6 - 18
6.6 Description of Commands
The commands used in a program are classified into commands that are entered from the panel switch and
special commands.
Table 6-2 shows a panel switch command list and Table 6-3 shows a special command list.
6.6.1 Description of variables
The variables usable in a program are described below.
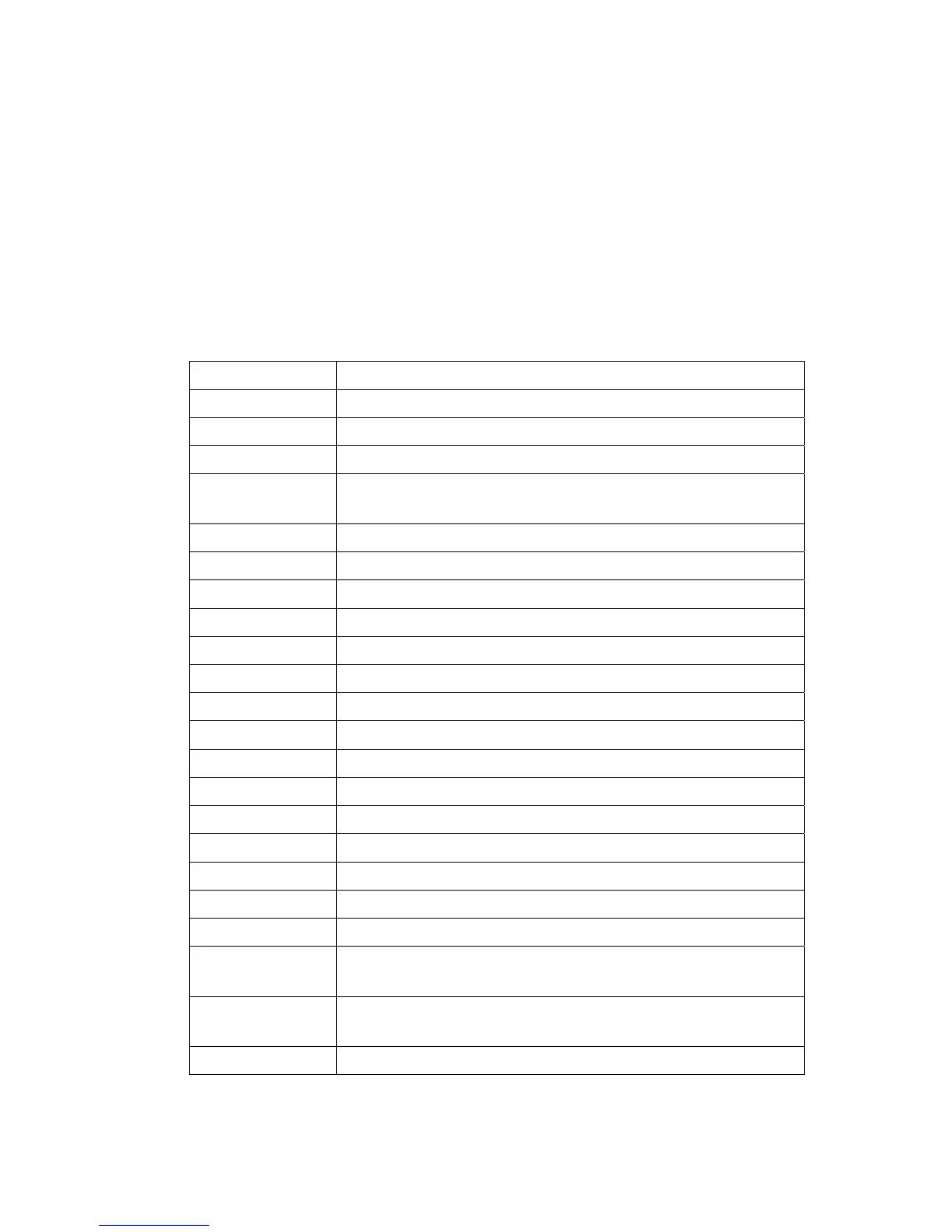
Variable name Contents
I Enters a general purpose variable.
J Enters a general purpose variable.
K Enters a general purpose variable.
S Performs serial polling and stores a received status byte and also used as a
general-purpose variable.
X Enters a general-purpose variable.
Y Enters a general-purpose variable.
Z Enters a general-purpose variable.
A$ Saves the data received by GP-IB 2 port.
FILE$ Enters the file name upon the last access to the floppy disk.
TIME$ Enters date and time (Example: 1994 Sep 08 20 : 45 : 37)
WM Enters the wavelength value of the moving marker.
W1 Enters the wavelength value of fixed marker 1.
W2 Enters the wavelength value of fixed marker 2.
W2-W1 Enters wavelength difference between fixed marker 2 and 1.
LM Enters the level value of the moving marker.
L1 Enters the level value of fixed marker 1.
L2 Enters the level value of fixed marker 2.
L2-L1 Enters the level difference between fixed marker 2 and 1.
SPWD Enters the spectral width upon execution of spectral width search.
PKWL Enters the peak (or bottom) wavelength value upon execution of peak (or
bottom) search or spectral width search.
PKLVL Enters the peak (or bottom) level value upon execution of peak (or bottom)
search or spectral width search.
MODN Enters the number of modes upon execution of spectral width search.

 Loading...
Loading...