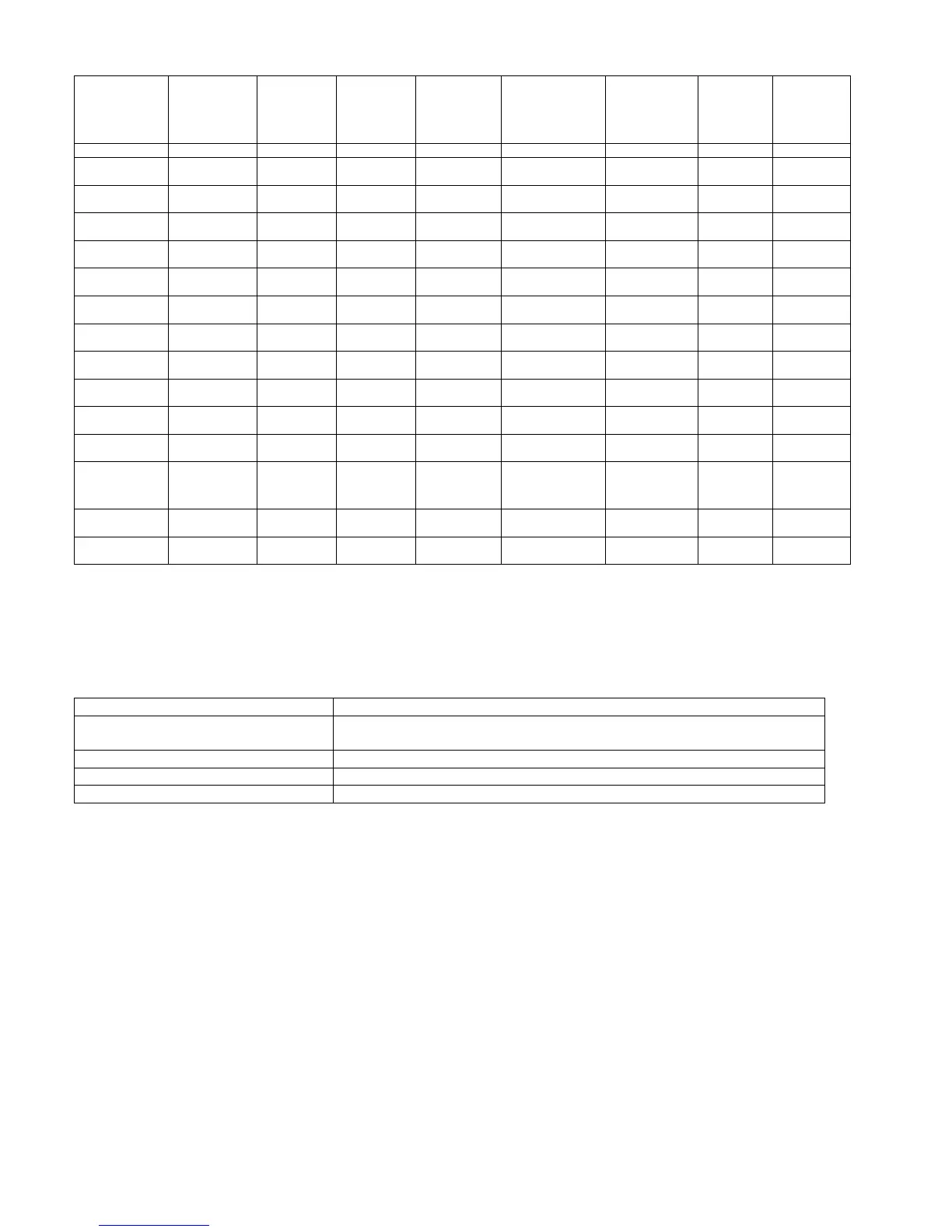
Mallee Roots Mallee 100 N.A Difficult Poor Excellent Few Good
Belah, Buloke Mallee
Box-Ironbark
100 70 /
1121
Good Poor Excellent Few Limited
Grey
Box
Box-Ironbark 100 70 /
1121
Difficult Poor Excellent Few Good
Black
Box
Box-Ironbark 97 69 /
1105
Difficult Poor Excellent Few Limited
Red
Ironbark
Box-Ironbark 97 69 /
1105
Difficult Poor Excellent Few Good
Yellow
Box
Box-Ironbark 91 65 /
1041
Difficult Poor Excellent Few Good
Red
Box
Box-Ironbark 91 67 /
1073
Difficult Poor Excellent Few Good
Yellow
Gum
Box-Ironbark 90 60 /
993
Difficult Poor Excellent Few Good
River
Red Gum
River
Red Gum
80 56 /
897
Difficult Poor Excellent Moderate Good
Blue
Gum
Foothill 80 61 /
977
Fair Fair Good Few Good
Red
Stringy Bark
Foothill 72 54 /
865
Good Good Good Few Good
Messmate
Foothill 68 45 /
721
Good Good Good Few Good
Mountain
Ash
Mountain 53 42 /
673
Excellent Excellent Fair Moderate Good
White Cypress
Pine
Box-Ironbark 60 42 /
673
Good Excellent Poor Many Limited
Radiata
Pine
Foothill
Plantations
45 32 /
512
Fair Excellent Poor Many Good
KNOW YOUR WOOD
A piece of dry wood produces an incredible amount of heat when burnt correctly. A piece of dry wood, however is also
like a sponge and can absorb up to 70% of its weight in water if exposed to the elements.
The fact that all wood heaters rely on dry fuel to perform at their best cannot be over-emphasized as it is critical to your
heater’s performance. The relevant moisture content (wetness) of wood is indicated in the following table.
Below 10% Very dry. Wood burns but less efficiently as some moisture is needed for
ideal combustion.
10% - 18% Ideal. Wood burns efficiently and economically
18% - 25% Wood will burn, but less efficiently
Above 25 % Wood too wet to burn efficiently
It is extremely difficult to light, let alone maintain, a fire using wet or green wood. A firebox filled with 20kg, wet or green
wood could contain up to 10 litres of water. As a result, the heater would naturally perform very poorly as most of the heat
generated would be directed to vaporizing the water. Be aware that if you purchase wood with 50% moisture content, the
50% of the money you paid for the wood, in fact, purchased water.
Ideally, firewood should be organised in the spring and under cover by mid-autumn. If you obtain next year’s wood in
spring, it should be open air dried over summer for a minimum of six months. The wood should then be stacked under
cover in such a way that air can flow between the pieces. A plastic sheet or tarpaulin is not sufficient, as condensation
may account for a high moisture content in the wood.
It is important to select firewood that will build a good base or bed of coals. It is actually the coals and not the flames,
which form the hottest part of the fire and provide the heat source for your heater.
Dry hardwood has over twice the density of pine, so double the volume of pine is required to provide the same amount of
heat. Firewood that has had the bark removed produces less ash. The table above provides a good indication of the
properties of various common type of firewood.

 Loading...
Loading...