DUAL
AXIS
®
CRT
PARAGON CRT DUAL AXIS
®
OPTIONS TO COMPENSATE
FOR PERIPHERAL CORNEAL ELEVATION DIFFERENCES
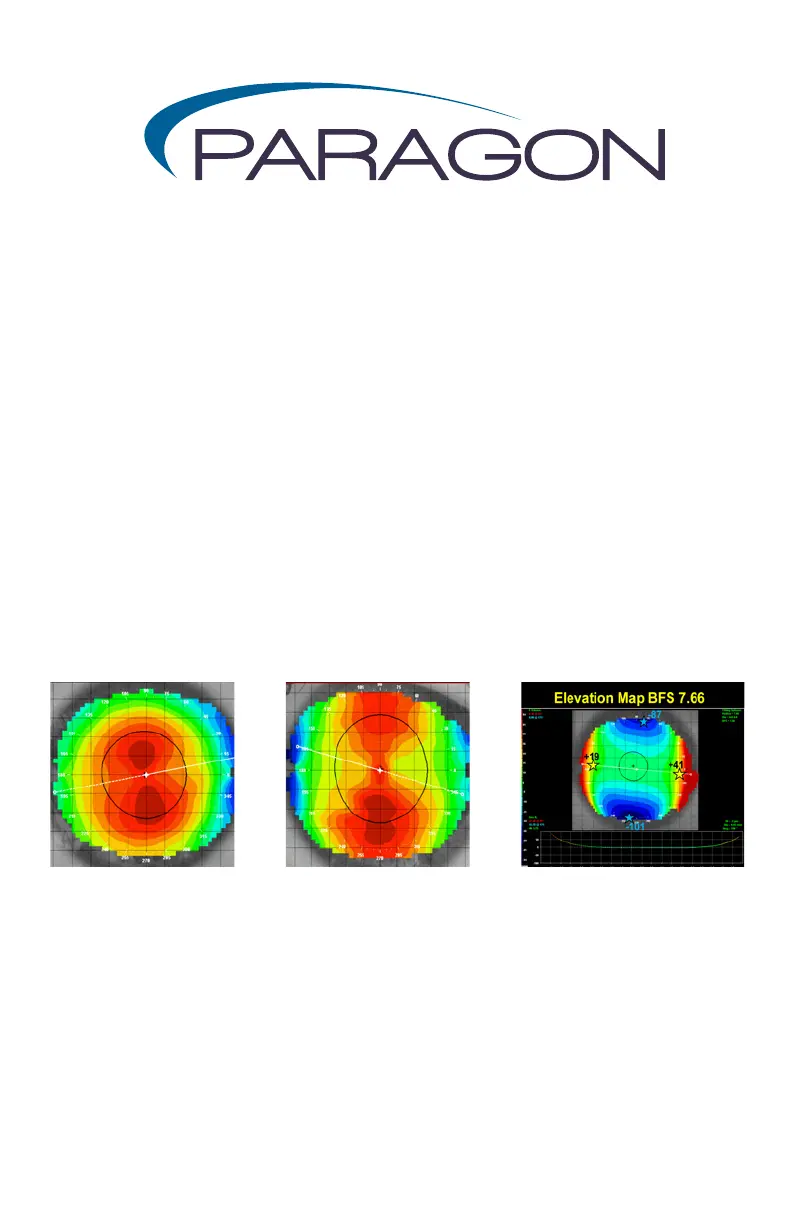
Most eyes with corneal astigmatism manifest a signicant dierence in
elevation between the steep and the at corneal meridians (Image A).
Some corneas that appear spherical may also manifest a peripheral corneal
elevation dierence. e Paragon CRT® lens design has a xed chord length
of 8 mm (6 mm treatment zone surrounded by a 1 mm return zone width).
When the elevation dierence exceeds approximately 30 microns at a chord
diameter of 8 mm, it may not be possible for the lens to reach the cornea
circumferentially in the landing zone (Image B). is creates a weakened
compressive force in the steep meridian and results in poor centration,
lens exure, and/or undertreatment. An example of an elevation map with
elevation values at 4 mm from reference center in each meridian is shown
in Image C.
A common rule in contact lens tting holds that spherical lenses will always
move freely along the steep meridian and exhibit restricted movement
along the at meridian. e clinician will observe that spherical lenses will
touch rst in the attest meridian peripherally and rock, ex or tilt over the
steepest meridian. In conventional corneal reshaping designs, the lens can
only reach the peripheral steep meridian by compressing or applanating the
at meridian or by way of lens exure. Oval treatment zones are commonly
observed with peripheral corneal elevation dierences.
Aptical Astigmatism
Image A Image B Image C
Limbus to Limbus
Astigmatism
8mm Chord Values

 Loading...
Loading...