the notches become more concentrated in
low frequencies. note: at high density and
warp values, notches may be so dense in low
frequencies that they interfere with the har-
monic pattern which may lead to unexpected
holes in the spectrum. At low peaking values,
notches of the comb response are very narrow.
At high peaking values, the notches become
wider and peaks become more narrow and
The tension parameter has a crucial impact
on the harmonicity of the signal. At the neutral
(middle) position, frequencies of all sinusoidal
partials are integer multiples of the fundamen-
tal: F
n
=n×F
1
, which is a necessary condition for
obtaining a periodic waveform. This results in
equidistant partials throughout the spectrum.
With tension above 0, the upper partials are
spread apart (the frequencies increase quicker
than the partial numbers) which yields an in-
harmonic, metallic timbre with an often more
tension below
0, the distances between upper partials be-
come smaller and smaller (the frequencies in-
crease slower than the partial numbers) which
yields a dense, rough, inharmonic cluster that
resembles noise. Large negative values of ten-
sion may even result in the spectrum folding
over itself to a degree where certain partials
have lower frequencies than the fundamental.
caution: Pitch and intonation behaves par-
adoxically with these inharmonic sounds and
-
tional sounds. Furthermore, these sounds can
cause ear fatigue and are best used sparingly
in musical contexts.
Bear in mind that inharmonic spectra yield
aperiodic waves due to individual sinusoids
being no longer synchronized in phase. When
you turn the tension parameter off the
central (zero) position, the relative phases
of all signal components begin to drift away
from each other. Thus the original waveform
becomes more distorted and will remain as
such, even after returning tension to zero. It
is possible to re-synchronize the phase and re-
store the waveform, however, this produces an
audible click in the signal due to discontinuity,
therefore it is not done automatically. To do
so, press the voices button. Besides selecting
the number of unison voices, this re-syncs the
individual voices and also restarts all sinu-
soids within each voice.
9
AmplitudeAmplitudeAmplitudeAmplitude
5 10 15 20 25 30
Partial number
0
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
5 10 15 20 25 30
Partial number
0
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
5 10 15 20 25 30
Partial number
0
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
AmplitudeAmplitude
comparison of tilted spectra in extreme and middle
positions of the tilt knob

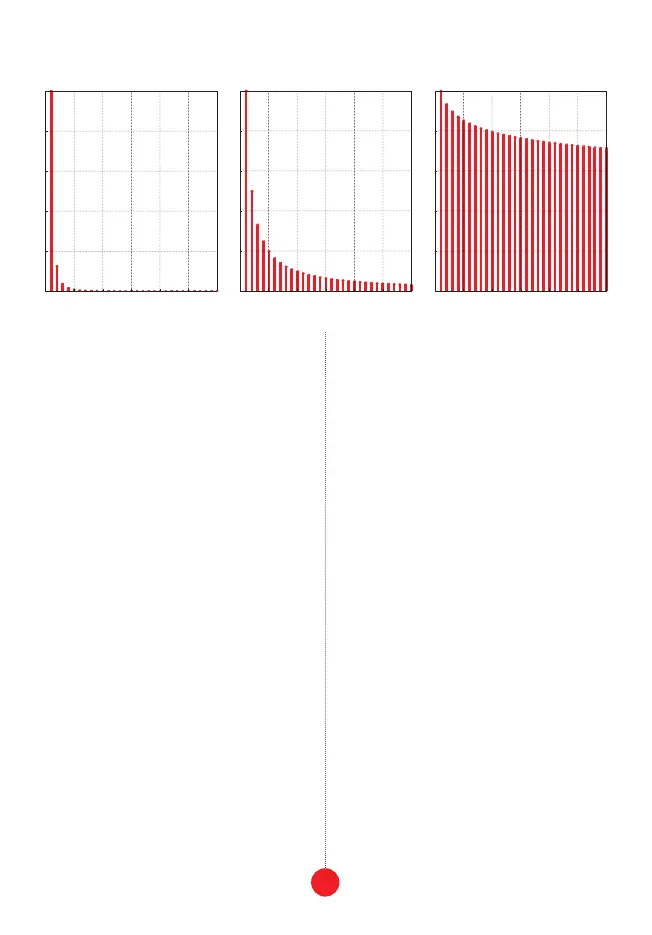 Loading...
Loading...