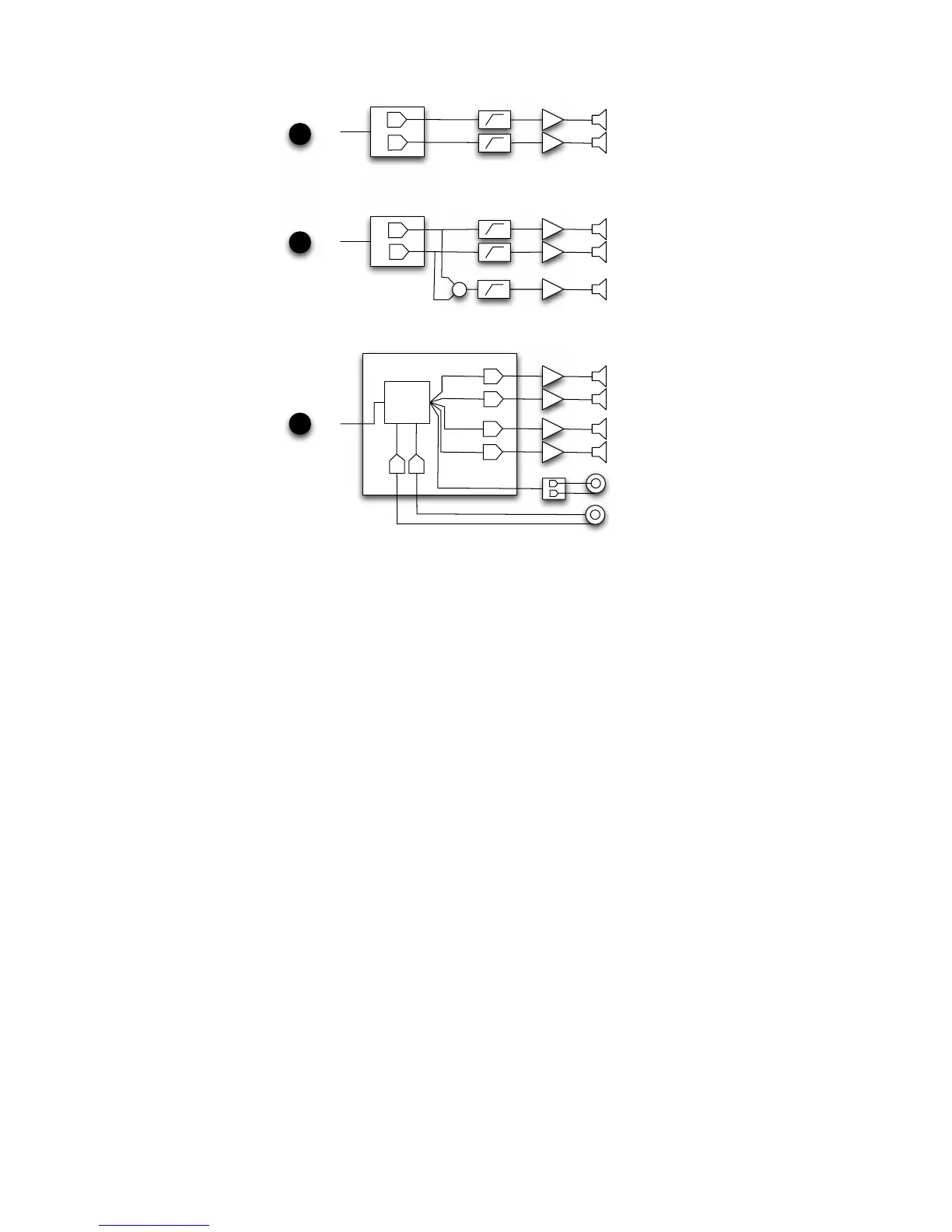
Figure 7: Comparison of different desktop speaker architectures.
In the figure above (Figure 7), Section A shows a typical 2.0 desktop speaker system with single
drivers for each channel, and two power amplifiers. This design will generally compromise low-
and high-frequency response.
Section B shows a desktop 2.1 system with stereo satellite speakers plus a subwoofer. This
type of system will make up the low-end and sound full, but it will lack a flat frequency response
to 20 kHz
Section C shows the design of Squeezebox Boom. Four separate speakers, four separate
amplifiers, and six DACs all digitally controlled with a high powered DSP provide the ultimate in
acoustic signal integrity and can produce great sound through the entire audio spectrum.
Without a subwoofer, the Squeezebox Boom goes from a -3 dB response at 50 Hz (at low
volume settings) to about 85 Hz (at high volume settings), all the way to 20 kHz. With the
addition of a subwoofer, the entire audio band, from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, is covered.
The Squeezebox Boom DSP
The Squeezebox Boom uses a 48-bit-by-24-bit, 135 MIPS (million instructions per second) DSP
core. With such significant DSP horsepower there are many ways to improve the sound quality;
good crossovers are just the beginning.
One may wonder why we need a 48-bit data path, providing 289 dB of dynamic range, when 16-
bits and 24-bits (96 dB to 144 dB) is good enough for most sound systems The answer is that
when performing mathematical operations (e.g., DSP) on a signal, the signal is often multiplied,
divided, and added to many times. With a 16-bit data signal, any 16-bit signal processing will
inevitably result in loss of signal fidelity, either by causing overflow, saturation, or extra
quantization noise. Quantization noise, saturation and overflow are undesirable.

 Loading...
Loading...