The most important things to avoid:
1. Freezing: Avoid locations where freezing temperature is expected. Keeping a battery at a high state of charge
will also prevent freezing. (See Table2)
2. Heat: Avoid direct exposure to heat sources, such as radiators or space heaters. Temperatures above 80°F
accelerate the battery's self-discharge characteristics.
Procedure:
1. Completely charge the battery before storing.
2. Store the battery in a cool, dry location, protected from the elements.
3. During storage, monitor the specific gravity (flooded) or voltage. Batteries in storage should be given a boost
charge when they show a 70% charge or less. See Table 1 in the Testing Section.
4. Completely charge the battery before re-activating.
5. For optimum performance, equalize the batteries (flooded) before putting them back into service. Refer to the
Equalizing section for this procedure.
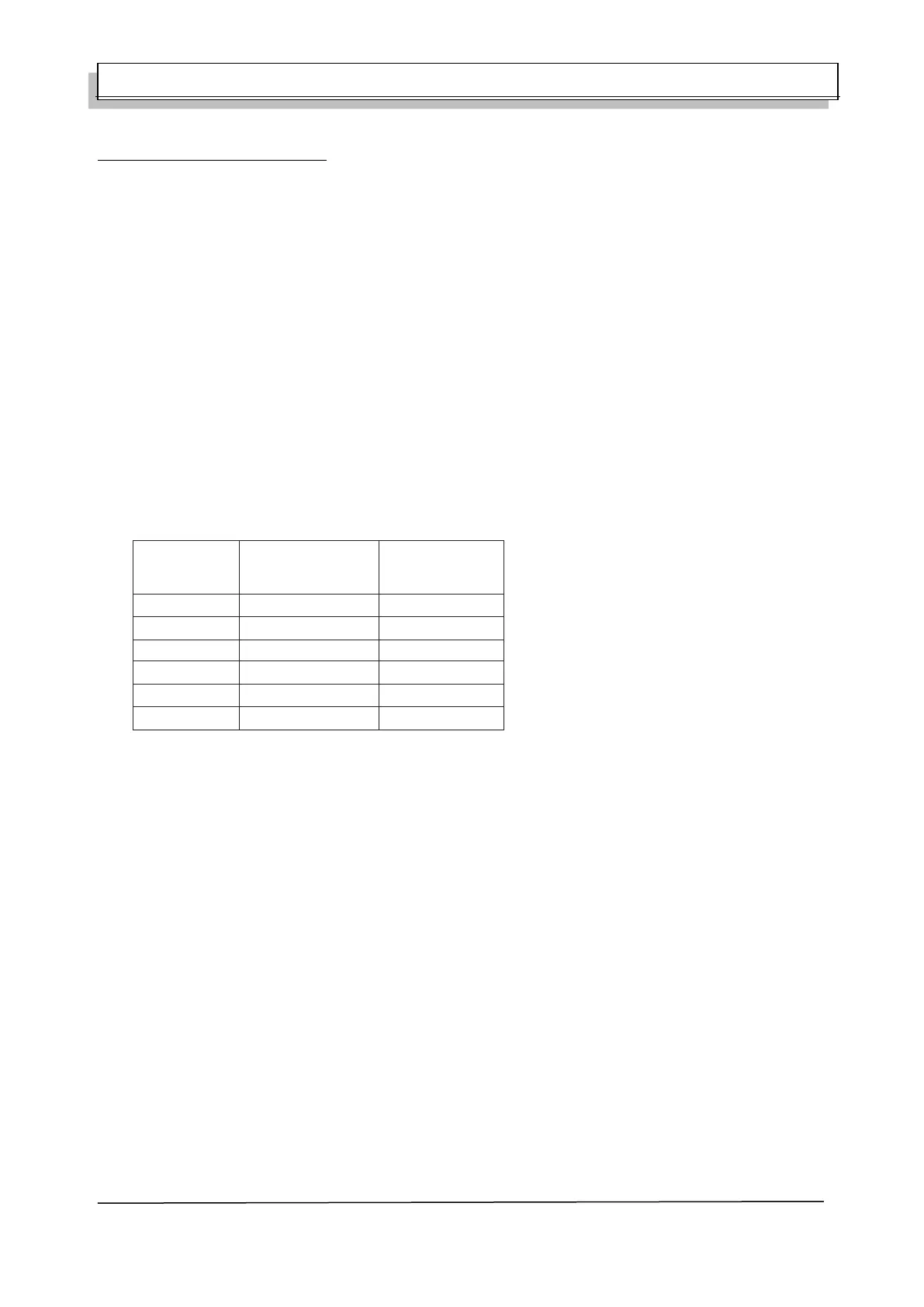
Table2 Electrolyte Freezing Point @ Various States of Charge
Battery Terms Explained
1. Active Material——In the positive plates, the active material is lead dioxide. In the negative, it is metallic
sponge lead. When a circuit is created, these materials react with sulfuric acid during charging and discharging.
2. Ampere (Amp)——A unit of measurement for the electron flow or current through a circuit.
3. Ampere-Hour (Amp. Hr., AH) ——A unit of measure for a battery’s electrical storage capacity, calculated
by multiplying the current in amperes by the time in hours. (Example: A battery which delivers 5 amps for 20
hours provides 5 amps ×20 hours = 100 AH of capacity.)
4. Capacity Rating——The time in minutes that a new, fully-charged battery will deliver 25 amperes or 75
amperes at 800F and maintain a terminal voltage equal to or greater than 1.75 volts per cell.
5. Cell——The basic current-producing unit in a battery. It consists of a set of positive plates, negative plates,
electrolyte, separators and casing, A cell’s nominal voltage is 2 volts. (Example: A 12-volt battery has 6 cells.)
6. Circuit——The path followed by a flow of electrons. A closed, or short, circuit is a complete path. An open
circuit has a broken path.
7. Cycle——One discharge of a battery plus one recharge.
8. Depth of Discharge (DOD)——The percentage of capacity actually removed from a battery compared to the total
rated capacity.
 Loading...
Loading...