COPYRIGHT©EDECOA, ALL RIGHT RESERVED,PSW-USA-Rev2.71
11 / 17
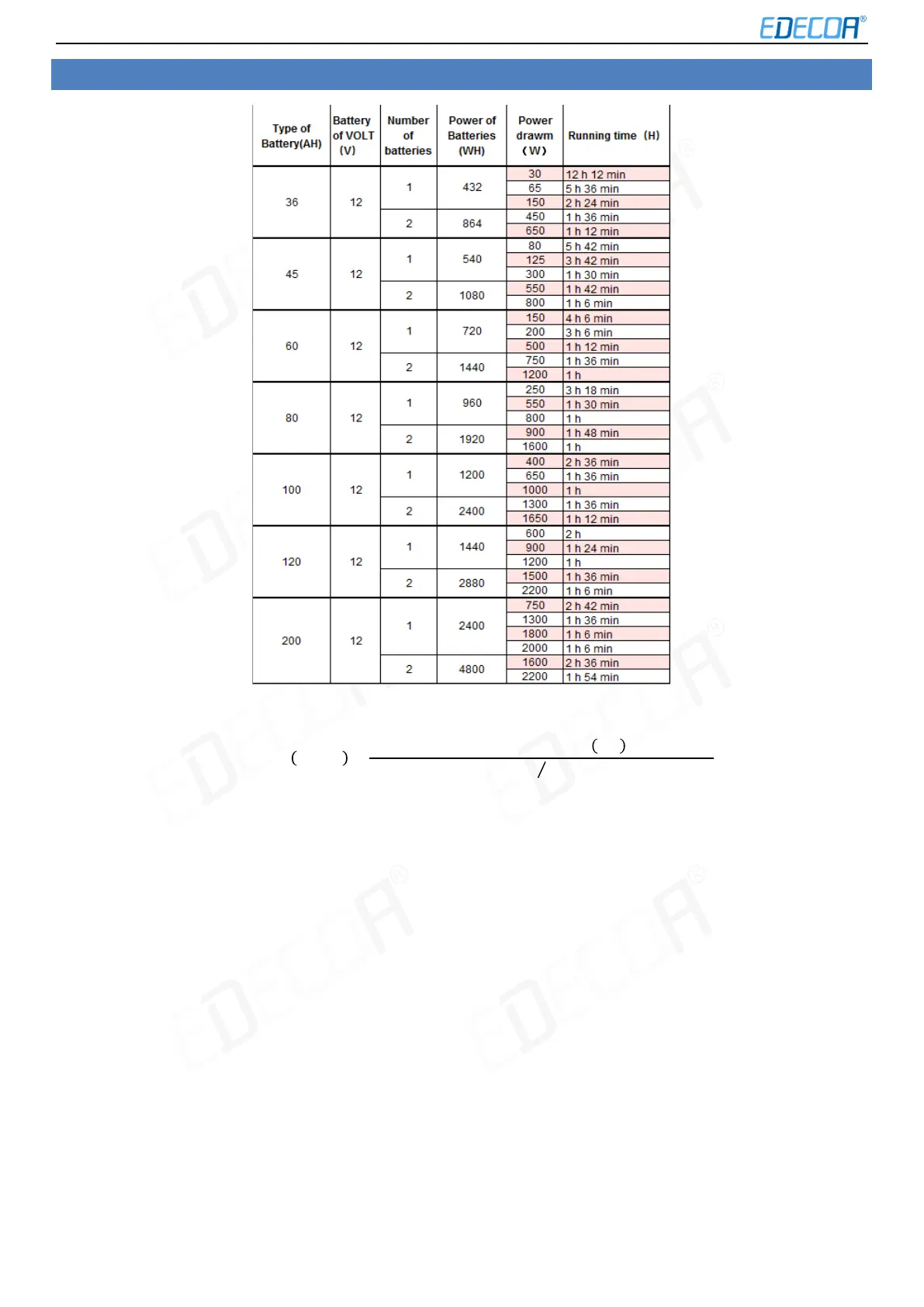
12.BATTERIES USING TIME
You can calculate that the storage battery’s use-time by this formula:
푈푠푖푛푔푇푖푚푒 퐻표푢푟푠 =
퐵푎푡푡푒푟푦퐶푎푝푎푏푖푙푖푡푦 퐴퐻
푙표푎푑푔푒푛푒푟푎푙
푝표푤푒푟(푊)
0.85/퐵푎푡푡푒푟푦voltage(V)
Attention:
If batteries of the same size are connected in parallel, the time is multiplied by the number of parallel batteries. For
example, four 12V 60AH batteries are connected in parallel, and 500W of load can be used continuously for 1 h 12
min*4=4 h 48 min
The above is the time that can be used when the new battery is fully charged. If it is an old battery, use it for more than
half a year and multiply it by 0.8. The battery has been used for more than one year. It needs to multiply the usage time by
0.5. For example, a 12V 100A battery has been used for half a year. If a 1000W load is used, it can be used continuously for
1h*0.8=48 min.
Tip: Use the inverter in your car. Engine start batteries should not be discharged below 90% charged state, and marine
deep cycle batteries should not be discharged below 50% charged state. Doing so will shorten the life of the battery based
on most battery manufacturers recommendations.
Note: If you intend to use power tools for commercial use, or any load of 200W for more than 1 hour regularly (between
battery recharging) we recommend installing an auxiliary battery to provide power to the inverter. This battery should be
a deep cycle type and sized to meet your run time expectations with the engine off. The auxiliary battery should be
connected to the alternator through an isolator module to prevent the inverter from discharging the engine start battery
when the engine is off.

 Loading...
Loading...