Communication
11.4 Communication via MODBUS TCP
Drive functions
866 Function Manual, 11/2017, 6SL3097-4AB00-0BP5
The response returns register address (bytes 8 and 9) and the value (bytes 10 and 11),
which the higher-level control had written to the register.
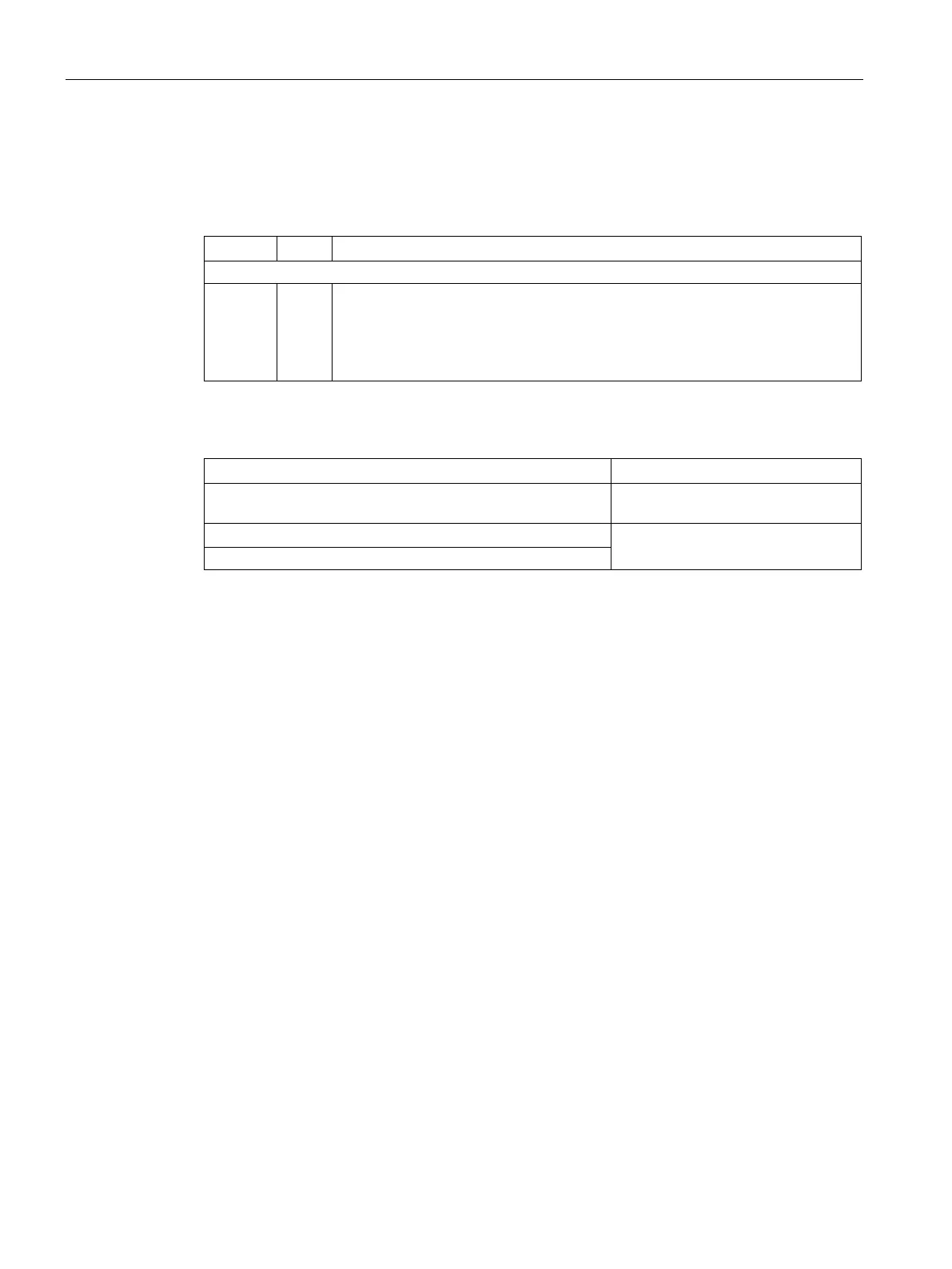
Table 11- 26 Device response to the write request, example
00 h
63 h
55 h
8
9
10
Register start address "High"
Register start address "Low"
Register data "High"
Table 11- 27 Invalid write request
Incorrect address (a holding register address does not exist) Exception Code 02 - invalid data
Write to a "read-only" register Exception Code 04 - device failure
Write to a reserved register
For Exception Code 4, via the holding register 40499, you can read out the internal drive
error code, which has occurred for the last parameter access via the holding register.
Communication via data set 47
Via FC 16, with one request, up to 122 registers can be written to directly one after the other,
while for Write Single Register (FC 06) you must individually write the header data for each
register.
In addition to the transfer type, the start address and the number of the following registers in
the header.
You control the access in the user data via register 40601.
In register 40602, you define the access as well as the length of the request data.
Register 40603 contains the request reference - it is defined by the user - and the access
type -reading or writing.
From register 40603 and higher, the request aligns communication via data set 47 according
to PROFIdrive.
Register 40604 contains the number of the drive object and the number of parameters that
are read out or written to.

 Loading...
Loading...























