1.27 Networking Features
204 Feature Guide
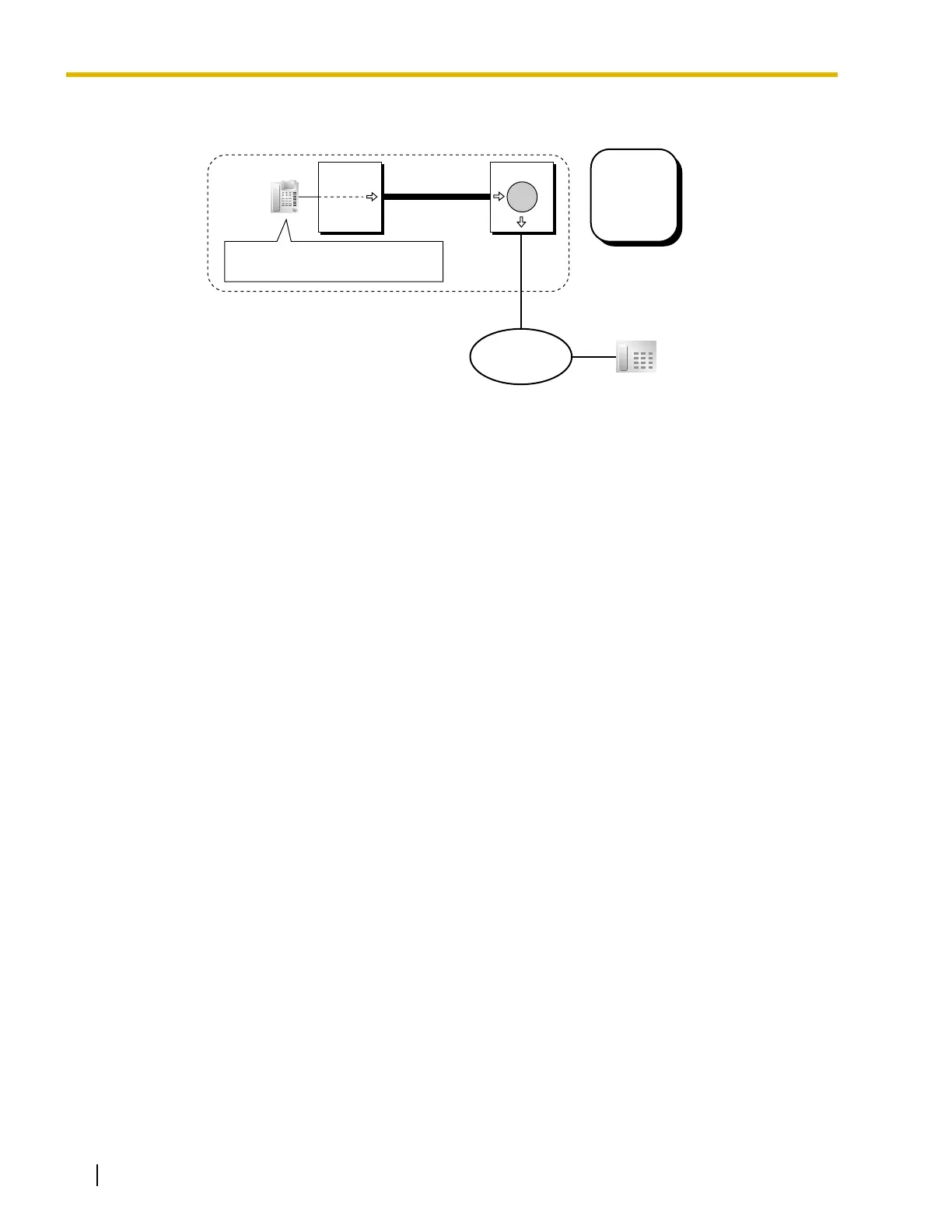
[Example of Bypassing TIE-to-CO Line Call Restrictions]
Explanations:
PBX-1 makes a call.
Extension 1001 dials the TIE line access number of PBX-1 "7", the PBX code of PBX-2 "902",
followed by a DISA floating extension number of PBX-2.
1. The TIE Line Access number was dialed, therefore PBX-1 checks its TIE Line Routing
and Modification Table (not shown here). Finds leading number "902". No modification is
programmed.
2. PBX-1 removes the TIE Line Access number and sends the remaining digits down the
TIE line. The number is now "902" plus the DISA floating extension number of PBX-2.
PBX-2 receives the call.
1. PBX-2 checks its Incoming Number Modification Table (not shown here). No modification
is programmed.
2. PBX-2 recognizes its own PBX code and sends the call to its DISA feature. From this
point, if the COS assigned to the caller's extension or verified code allows, the caller can
use Walking COS or Verified Code Entry to bypass the restrictions and make a CO line
call.
Dials "7-902" + a DISA
floating extension number of PBX-2
Outside Party
CO Line Grp. 1
(COS: 3)
CO Line
Grp. 3
Private Network
Extn. 1001
Telephone
Company
PBX-2PBX-1
PBX Codes
PBX-1: 901
PBX-2: 902
DISA

 Loading...
Loading...


















