Maintenance techniques, tools and
working facilities
o- 9
Fastener sizes
For a number of reasons, automobile manufacturers are making wider
and wider use of metric fasteners. Therefore, it is important to be able to
tell the difference between standard (sometimes called U.S. or SAE) and
metric hardware, since they cannot be interchanged.
All bolts, whether standard or metric, are sized according to diameter,
thread pitch and length. For example, a-standard l/2 - 13 x 1 bolt is l/2
inch in diameter, has 13 threads per inch and is 1 inch longiAn M12- 1.75
x 25 metric bolt is 12 mm in diameter, has a thread pitch of 1.75 mm (the
distance between threads) and is 25 mm long. The two bolts are nearly
identical, and easily confused, but they are not interchangeable.
In addition to the differences in diameter, thread pitch and length, met-
ric and standard bolts can also be distinguished by examining the bolt
heads. To begin with, the distance across the flats on a standard bolt head
.is measured in inches, while the same dimension on a metric bolt is sized
in millimeters (the same is true for nuts). As a result, a standard wrench
should not be used on a metric bolt and a metric wrench should
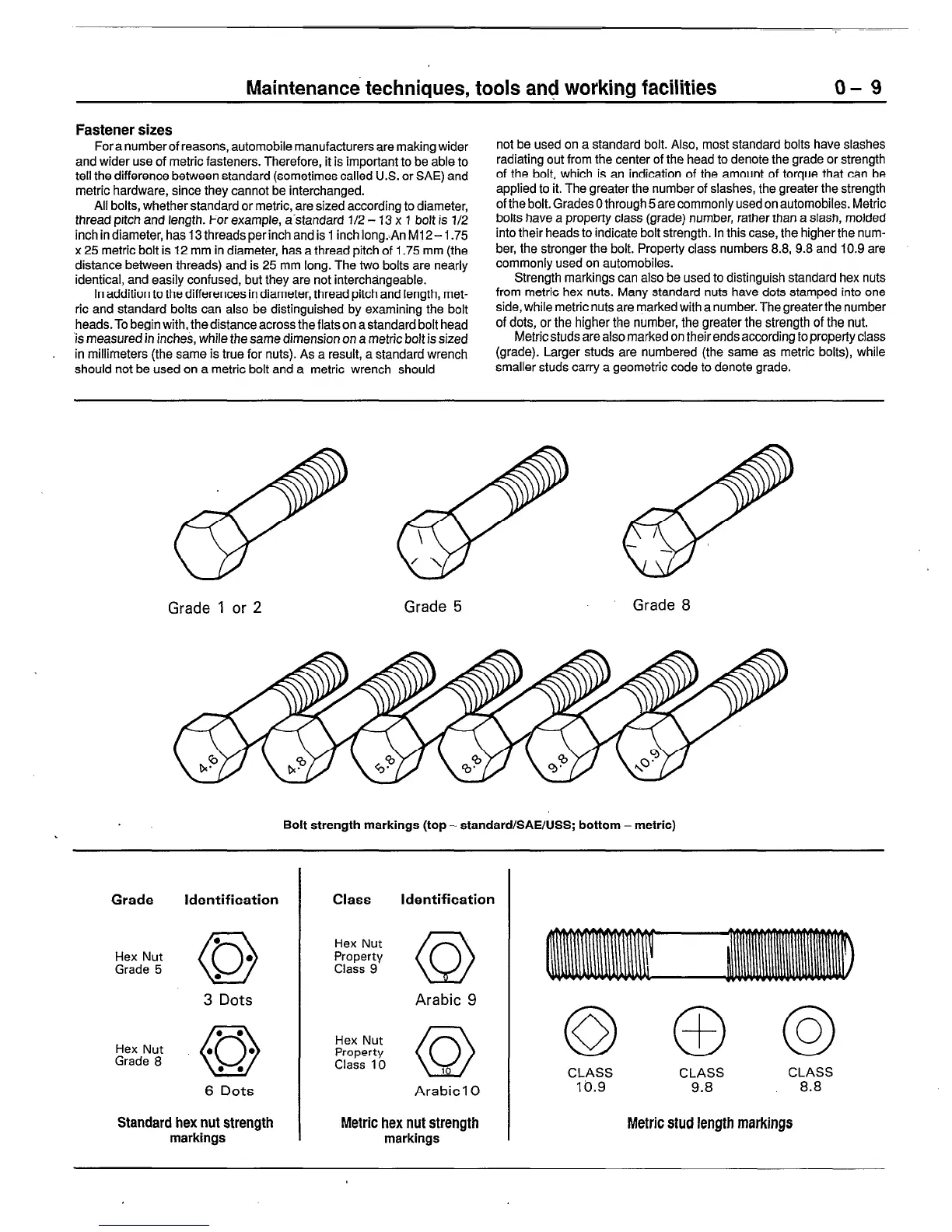
not be used on a standard bolt. Also, most standard bolts have slashes
radiating out from the center of the head to denote the grade or strength
of the bolt, which is an indication of the amount of torque that can be
applied to it. The greater the number of slashes, the greater the strength
of the bolt. Grades 0 through 5 are commonly used on automobiles. Metric
bolts have a property class (grade) number, rather than a slash, molded
into their heads to indicate bolt strength. In this case, the higher the num-
ber, the stronger the bolt. Property class numbers 8.8, 9.8 and 10.9 are
commonly used on automobiles.
Strength markings can also be used to distinguish standard hex nuts
from metric hex nuts. Many standard nuts have dots stamped into one
side, while metric nuts are marked with a number. The greater the number
of dots, or the higher the number, the greater the strength of the nut.
Metric studs are also marked on their ends according to property class
(grade). Larger studs are numbered (the same as metric bolts), while
smaller studs carry a geometric code to denote grade.
Grade 1 or 2
Grade 5
Grade 8
.
Bolt strength markings (top - standard/SAE/USS; bottom-metric)
Grade Identification
l
Hex Nut
0
0
0
Grade 5
l
3
Dots
. 0
Hex Nut
0
.
0
.
Grade 8
. .
6
Dots
Standard hex nut strength
markings
Class Identification
Hex Nut
f+&y 0
Arabic 9
Hex Nut
Property
Class 10 0
1
Arabic1 0
Metric hex nut strength
markings
CLASS CLASS
CLASS
10.9 9.8 8.8
Metric stud length markings

 Loading...
Loading...











