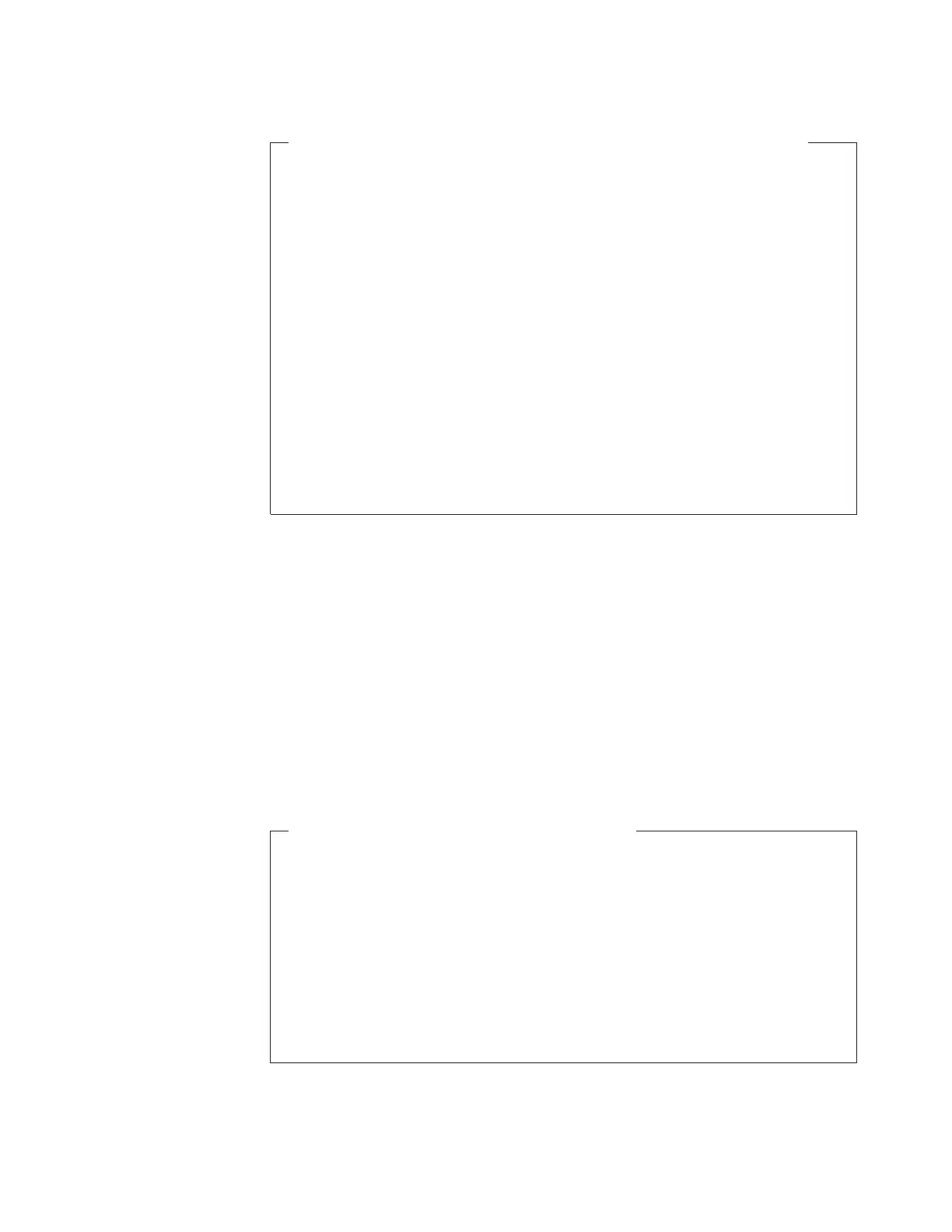
Example of a Problem Caused by Passing Information in a Variable
/******************************* REXX ******************************/
/* NOTE: This exec contains an error. */
/* It uses a DO loop to call an internal subroutine and the */
/* subroutine also uses a DO loop with same control variable as */
/* the main exec. The DO loop in the main exec repeats only once. */
/*******************************************************************/
number1 = 5
number2 = 10
DOi=1TO5
CALL subroutine
SAY answer /* Displays 105 */
END
EXIT
subroutine:
DOi=1TO5
answer = number1 + number2
number1 = number2
number2 = answer
END
RETURN
To avoid this kind of problem in an internal subroutine, you can use:
v The PROCEDURE instruction as described in the next topic.
v Different variable names in a subroutine and pass arguments on the CALL
instruction as described in “Passing Information by Using Arguments” on page 74.
Protecting Variables with the PROCEDURE Instruction: When you use the
PROCEDURE instruction immediately after the subroutine label, all variables used
in the subroutine become local to the subroutine and are shielded from the main
part of the exec. You can also use the PROCEDURE EXPOSE instruction to protect
all but a few specified variables.
The following two examples show the differing results when a subroutine uses the
PROCEDURE instruction and when it doesn’t.
Example Using the PROCEDURE Instruction
/******************************* REXX ******************************/
/* This exec uses a PROCEDURE instruction to protect the variables */
/* within its subroutine. */
/*******************************************************************/
number1 = 10
CALL subroutine
SAY number1 number2 /* displays 10 NUMBER2 */
EXIT
subroutine: PROCEDURE
number1 = 7
number2 = 5
RETURN
Writing a Subroutine;
Chapter 6. Writing Subroutines and Functions 73
 Loading...
Loading...











