Reference
WFM 1125 Option 0A/0B/0C/0D User Manual
3-9
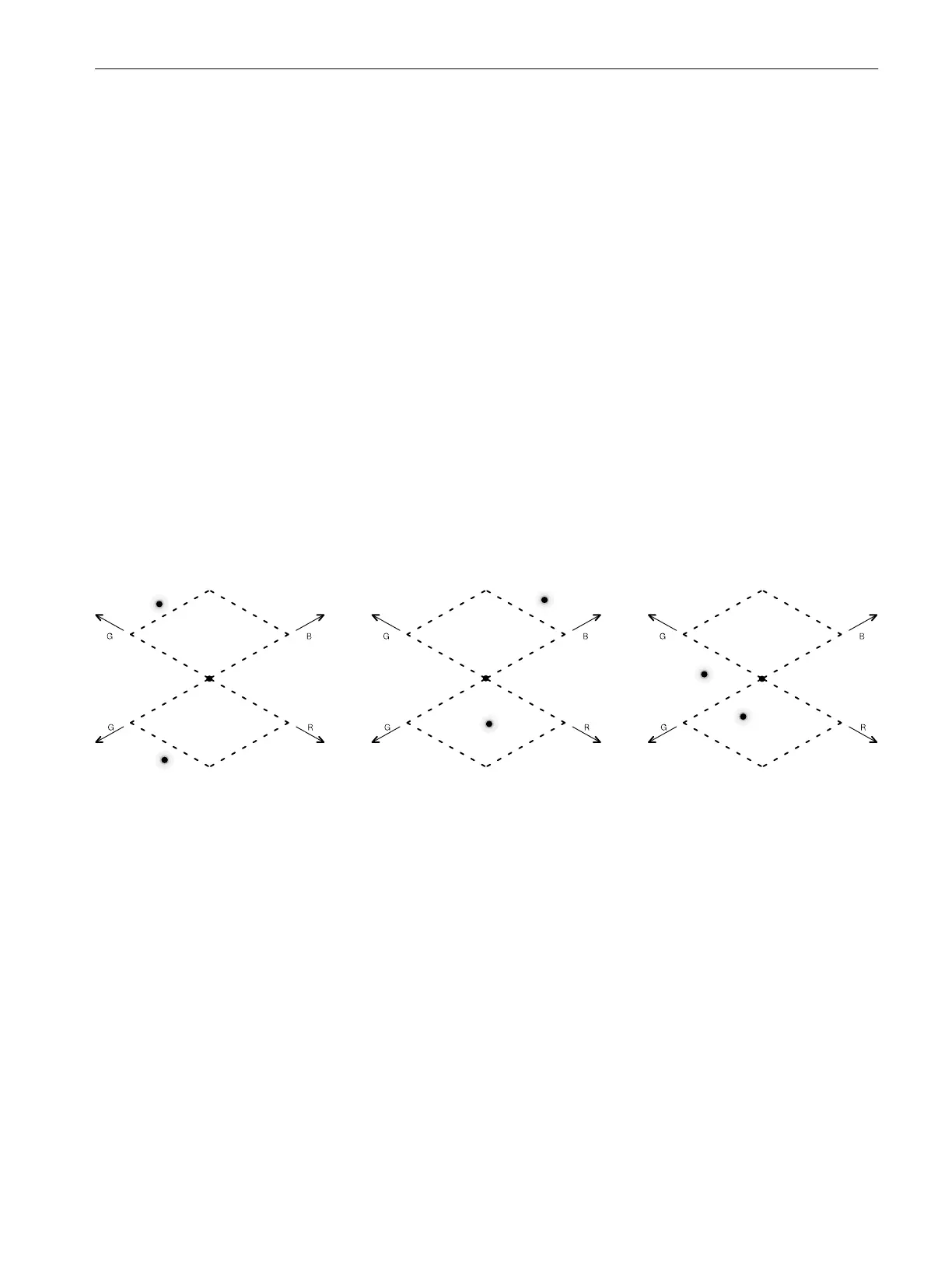
For a signal to be in gamut, all signal vectors must lie within the G-B and G-R
diamonds. Conversely, if a vector extends outside the diamond, it is out of gamut.
The direction of an excursion out of gamut indicates which signal is excessive.
Errors in green amplitude affect both diamonds equally, while blue amplitude
errors affect only the top diamond and red errors affect only the bottom diamond.
If ON is selected in the GAMUT menu, when the signal exceeds the RGB gamut
by more than 5%, the GAMUT LED on the front panel lights, even if the signal
is only momentarily out of gamut.
In the Diamond display, the intensity of a vector indicates its duration. A
momentary out-of-gamut condition appears as a faint trace outside the diamonds.
Long duration violations show as a bright trace outside the diamonds. Figure 3–6
gives some sample out-of-gamut signals on the Diamond display.
On the Diamond display, monochrome signals appear as vertical lines. Signals of
constant hue and variable saturation or intensity appear as straight lines.
Nonlinear component processing, such as from a gamma corrector that alters
white balance, can cause deviations.
As with the Lightning display, bending transitions on test signals, such as
color-bars, indicate timing delays. When a color bar signal is applied, the vertical
axis becomes an indicator of delay errors.
Example A:
R-OK
G > 700 mV
B-Ok
Example B:
R-OK
G-OK
B > 700 mV
Example C:
R-OK
G - OK, 350 mV
B<0mV
Figure 3-6: OutĆofĆgamut signals on a Diamond display
Checking RGB Gamut

 Loading...
Loading...