’05 MATRIX_U (L/O 0409)
209
2005 MATRIX from Sep. ’04 Prod. (OM12892U)
4. The resulting figure equals the
available amount of cargo and lug-
gage load capacity. For example,
if the “XXX” amount equals 1400
lbs. and there will be five 150 lb.
passengers in your vehicle, the
amount of available cargo and lug-
gage load capacity is 650 lbs.
(1400–750 (5x150)=650 lbs).
5. Determine the combined weight of
luggage and cargo being loaded
on the vehicle. That weight may
not safely exceed the available
cargo and luggage load capacity
calculated in Step 4.
6. If your vehicle will be towing a
trailer, load from your trailer will
be transferred to your vehicle.
Consult this manual to determine
how this reduces the available car-
go and luggage load capacity of
your vehicle.
For details about trailer towing, see
page 217.
Cargo
capacity
Total load
capacity
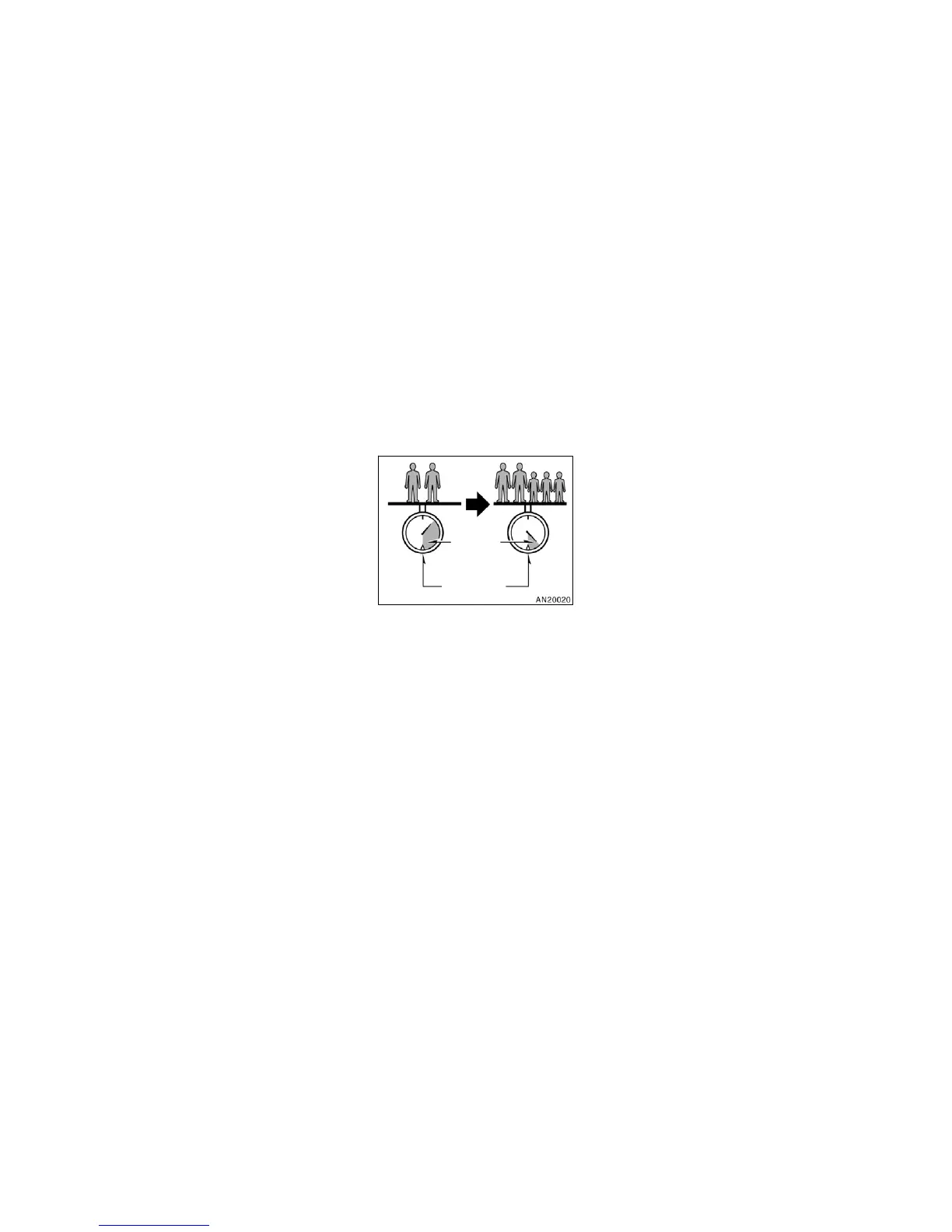
EXAMPLE ON YOUR VEHICLE
In case that 2 people with the com-
bined weight of 166 kg (366 lb.) are
riding in your vehicle with the total
load capacity of 385 kg (850 lb.), the
available amount of cargo and lug-
gage load capacity will be as follows:
385 kg – 166 kg = 219 kg.
(850 lb. – 366 lb. = 484 lb.)
From this condition, if 3 more passen-
gers with the combined weight of 176
kg (388 lb.) get on, the available car-
go and luggage load will be reduced
as follows:
219 kg – 176 kg = 43 kg.
(484 lb. – 388 lb. = 96 lb.)
As shown in the above example, if the
number of occupants increases, the
cargo and luggage load equaling the
combined weight of occupants who
got on later must be reduced. In other
words, if the increase in the number
of occupants causes the excess of
the total load capacity (combined
weight of occupants plus cargo and
luggage load), you have to reduce the
cargo and luggage on your vehicle.
For details about total load capacity,
see “Vehicle load limits” on page 207.

 Loading...
Loading...











