- 11 -
SHUTDOWN OF THE MOTOR IN THE CASE OF LOW MOTOR OIL
(where fitted)
WARNING! The motor is equipped with a device for automatic
emergency shutdown of the motor if there is not enough oil. This de-
vice prevents serious damage to the motor. If the device intervenes,
check and replenish to the correct level (see previous chapters).
STOPPING THE MOTOR
1. Move the power supply switch to “OFF” (Fig. A pos. 9) and
disconnect all of the plugs from the sockets.
2. Move the motor ON/OFF switch/key to “STOP” (Fig. A pos. 4).
3. Close the petrol cock, lever in “OFF” position (Fig. E1).
USE OF THE GENERATOR
WARNING! Before connecting any electric load, be sure you fully under-
stand the safety regulations stated above.
WARNING! The load is applied after the motor has been started.
WARNING! The load connected to the generator must never exceed the PRP
supplied power indicated in the technical data.
WARNING! Observe the maximum current indicated on each socket.
WARNING! The alternator has a trip switch to protect against overloads. In
the case of an excessive load, it could intervene to protect the alternator. If
the trip switch intervenes, reduce the applied load and reset.
WARNING! Pay attention to the power factor of your load.
Always calculate the absorption of the load to be applied to the generator
beforehand.
Guidelines for the type of load that may be applied to the generator are
shown below.
Note: For the generator’s power, refer to the technical data label.
For the powers of the connected appliances, refer to the power consumption
indicated on their technical data labels.
100% of the generator’s PRP
Examples of load:
- Purely resistive loads with cos ϕ= 1
- Incandescent luminaries
- Electric heaters with resistance
- Electric geysers
- Clothes irons
65% of the generator’s PRP
Loads with high starting power and power factor near 1.
Examples of load:
- Power tools with universal motors (brush)
- Angle grinders
- Portable jigsaws
- Portable circular saws
- Heat guns
50% of the generator’s PRP
Loads with high starting power and power factor other than 1.
Examples of load:
- Asynchronous motors
- Compressors
- Hoists
- Concrete mixers
- Fluorescent lights
20% of the generator’s PRP
Loads with very high starting power
Examples of load:
- Refrigerators
- Air conditioners
USE OF AN EXTENSION CABLE
Extension cables must be chosen carefully. Refer to the related safety
regulations. To prevent excessive drops in voltage, use cables that
are an adequate size for the load.
See the table below.
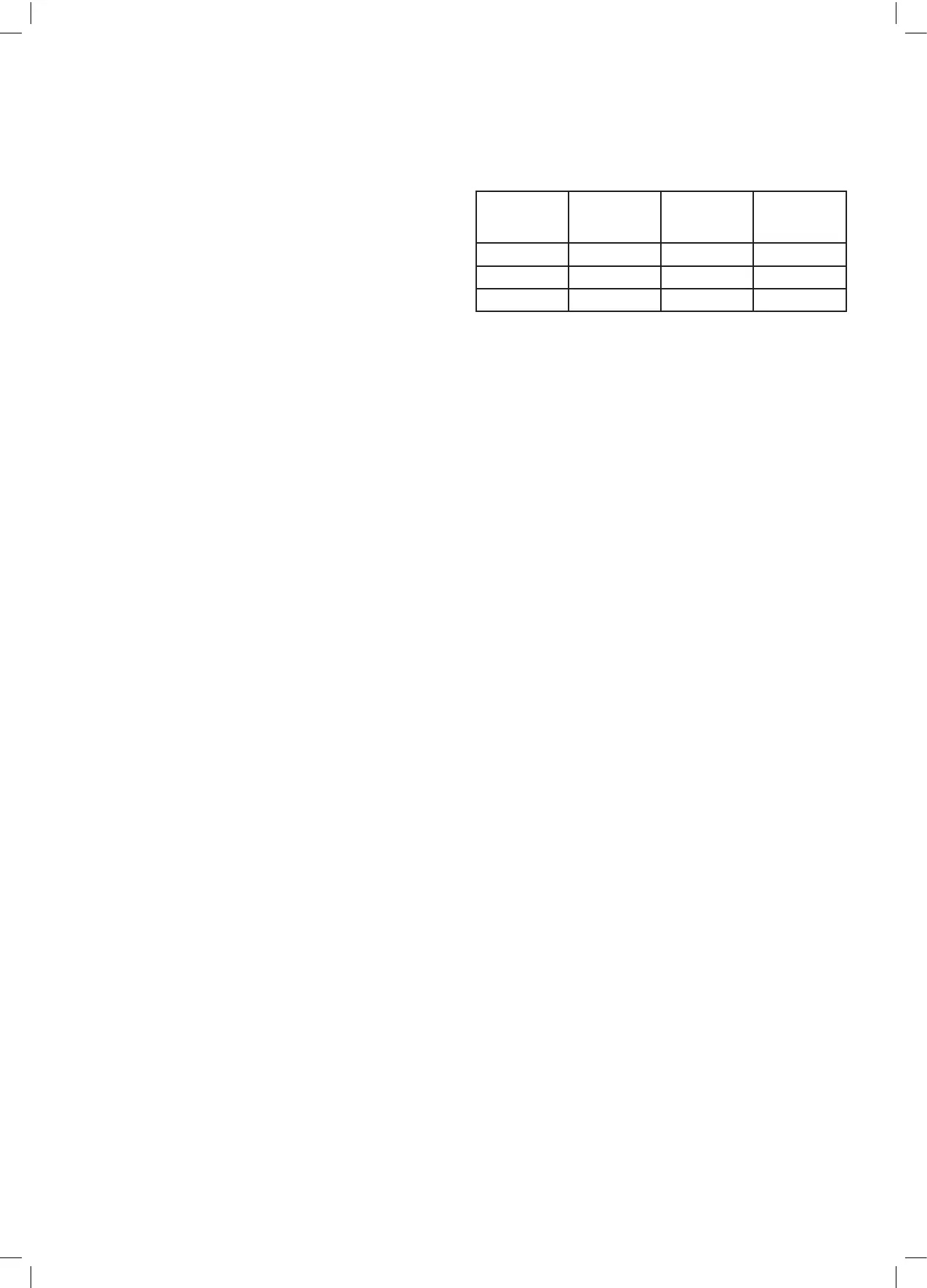
Diameter
cable(mm
2
)
Length(m) Current in A Gener. power
(kW) cos
ϕ=1
1.5 25 10 2
2.5 40 16 3.3
4 60 28 5
CONNECTING THE LOAD (FIG. E)
1. Connect a suitable plug, coming from the appliance, to the gene-
rator’s socket.
2. Place the power switch on “ON” (Fig. A pos. 9).
WARNING! The load must always be disconnected before turning
off the motor.
Disconnecting the load
1. Place the power switch on “OFF” (Fig. A pos. 9).
2. Remove the plugs from the sockets.
MAINTENANCE (FIG. F)
WARNING! Each operation indicated below must be carried out
while the motor is off, the power switch is on “STOP” (Fig. A pos.
9) and the load’s plug is disconnected.
WARNING! If in doubt, contact an authorised assistance centre.
WARNING! Contact an authorised assistance centre for any operations
not included below.
Cleaning after every use
Take care of your machine and clean it regularly to ensure that it
remains perfectly efficient and has a long lifetime.
Clean the machine using a soft brush or cloth.
Do not spray or soak the machine with water.
Do not use inflammable substances, detergents or solvents as these
may damage the machine beyond repair. The plastic parts are prone
to damage by chemical agents.
Replacing the motor oil
Check the oil level before each start and top up if necessary.
Replace the oil after the first month or after the first 20 hours of use.
Then replace it every 6 months or after every 80 hours of use.
See the previous chapters.
Spark plug
Check it after every 50 hours of use, and replace it if necessary.
See the technical data in reference to the spark plug type.
1. Remove the pipette and unscrew the spark plug using the relative
spanner.
2. Examine the spark plug and remove any carbon residue with a
metal brush. Replace the spark plug if the electrode is excessively
worn or the insulation is damaged.
3. Measure the distance between the electrodes: it should be betwe-
en 0.7 and 0.8 mm (Fig. F1).
4. Screw the spark plug back in by hand.
5. Secure a used spark plug with around ¼ turn of the spanner, and
a new one with around ½ turn of the spanner.
Air filter
Clean it after every 50 hours of use, and replace it if necessary.
If used in dusty environments, clean more frequently.
1. Open the cover of the filter box (Fig. A pos. 14).
2. Remove the sponge.
3. Wash it with soap and water and rinse completely.
4. Leave it to dry.

 Loading...
Loading...