MAINTENANCE
7-90
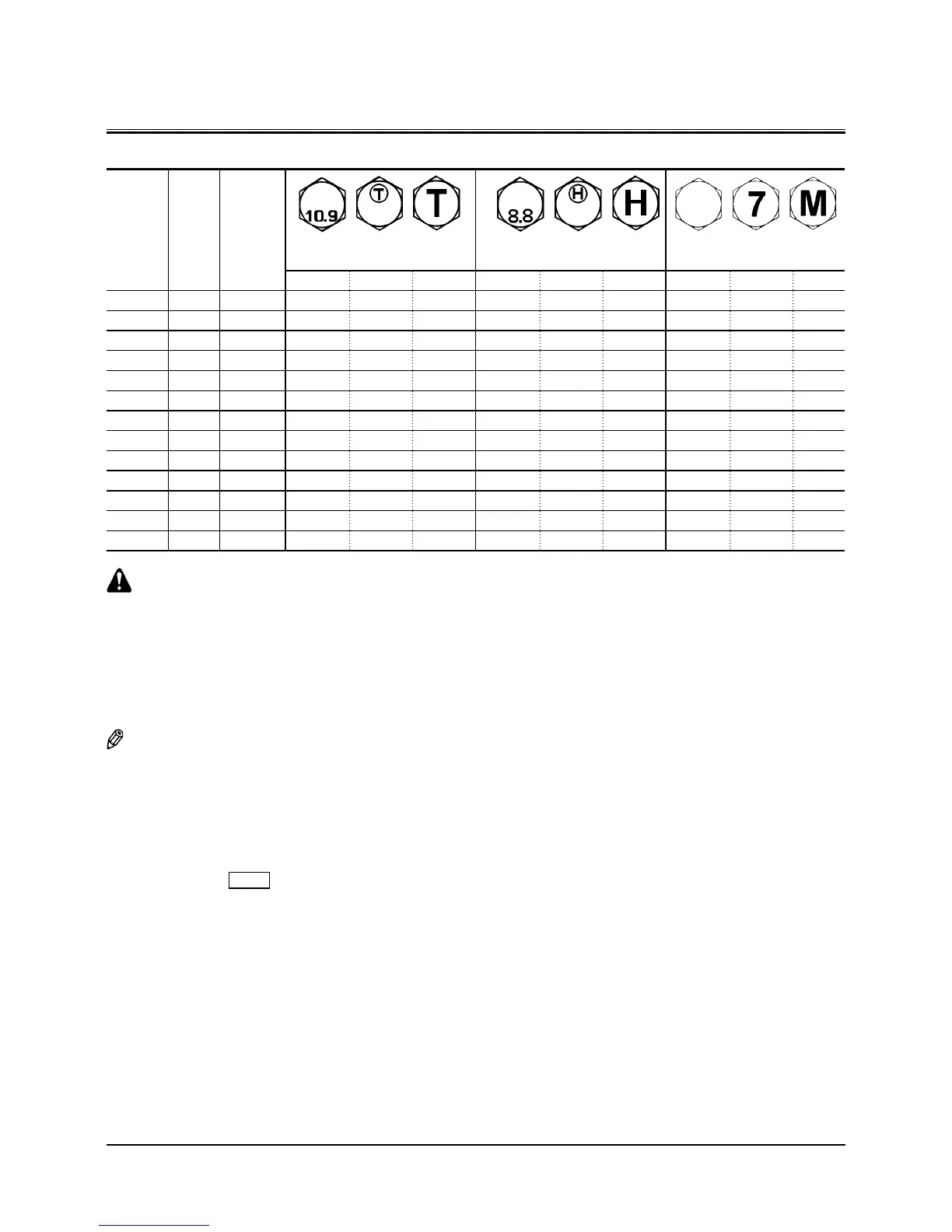
Tightening Torque Chart
Bolt Dia.
Wrench
Size
Hexagon
Wrench Size
M55207091
M55207090
Socket Bol
t
M15707225
N
•
m (kgf
•
m) (lbf
•
ft) N
•
m (kgf
•
m) (lbf
•
ft) N
•
m (kgf
•
m) (lbf
•
ft)
M8 13 6 30 (3.0) (22) 20 (2.0) (15) 10 (1.0) (7.4)
M10 17 8 65 (6.5) (48) 50 (5.0) (37) 20 (2.0) (15)
M12 19 10 110 (11) (81) 90 (9) (66) 35 (3.5) (26)
M14 22 12 180 (18) (135) 140 (14) (103) 55 (5.5) (41)
M16 24 14 270 (27) (200) 210 (21) (155) 80 (8.0) (59)
M18 27 14 400 (40) (295) 300 (30) (220) 120 (12) (89)
M20 30 17 550 (55) (410) 400 (40) (295) 170 (17) (125)
M22 32 17 750 (75) (550) 550 (55) (410) 220 (22) (160)
M24 36 19 950 (95) (700) 700 (70) (520) 280 (28) (205)
M27 41 19 1400 (140) (1030) 1050 (105) (770) 400 (40) (295)
M30 46 22 1950 (195) (1440) 1450 (145) (1070) 550 (55) (410)
M33 50 24 2600 (260) (1920) 1950 (195) (1440) 750 (75) (550)
M36 55 27 3200 (320) (2360) 2450 (245) (1810) 950 (95) (700)
CAUTION: If fixing bolts for counterweight are loos
-
ened, consult your nearest authorized dealer.
IMPORTANT: Make sure bolt and nut threads are clean
before installing.
Apply lubricant (e. g. white zinc B solved
into spindle oil) to bolts and nuts to stabilize
their friction coefficient.
NOTE: Tightening torque required is shown in N•m.
For example, when tightening a bolt or nut with a
wrench of 1 m length, turning the end of it with a force
of 120 N, the torque produced will be:
1 m ×120 N = 120 N•m
To produce the same torque with a wrench of 0.25 m:
0.25 m × N = 120 N•m
Necessary force will be:
120 N•m ÷ 0.25 m = 480 N

 Loading...
Loading...











