Description
The LED Array™ is a robust and attractive
device comprising 1 white LED and a set
of 10 coloured LEDs from red to violet,
wavelengths from 641 to 411 nanometres.
Purpose
It can be used to explore the interaction
between colour filters and specific colours
of light, to illustrate and explain the
behaviour of different wavelengths of light,
and to prove and work out a value for
Planck's constant.
The experimental method for Planck’s
constant involves simple measurements,
but requires appreciation of errors and an
awareness of underlying assumptions.
Kit Contents
LED Array™
Plugtop 5V 1A d.c. power supply
For the suggested experiments, you will
also need:
Colour filters, at least two each of:
red, green, blue, cyan, magenta, yellow
A diffraction grating (300 lines/mm)
Diffraction gratings with different
spacings, e.g. 200 and 600 lines/mm
A metre rule
A sheet of A3 white card and marker pen
A voltmeter to read 0 to 6V d.c.
The LED Array™ LED data
Voltages measured between the common
connection point and the individual LED
contacts, are in the range 1.8 to 4V.
Safety
The LED Array™ should be used under the
supervision of a qualified teacher, and with
the plugtop power supply provided. A risk
assessment prior to use is recommended.
The LEDs in this product are “ultra bright”.
Do not look directly at them from close
range. Do not stare at any bright LED
source.
When working in low ambient light levels,
extra caution must be taken. Advise
pupils not stare, and to look at the LEDs
for the minimum time during experimental
procedures.
FifeX and UNILAB accept no responsibility
for injury or damage caused by misuse of
the LED Array™.
Power supply
It is recommended that you use the 5V d.c.
plugtop power supply provided.
Connect the plug top power supply lead to
the socket on the left side of the LED
Array™.
Plug the power supply into a mains
socket.
Locate the on-off switch above the power
supply socket. Switch on.
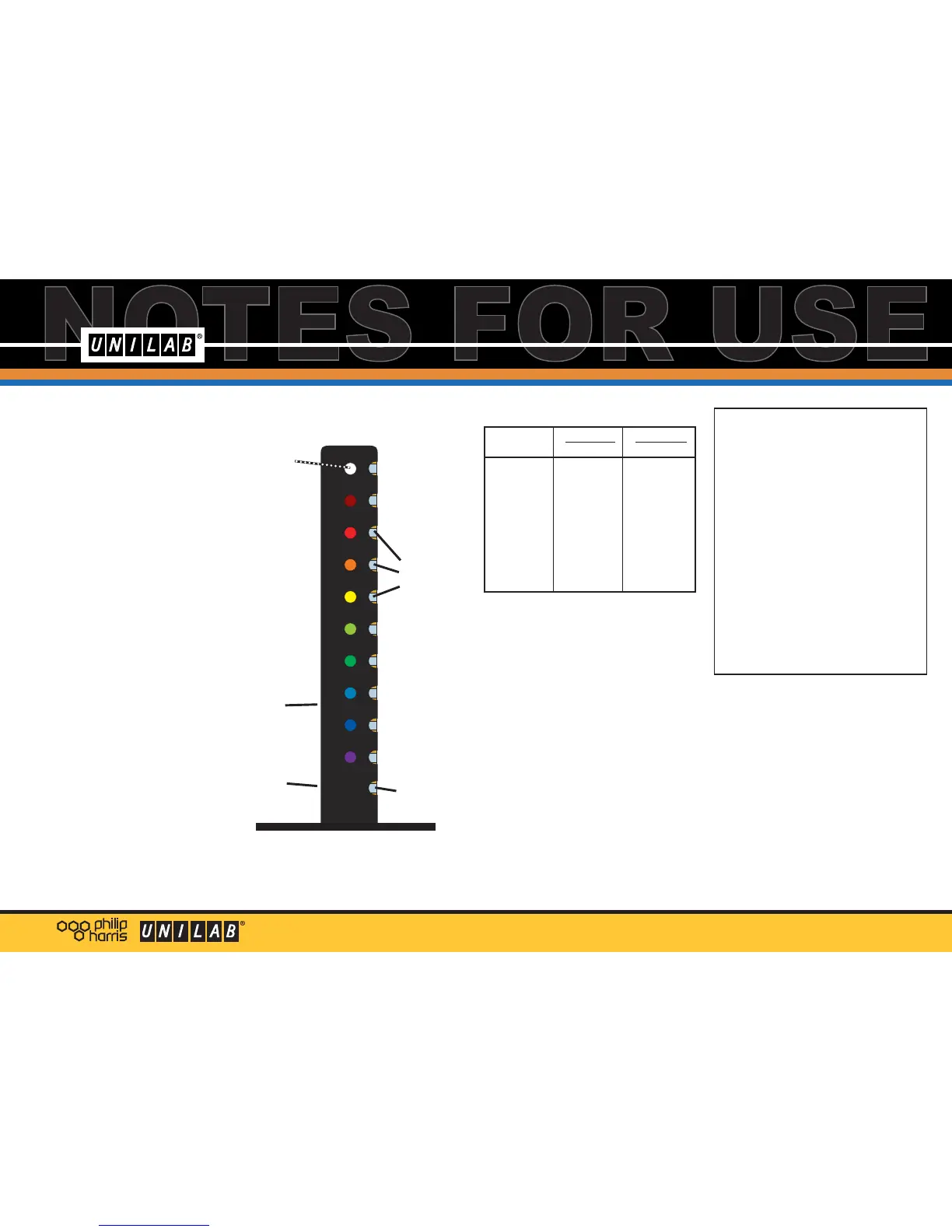
on-off
switch
power
supply
socket
common
contact for
voltmeter
positive (+)
contact
points for
each LED
white
LED
LED colour
deep red
red
orange
yellow
green
bright green
turquoise
blue
deep blue
violet
wavelength
nm
641
627
609
600
574
539
494
468
451
411
frequency
10
14
Hz
4.68
4.78
4.93
5.00
5.23
5.57
6.07
6.41
6.65
7.30
Suggested experiments
1. Colour, and the effects of colour filters
2. Effect of a diffraction grating, and the
link to colour and wavelength.
3. Prediction from initial observations, of
the effect of using a different grating.
4. Calculation of wavelength for any
colour
5. How LEDs generate light
6. Determination of Planck’s constant, h
6b. Alternative method - measuring the
striking voltages for the LED Array
7. Assumptions underlying the
measurement of Planck's constant
 Loading...
Loading...