
Do you have a question about the Mercedes-Benz OM 471 and is the answer not in the manual?
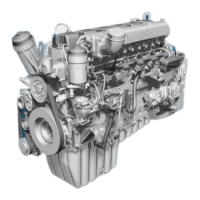
| Engine Type | Inline 6-cylinder |
|---|---|
| Displacement | 12.8 L |
| Fuel System | Common Rail Direct Injection |
| Bore | 132 mm |
| Aspiration | Turbocharged |
Details the plastic cylinder head cover, its prefilter, and acoustic decoupling elements.
Describes the one-piece cylinder head with intake/exhaust valves and bolt tightening procedures.
Explains the multi-layered stainless steel cylinder head gasket and its elastomer elements.
Details the crankcase structure, coolant and oil ducts, and major assemblies located on it.
Describes the forged steel connecting rods, their strength, and the cracked connecting rod bearing cap.
Details the piston structure, crown, ring zone, skirt, and cooling duct.
Explains the crankshaft mounting, bearing journals, counterweights, and oil holes.
Describes the valve control system, including camshafts, rocker arms, and valves.
Details the gear drive system on the engine's output side, driven assemblies, and spatial transfer levels.
Explains the engine's two overhead camshafts, their drives, and the function of cams and brake cams.
Describes the two belt variants, tandem clamping device, and poly-V belt functions.
Explains the system's role in relieving crankcase pressure by directing blow-by gases to the air intake pipe.
Details how the turbocharger compacts air for increased engine power and torque.
Covers boost pressure regulation via wastegate and turbocharger speed monitoring for protection.
Explains the MCM control unit's role in optimizing injection timing and quantity for efficient combustion.
Details the engine management network, control units, and CAN bus connections.
Describes how the MCM handles faults and enters limp-home mode.
Explains the engine start sequence, requirements, and fuel injection timing.
Details how the MCM controls idle speed based on CPC unit specifications and operating conditions.
Explains setting working speed via accelerator or steering wheel for power take-off.
Describes normal driving mode, adjusting injection quantity based on driver requests and engine torque.
Explains how the MCM initiates engine shutdown by interrupting fuel injector actuation.
Details how engine speed and crankshaft angle are determined using flywheel signals.
Explains determining cylinder 1 compression stroke using crankshaft and camshaft sensor signals.
Describes how coolant temperature is determined using intake and outlet sensors.
Explains how air mass is determined using various sensors for injection quantity calculation.
Details how fuel temperature is determined using the fuel temperature sensor for injection period calculation.
Explains how the CPC unit calculates target engine torque based on driver input and vehicle status.
Describes the decompression brake system and its operation in different brake stages.
Explains the EGR system's role in reducing NOx emissions by mixing exhaust gas with fresh air.
Explains the EATS compliance with Euro V/EEV standards and its components like SCR, DOC, DPF.
Covers the low-pressure and high-pressure fuel circuits and their components.
Details the CGW's role in vehicle networking, routing CAN messages, and monitoring control units.
Explains the CPC unit's function in calculating driving factors and communicating with other control units.
Describes the MCM unit's role as an interface for engine systems and its control tasks.
Details the MCM's task in regulating APCRS injection using sensor data.
Explains EGR rate regulation via the positioner and its dependency on various sensors.
Covers DPF regeneration phases and the role of the MCM in actuating fuel shutoff and metering valves.
Describes the ICUC's function in displaying engine data and using various sensor values.
Explains fan control using coolant temperature sensors and engine speed.
Details how the MCM actuates engine brake solenoid valves based on driver input.
Explains the EBS unit's role in recording driver commands and actuating brake pressures.
Describes the PSM unit's integration in vehicle networking and its implementation of complex controls.
Details the BESO unit's function in disconnecting the onboard electrical system via EMERGENCY OFF switches.
Explains the EATU output NOx sensor's role in measuring exhaust NOx concentration before SCR conversion.
Describes the outlet NOx sensor's function in calculating raw NOx concentration in the exhaust.
Details the ACM unit's regulation of all exhaust aftertreatment functions and sensor data processing.
Describes the EATU input NOx sensor's role in computing NOx concentration before SCR and ammonia slip stages.
Explains the AdBlue metering device's function in injecting AdBlue into the exhaust flow.
Details the auxiliary water heater unit's function for preheating, continuous, and stationary heating.
Explains the circulation pump's function in pumping coolant through the heater unit's heat exchanger.
Describes the travel and speed sensor's task at initialization and while driving.
Explains the upstream pressure sensor's function in measuring exhaust pressure before the DOC.
Details the downstream pressure sensor's role in recording exhaust pressure after the DPF.
Describes the accelerator pedal sensor's function in detecting pedal position via Hall sensors.
Explains the upstream exhaust temperature sensor's function in measuring temperature before the DOC.
Details the downstream exhaust temperature sensor's role after the upper DOC for temperature measurement.
Describes the downstream exhaust temperature sensor's function after the lower DOC for temperature measurement.
Explains the downstream exhaust temperature sensor's role after the DPF for temperature measurement.
Details the upstream exhaust temperature sensor's function before the SCR catalytic converter.
Describes the downstream exhaust temperature sensor's role after the SCR catalytic converter.
Explains the AdBlue sensor's function in recording fluid level and temperature in the AdBlue® container.
Details the coolant pressure sensor's role in monitoring coolant circuit pressure for solenoid valve control.
Explains the crankshaft sensor's function in determining engine speed and crankshaft position.
Describes the camshaft sensor's role in detecting compression cycles and engine speed.
Details how the fuel temperature sensor determines fuel temperature for injection period calculation.
Explains the oil pressure sensor's function in determining current engine oil pressure.
Describes the oil fill level sensor's role in determining engine oil level and temperature.
Explains the exhaust coolant sensor's function in determining current coolant temperature at engine outlet.
Describes the intake coolant sensor's role in determining current coolant temperature downstream of the coolant pump.
Details the charge air sensor's function in determining air pressure and temperature for combustion air.
Explains the turbine wheel sensor's role in detecting turbocharger rotor speed for protection.
Describes the air filter sensor's function in detecting intake air temperature for boost pressure and injection adaptation.
Details the charge air housing sensor's role in detecting air temperature before combustion.
Explains the EGR sensor's function in supplying data for calculating EGR volumetric flow rate.
Describes the rail pressure sensor's role in determining current rail pressure for the MCM.
Details the diesel fuel metering device's use in providing fuel quantity for DPF regeneration.
Explains the fuel filter sensor's role in detecting filter condition and for diagnostics.
Describes the quantity control valve's tasks in regulating fuel feed, rail pressure, and fuel supply.
Explains the pressure limiting valve's function as a safety element limiting maximum rail pressure.
Details the fuel pump's design as a gear pump and its supply of fuel to the high-pressure circuit.
Explains the fuel cooler's function in cooling warmed fuel from injector pressure boosters.
Describes the fuel filter module's function in separating water and filtering dirt particles in two stages.
Explains the turbocharger's function in converting exhaust energy into mechanical energy and compacting air.
Details the EGR cooler's role in cooling exhaust gas before it enters the charge air pipe.
Explains the SCR converter's function in reducing NOx into nitrogen and water.
Describes the exhaust aftertreatment unit's function in limiting emissions and noise.
Explains the DPF's role in filtering and storing soot particles and its regeneration process.
Details the auxiliary water heater unit's function for preheating, continuous, and stationary heating.
Explains the circulation pump's function in pumping coolant through the heater unit's heat exchanger.
Describes the travel and speed sensor's task at initialization and while driving.
Explains the EGR positioner's role in regulating recirculated exhaust gas volume.
Details the engine brake solenoid valves' task in supplying oil pressure to hydroelements.
Explains the AdBlue heater coolant valve's function in heating AdBlue lines and the container.
Describes the boost pressure regulator's function in limiting boost pressure and rotor speed.
Describes the quantity control valve's tasks in regulating fuel feed, rail pressure, and fuel supply.
Explains the pressure limiting valve's function as a safety element limiting maximum rail pressure.
Details the fuel pump's design as a gear pump and its supply of fuel to the high-pressure circuit.
Explains the fuel cooler's function in cooling warmed fuel from injector pressure boosters.
Describes the fuel filter module's function in separating water and filtering dirt particles in two stages.
Explains the turbocharger's function in converting exhaust energy into mechanical energy and compacting air.
Details the EGR cooler's role in cooling exhaust gas before it enters the charge air pipe.
Explains the SCR converter's function in reducing NOx into nitrogen and water.
Explains the DPF's role in filtering and storing soot particles and its regeneration process.
Explains the nozzle unit's function in injecting diesel fuel for DPF regeneration.
Describes the heat exchanger's role in transferring coolant heat to airflow for cabin temperature control.
Details the oil pump's design and function in supplying oil to the engine's oil circuit.
Details the module's use in filtering oil, regulating oil and coolant temperature, and supporting the coolant pump.
Explains the oil thermostat's function in regulating engine oil temperature.
Describes the heat exchanger's role in cooling engine oil using engine coolant.
Explains the coolant thermostat's function in regulating coolant flow and engine inlet temperature.
Details the secondary water retarder's design and task in converting coolant flow energy into braking energy.











 Loading...
Loading...