69
4-2 Performing Complex Number Calculations
The following examples show how to perform each of the complex number
calculations available with this calculator.
kk
kk
k Arithmetic Operations [OPTN]-[CPLX]-[i]
Arithmetic operations are the same as those you use for manual calculations. You
can even use parentheses and memory.
Example 1 (1 + 2i) + (2 + 3i)
AK3(CPLX)
(b+c1(i))
+(c+d1(i))w
Example 2 (2 + i) × (2 – i)
AK3(CPLX)
(c+1(i))
*(c-1(i))w
kk
kk
k Reciprocals, Square Roots, and Squares
Example
(3 + i)
AK3(CPLX)
!9(d+1(i))w
kk
kk
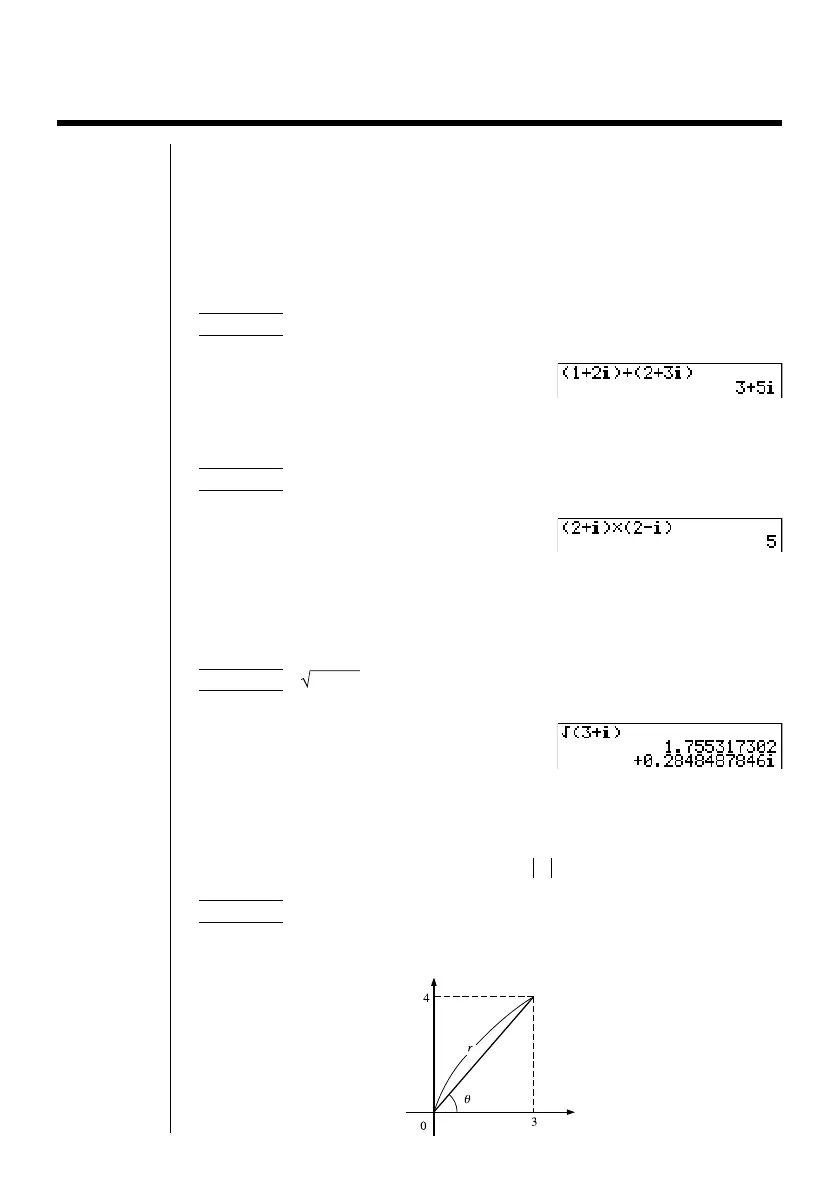
k Absolute Value and Argument [OPTN]-[CPLX]-[Abs]/[Arg]
The unit regards a complex number in the form a + bi as a coordinate on a
Gaussian plane, and calculates absolute value Z and argument (arg).
Example To calculate absolute value (r) and argument (
θ
) for the
complex number 3 + 4i, with the angle unit set for degrees
Imaginary axis
Real axis
 Loading...
Loading...























