be observed (with anesthetics containing vasopressor). Care should be taken
upon needle removal to reduce anesthetic solution dripping down the palate. Do
not advance the needle beyond 1/2” (1 cm) since the floor of the nose can be
penetrated which may lead to an infection.
CLINICAL TECHNIQUES
P-ASA
Note: It is critical that only the slow rate be used for this injection. Using
the fast rate of flow may cause excessive ischemia and tissue damage. It is
recommended that anesthetic containing vasopressor concentration of 1:100,000
or 1:200,000 be used. Caution should be exercised with 1:50,000 concentration
of vasopressor. Excessive ischemia can result in soft tissue damage.
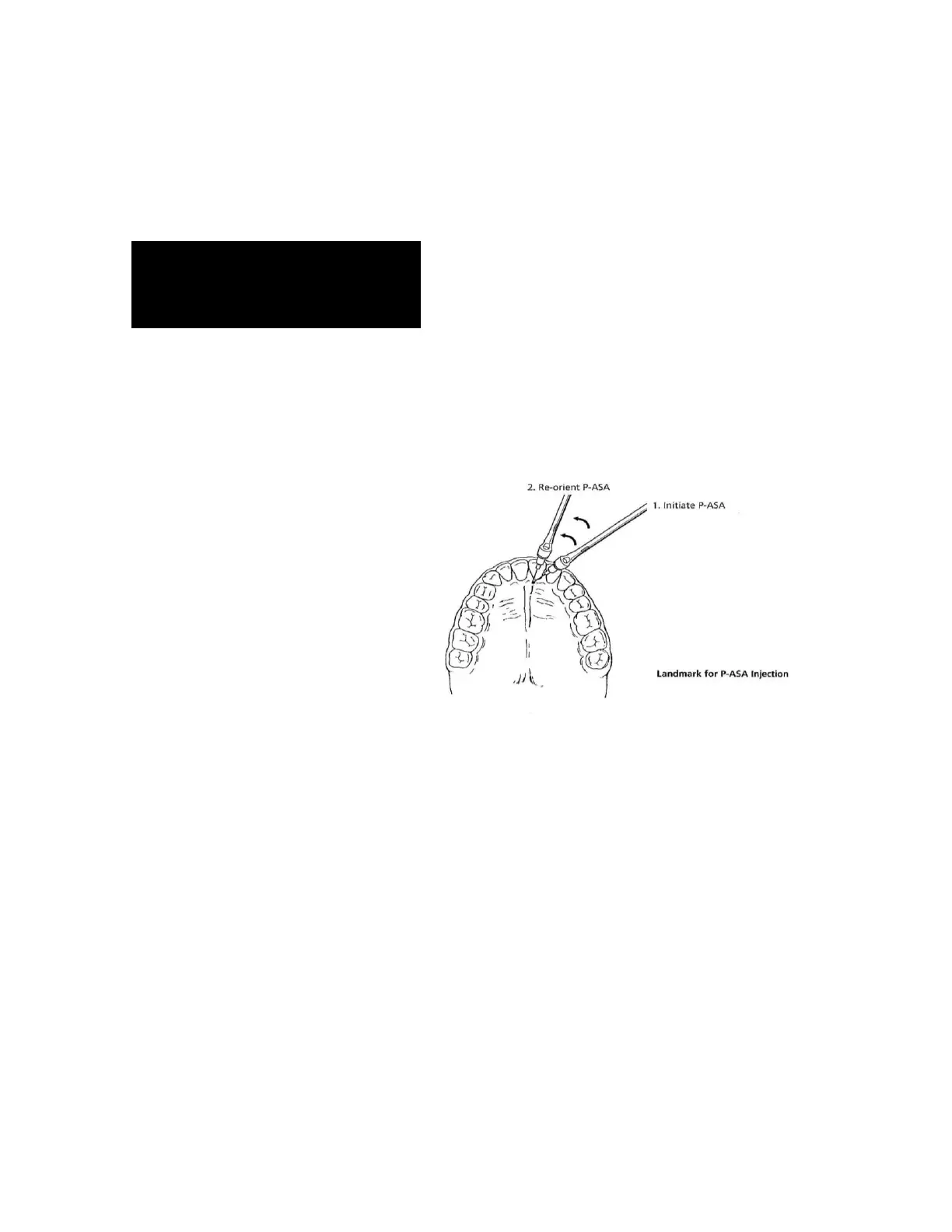
REVIEW OF THE P-ASA INJECTION TECHNIQUE
1. Prepare the patient for a slow injection experience.
2. Place topical anesthetic on the incisive papilla if desired.
3. Orient a 30 gauge extra-short needle in the groove just lateral to the
incisive papilla.
4. Use a sterile cotton tip applicator for the pre-puncture technique.
5. Initiate the slow flow rate and maintain this rate throughout the injection.
6. After 8 - 10 beeps initiate axial rotation and VERY SLOW forward
movement but continue slow flow rate.
7. Once the needle bevel enters below the papilla, pause movement for 5 - 6
seconds.
8. After papilla is blanched, re-orient the needle vertically to gain entrance to
the nasopalatine canal with slow axial rotation.
9. When the needle is in the canal and contacting the inner bony wall, stop
movement and aspirate. DO NOT EXCEED 1 cm (length of 1/2” needle)
penetration into the canal.
 Loading...
Loading...