6
1 DESIGN
Control the damping force
When you turn the compression or rebound
adjuster you change the size of the bleed
valve. Depending on which direction you turn
the adjuster you either increase or decrease
the damping force. The characteristics of the
damping action can be changed by changing
the shim stack set up, like for example shim
thickness, diameter and shape as well as
number of shims. Please note that only
approved Öhlins personnel must change the
shim stack set up.
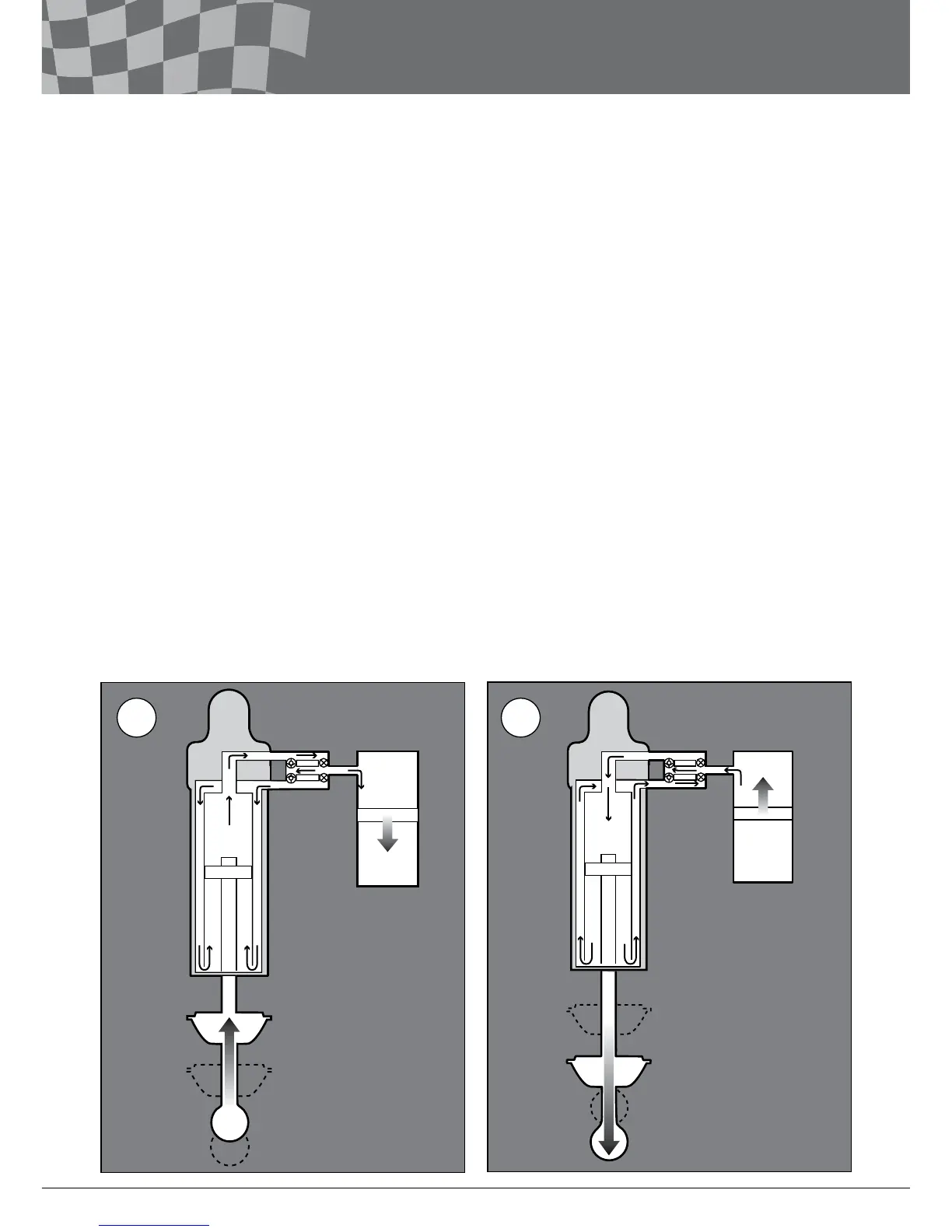
Compression damping
When the motorcycle movement compresses
the shock absorber, the uid above the main
piston is pressurized (more than the gas
pressure set in the shock absorber). The
pressurized uid then goes through:
• the compression adjuster bleed valve
• the compression adjuster shim valve
• the channel connected to the reservoir
• the rebound adjuster check valve and
between the inner and the outer tube to the
other side of the main piston.
During compression stroke the piston rod goes
into the shock absorber body and the displaced
volume of damper uid ows into the reservoir.
The uid moves the separating piston inside the
reservoir.
Rebound damping
When the spring forces the shock absorber to
extend, the uid below the piston is pressurized
(more than the gas pressure set in the shock
absorber) and must move. The ow goes
through:
• the rebound adjuster bleed valve
• the rebound adjuster shim valve
• the channel connected to the reservoir
• the compression adjuster check valve into
the inner tube and to the upper side of the
main piston.
The uid that was displaced into the reservoir
during compression stroke is now pushed back
into the shock absorber main body by the gas
pressure. The separating piston will move inside
the reservoir as the uid is pushed out.
2 3
 Loading...
Loading...