MAINTENANCE MANUAL OF ENGINE
129
Chapter 3 Inspection and adjustment
1. Inspecting valve clearance (mm)
Cause:
The compressive force of the cylinder is insufficient,
and there is black smoke and abnormal sound dur-
ing exhausting.
Equipment:
Open-end spanner, flat-tip screw driver, and feeler
gauge
Test steps and adjustment:
1. Dismantle the cylinder head cover, and inspect
and tighten the hold-down nut for the rocker arm
seat.
2. Turn the crankshaft to the position where the pis-
tons of the 1st cylinder and 4th cylinder are placed
at the upper dead point (the "0" scale line on the
crankshaft pulley is aligned with the pointer on the
timing gear chamber cover at this moment; among
them, if the intake valve and exhaust valve of one
cylinder must be closed simultaneously, the piston
of this cylinder is placed at the upper dead point in
the compression stroke).
3. Release the locknut, and use a screwdriver to turn
the adjusting screw, as well as insert the feeler
gauge into the intake valve and exhaust valve of the
1st cylinder, intake valve of the 2nd cylinder and
exhaust valve of the 3rd cylinder to inspect and ad-
just the clearance, so that the cold clearance is kept
within 0.30~0.35mm.
4. During adjustment, the valve should be tightened
by such means that the valve push rod can be turned
evenly by fingers. After being adjusted properly, it
is required to tighten the locknut firmly to prevent
looseness during operation.
5. According to the operating sequence of the
cylinders (the cylinders are operated in such se-
quence of 1-3-2 for the three-cylinder engine, and
1-3-4-2 for the four-cylinder engine), rotate the
crankshaft by one turn (namely 360°), and inspect
and adjust clearance of the remaining valves by the
method above (note that the valve clearance cannot
be adjusted by turning the crankshaft in reverse di-
rection).
Specification:
Intake valve clearance (cold state): 0.20-0.25 mm
Exhaust valve clearance (cold state): 0.25-0.30 mm
Test results:
If the problem remains unresolved after being ad-
justed as per requirements, other causes should be
taken account of.
1. The piston ring is deposited with carbon, jammed
or worn.
2. The cylinder head gasket is air-leaked.
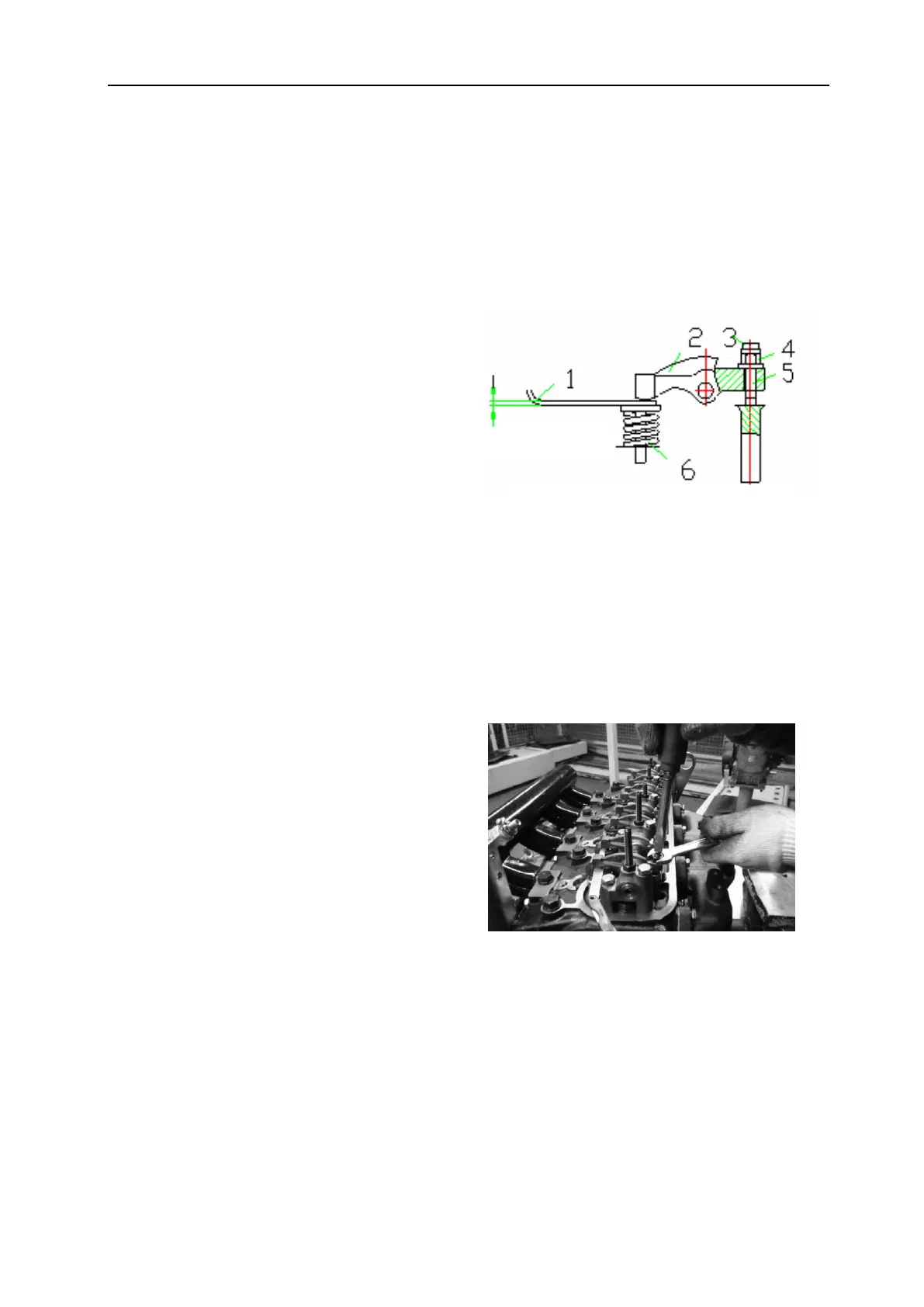
1-Feeler gauge
2-Rocker arm
3-Adjusting screw
4-Locknut
5-Push rod
6-Valve spring
7-Valve clearance

 Loading...
Loading...