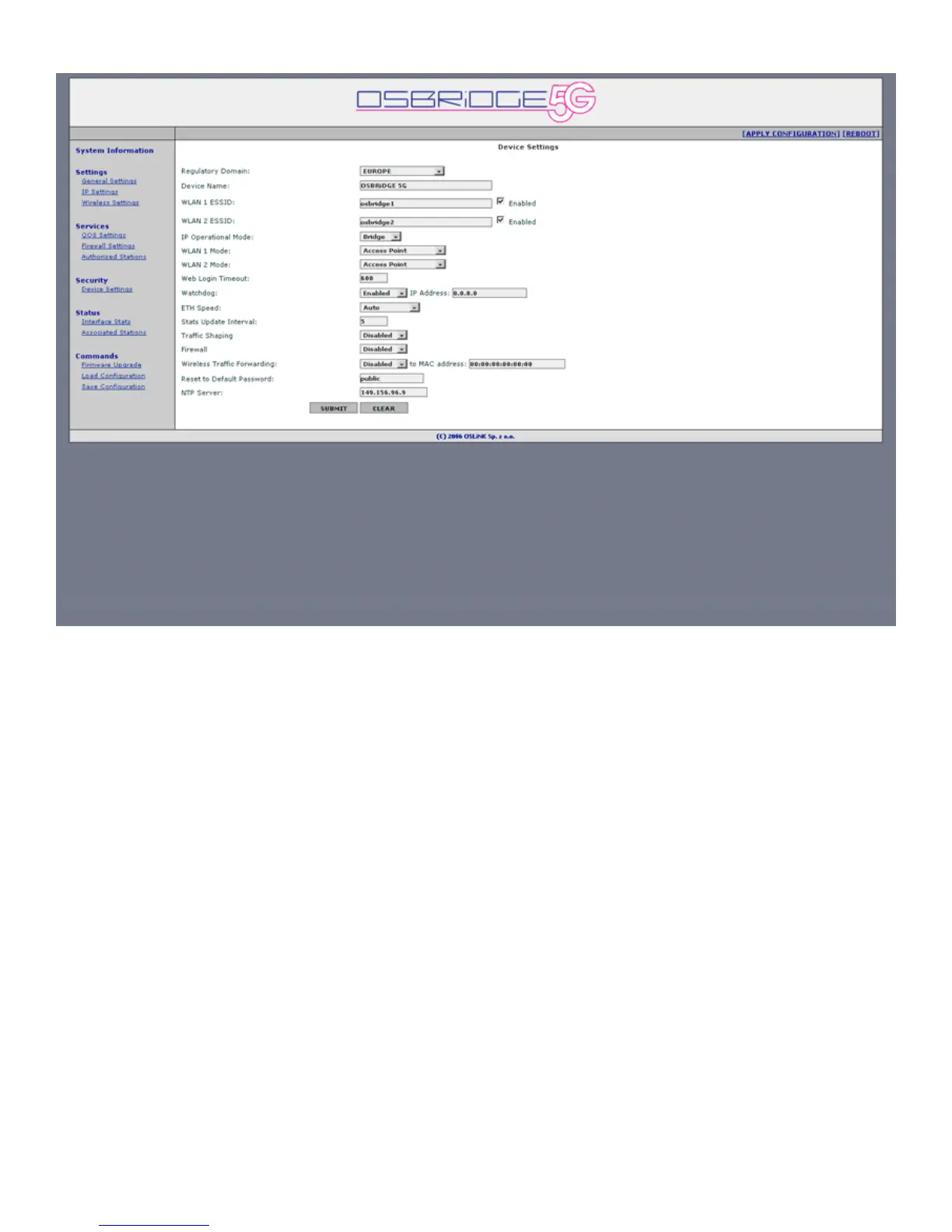
3. General Settings
Regulatory Domain – Please select regulatory domain that is most appropriate to your
location.
Supported Regulatory Domains and allowed frequency ranges are as follows:
Europe – 5500 – 5700 MHz with 20MHz channel step (11 channels) and DFS;
OFCOM UK – 5735 MHz, 5755 MHz, 5775 MHz, 5835 MHz with DFS;
USA – 5180 – 5320 MHz with 20MHz channel step, 5745 - 5825MHz with 20 MHz channel
step (13 channels);
Far East & Africa – 4920 – 6100 MHz with 10 MHz channel step, 802.11a and 802.11a
Turbo modes (118 channels).
Device Name - This is the system name for easy identification of the OSBRiDGE 5G unit.
WLAN 1 ESSID - An ESSID is the unique name shared among all peers in your wireless
network. The name must be identical for all devices attempting to connect to the same network.
It shall be up to 32 characters length.
WLAN 2 ESSID - An ESSID is the unique name shared among all peers in your wireless
network. The name must be identical for all devices attempting to connect to the same network.
It shall be up to 32 characters length.
IP Operational Mode –
Bridge - Bridge works at OSI model Layer 2. This means it does not know anything about
protocols, but just forwards data depending on the destination address in the data packet.
This address is not the IP address, but the MAC (Media Access Control) address that is
unique to each network adapter card. With a Bridge, all your computers are in the same
network subnet, so you don't have to worry about not being able to communicate between
 Loading...
Loading...