25
The biggest cause of recovery score dropping a large amount on any given day is a significant jump up or
down in HRV (as compared to the rolling 10-day average HRV). The next biggest cause of recovery score
dropping a large amount on any given day is a proportionally large amount of time spent in the Overload (red)
Zone.
There are very specific recovery strategies that can be implemented each day depending on both your
recovery score and your HRV. Below is how to look at this.
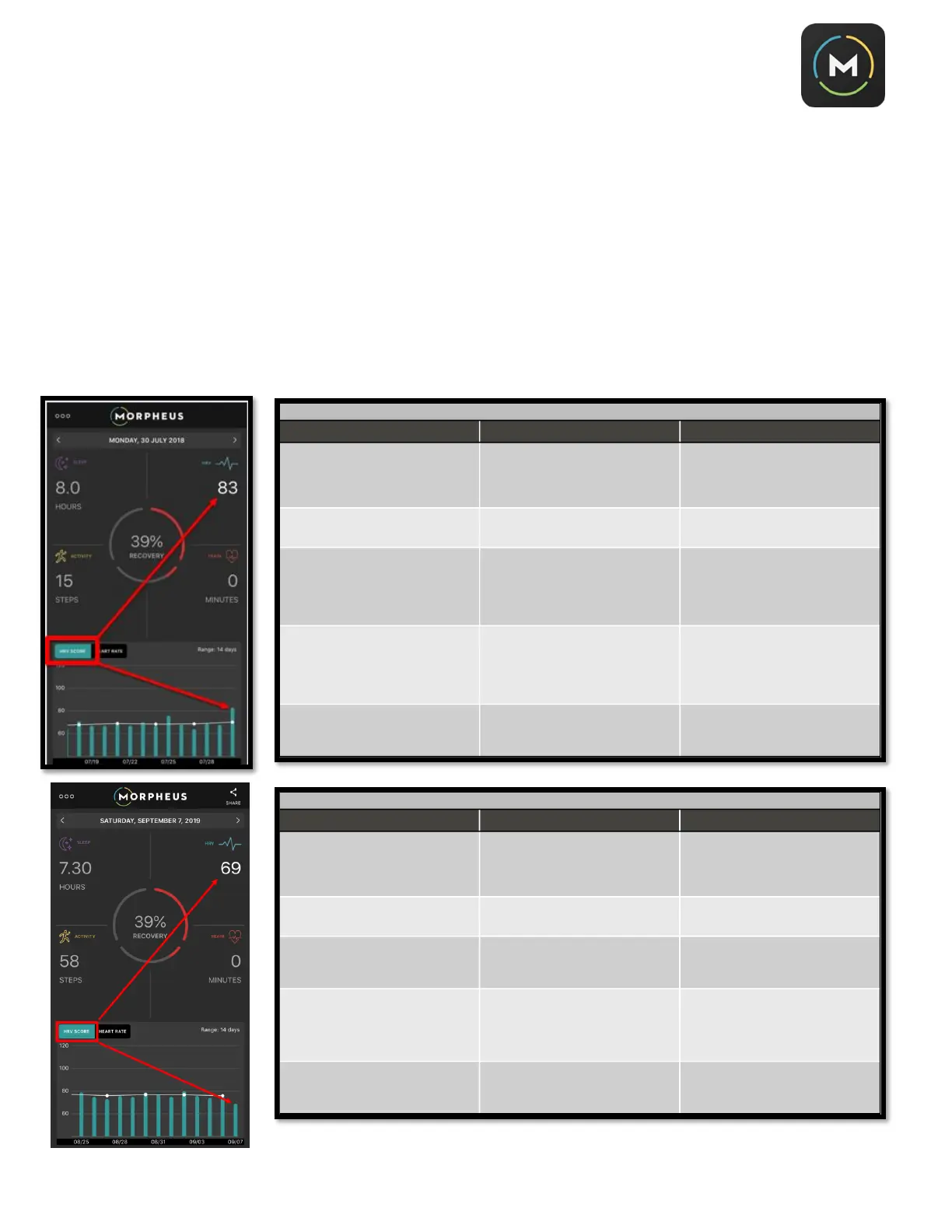
If after your recovery test, your recovery score is less than 60%, click on the HRV quadrant on the upper right
of the screen. Check to see if your HRV jumped up or dropped down a lot relative to your previous day and
your average HRV (the white line). There are different recovery strategies to implement when recovery score
is low and HRV has jumped up versus when recovery score is low and HRV has dropped down.
Recovery Technique Purpose Protocol
•A variety of low load activities can be
performed from bike, jog, swim,
bodyweight exercises, etc. for less than 30
minutes.
•Heart rate in recovery zone.
Intensive Deep Tissue Therapy
•Increase proprioceptive input to CNS
through physical contact in order to affect
change in neuromuscular system
•Deep tissue work = higher level of stimulus
•May reduce feelings of fatigue and
soreness if used post-workout
•Can be used after training sessions,
particularly when performed in heat
•Produces sympathetic response
•May be performed in between workouts
for sympathetic stimulation
•May reduce resulting inflammation from
training
•1-3 minutes cold, 2-5 repeats most
common protocols
•Increase core temperature
•Greater temperature = greater stress
response
•Sympathetic increase during sauna use,
but parasympathetic increase in period
following
•5-10 minutes, 1-3 repetitions
•Increases speed of metabolic processes •Finish with 2-3 minutes warm water rinse
•Greater temperature difference between
hot/cold generally improves effectiveness
•2 or 3 to 1 hot to cold ratio, 2-4 repeats is
general guideline
Low Recovery % When HRV Rises
•Increase cardiovascular function and
blood flow to muscles, brain, etc. to speed
up processes of aerobic metabolism
inherent in recovery
Contrast Therapy (hot/cold)
•Stimulate sympathetic system through
moderate stress – large change in
temperature
Recovery Technique Purpose Protocol
•A variety of low load activities can be
performed from bike, jog, swim,
bodyweight exercises, etc. for less than
30 minutes.
•Heart rate in recovery zone.
•Increase proprioceptive input to CNS
through physical contact in order to affect
change in neuromuscular system
•For parasympathetic function, low
intensity relaxation techniques should be
used
•Increase parasympathetic function
through relaxation effect of hot water.
•Research shows decreased
sympathetic function at 102 degrees
•Stimulatory changes from total body
immersion and hydrostatic pressure
•5-25 minutes is common duration
•Reduced impact of gravity decreases
sympathetic drive
•Minimum of 10 feet deep water
•10-20 minutes floating using support to
increase buoyancy
•Reduce sympathetic tone and increase
parasympathetic function.
•Ideally should be done in dark, quiet
environment
•Music, breathing, biofeedback,
meditation techniques, etc.
•Increase cardiovascular function and
blood flow to muscles, brain, etc. to
speed up processes of aerobic
metabolism inherent in recovery
Deep Water Floating / Light Swim
Mental Relaxation + Breathing Tech
Low Recovery % When HRV Drops
 Loading...
Loading...