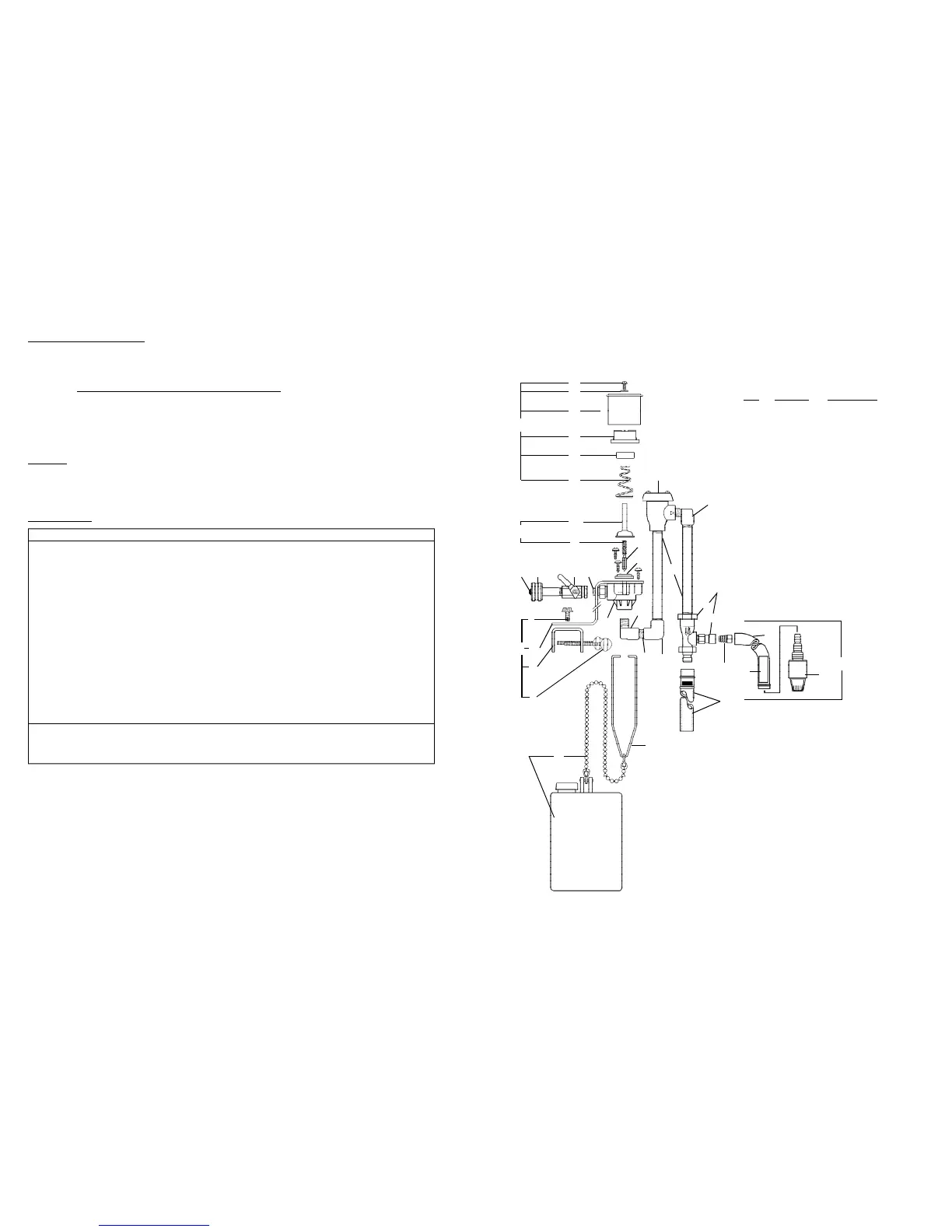
HydroMinder Model 511 Parts Diagram/List
1 2 3 4
i
h
k
m
6
n
p
q
r
9
13
18
x
KEY PART NO. DESCRIPTION
1 238100 strainer washer
2 506500 hose swivel
3 502000 ball valve
4 360900 nipple
5 10080500 magnet parts kit
a. screw
b. washer
c. magnet cover
d. magnet cap
e. magnet
f. magnet spring
g. magnet yoke
6 5030-K mounting bracket kit
(specify model 511)
h. Z bracket
i. U clamp
j. lockwasher (not shown)
k. screw
m.thumbscrew
7 665520 valve parts kit
n. valve guide ("bonnet")
p. armature spring
q. armature
r. diaphram
8 520000 water valve body
9 505600 street elbow
10 519000 close nipple, 1/4"
11 506000 elbow
12 505900 nipple, 6"
13 506300 vacuum breaker
14 440121 eductor assembly
440100 s. eductor body only
440101 t. suction stub only
15 690015 metering tip (kit)
16 5057-A discharge tube assembly
17 5058-9A suction tube assembly
505809 u. tubing, 1/2" x 9'
250006 v. ceramic weight
10076301 w. foot valve, Viton
250700 (foot valve & weight)
18 5043-A float & chain assembly
507200 x. bead chain only
5g
8
9
10
11
12
14
s
t
u
17
15
v
w
16
5
a
b
c
d
e
f
7
Measurement of Concentration:
You can determine the dispensed water-to-product ratio for any metering tip size and product viscosity. All that is required
is to operate the primed dispenser for a minute or so and note two things: the amount of dispensed water/product mixture,
and the amount of concentrate used in preparation of the solution dispensed. The water-to-product ratio is then calculated
as follows:
Dilution (X) = Amount of Mixed Solution — Amount of Concentrate Drawn
Amount of Concentrate Drawn
Dilution ratio, then, equals X parts water to one part concentrate (X:1). If the test does not yield the desired ratio, choose
a different tip and repeat the test.
Alternative methods to this test are 1) pH (using litmus paper), and 2) titration. Contact your concentrate supplier for further
information on these alternative methods and the materials required to perform them.
Operation:
Open the water supply ball valve. When the solution in the reservoir reaches the level set by the float, the valve will close.
This will stop the water flow and siphoning of concentrate. When withdrawal of solution from the reservoir causes the level
to drop more than 1-1/2 inches, the valve will open, and the reservoir will be refilled to the previous, pre-set level. This cycle
will be repeated automatically until the supply of concentrate is depleted. The ball valve should be fully closed when
changing metering tips or concentrate container, when reservoir is drained, or when the unit is not in use.
Troubleshooting:
Problem Probable Cause Remedy
1. No discharge a. No water a. Open water inlet
b. Defective magnetic b. Replace assembly
valve assembly
c. Excessive water pressure c. Install regulator if pressure exceeds 85 PSI
2. No concentrate a. Clogged foot valve a. Clean or replace foot valve
draw b. Metering tip or eductor b. Clean* or replace
clogged
c. Low water pressure c. Minimum 25 PSI flowing required
d. Discharge tube or d. Check position: Replace discharge tube if
flooding ring not in place flooding ring is missing.
3. Failure of unit to a. Valve parts dirty or a. Clean or replace
turn off defective
b. Magnet spring too short b. Replace
c. Clogged valve orifice c. Clean or replace
4. Backflow into a. Diluted solution being a. Replace or repair foot valve
concentrate siphoned into container
b. Water being siphoned b. Replace eductor
into container
* In hard water areas, scale may form at the discharge of the eductor. This scale may be removed by
soaking the eductor in a descaling solution or by running the descaling solution through the system. If
descaling solution is educted through the system, flush the unit by educting water only before returning
the system to regular use.

 Loading...
Loading...