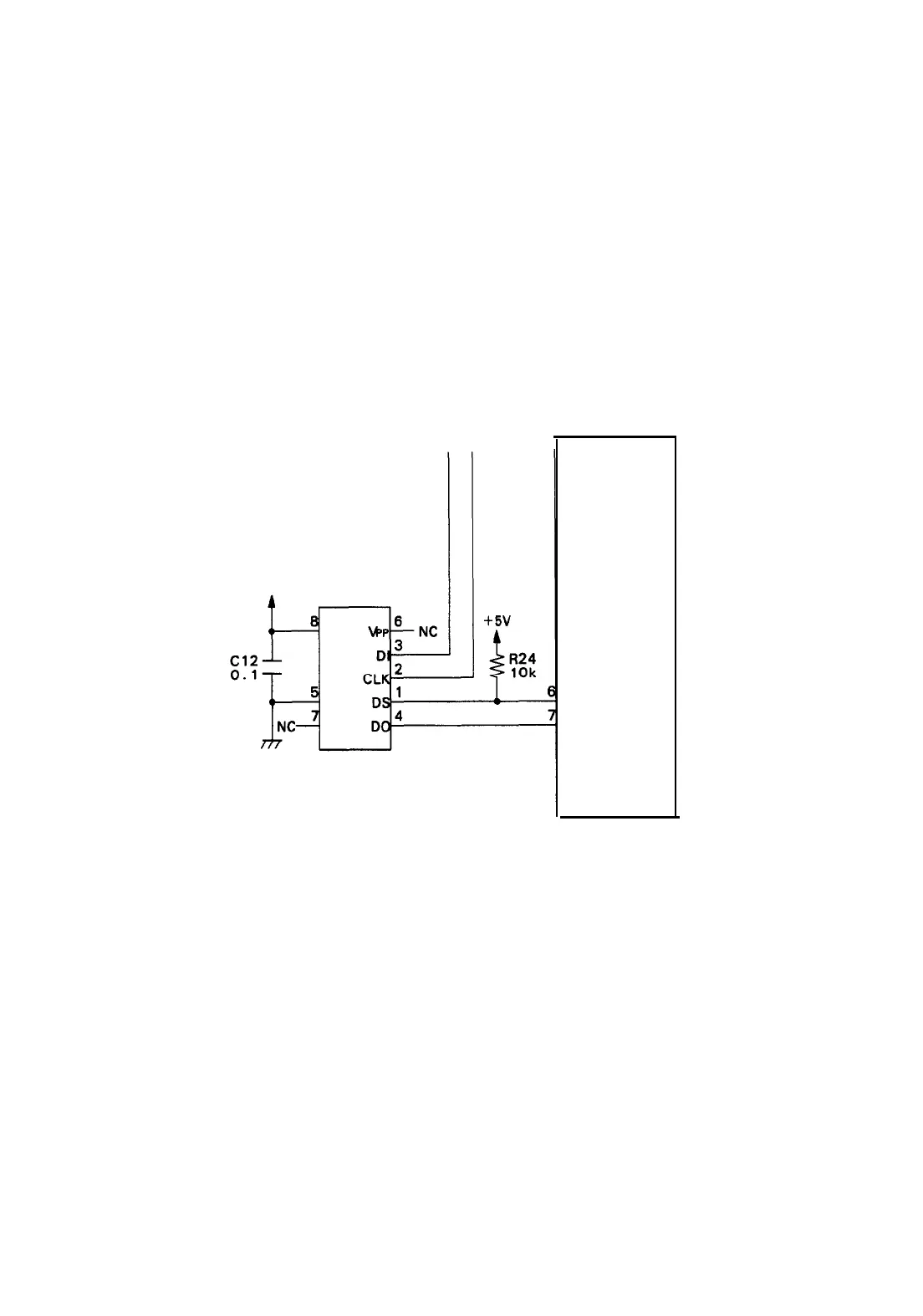
2.3.9 EEPROM CIRCUIT
The EEPROM can store the position of continuously fed paper, so that this information can be maintained
even if power goes off. Figure 2-70 shows the EEPROM circuit. Note that this is external to the CPU’s memory
space.
In order to write to the EEPROM, CPU port PA5 goes HIGH. Once the EEPROM has been selected, the
data to be sent is set in bank line B2, and is fed bit-by-bit to the EEPROM in line with rising pulses from
bank line B1’s clock. Data is read, bit-by-bit, in line with falling clock pulses. The EEPROM receives com-
mands to indicate whether to read or write data, and to indicate addresses.
B2 B1
CPU
µPD
7810HG
(5B)
PA5
PA6
Figure 2-70. EEPROM Circuit
2-64
LQ-510

 Loading...
Loading...