l
Oxygen (O
2
)
Fish and plants need oxygen to survive. During the
day, aquarium plants absorb carbon dioxide and
emit oxygen, due to photosynthesis. Fish breathe
by absorbing oxygen via their gills. Oxygen is also
required by micro-organisms, especially by important
filter bacteria. If your aquarium contains roots,
they will also need oxygen. At night, on the other
hand, aquatic plants emit CO2 and absorb oxygen.
For this reason, the oxygen content in non-aerated
aquariums is lower, sometimes even dramatically
lower, in the morning than in the evening. Make
sure that the oxygen saturation value does not
fall below 20% and that the oxygen concentration
is always between 6 and 8 mg/l. The maximum
oxygen solubility in water depends on the water
temperature and the salt content. It is given in
mg/l. In the long run, a lack of oxygen can cause
your fish to become susceptible to disease, which
is why we advise you to always aerate at night.
The test procedure
Note: The oxygen content in unaerated aquariums
is lower in the morning than later on in the day.
At night, aquatic plants do not produce oxygen,
but absorb it instead. We therefore recommend
that you measure the oxygen content in the
Water temperature °C O
2
per litre
5° 12,8 mg/l
10° 11,3 mg/l
15° 10,1 mg/l
20° 9,1 mg/l
25° 8,3 mg/l
30° 7,6 mg/l
35° 6,9 mg/l
Oxygen saturation concentrations of fresh water.
Corresponds to 100% saturation.
morning. The test measures oxygen contents
ranging from 2 mg/l to 14 mg/l. The illustrations
below should simplify the procedure.
1. Rinse the test vial with the sample water.
2. Fill the test vial up to the 15 ml mark with sample
water.
3. Hold reagent bottle 1 upside down and add 5 drops
to the test vial.
4. Hold reagent bottle 2 upside down and add 5 drops
to the test vial.
5. Immediately place the lid on the test vial; turn
the vial upside down once to mix the content,
then bring it to the upright position again.
6. A precipitate is formed. Let the test vial stand
for 30 seconds.
7. Remove the lid. Hold reagent bottle 3 upside
down and add 5 drops to the test vial.
8. Immediately press the lid onto the test
vial and turn it upside down and back again
twice. The precipitate dissolves and the
test solution turns a reddish-purple colour.
9. Shake the test vial gently and match the shade
of the test solution to the colour it comes
closest to on the colour chart. Read the value by
holding the test vial approximately 1 cm (a finger‘s
breadth) from the white area on the colour chart.
of the test solution to the colour it comes
closest to on the colour chart. Read the value by
holding the test vial approximately 1 cm (a finger‘s
breadth) from the white area on the colour chart.
After each test, rinse the test vial thoroughly with
tap water.
What action shall I take if...
...the phosphate content is too high?
To reduce the phosphate content immediately,
we recommend changing at least 30% of
the aquarium water. To keep this favourable
water parameter stable, we recommend
the regular use of Tetra EasyBalance.
l
Iron (Fe)
In addition to nitrate and phosphate, such trace
elements as iron are also essential nutrients for
healthy aquatic plant growth. Iron encourages the
formation of chlorophyll (green pigment of plants).
The iron concentration in your aquarium should
range between 0.25 and 0.5 mg/l – a value suitable
for all aquatic plants. If the iron value is below 0.1
mg/l for a long period, the plants will be unable to
grow and their leaves will turn yellow.
The test proceduref
Please read this section carefully before starting
the test. The test measures iron contents
ranging from 0 mg/l to 1 mg/l. The illustrations
below should simplify the procedure.
1. Rinse the test vial with the sample water.
2. Fill the test vial up to the 5 ml mark with sample
water.
3. Half-fill both chambers of the test vial lid with the
test powder (halfway up to the bar) from
the powder tin.
4. Pour the test powder into the test vial and
shake the vial gently.
5. Hold the bottle with the liquid test reagent
upside down and add 5 drops to the test vial.
6. Shake the test vial gently.
7. Allow 10 minutes for the colour to develop,
shaking the vial gently several times in between.
8. Shake the test vial gently, match the shade of
the test solution to the colour it comes closest
to on the colour chart and read the value.
Compare the shade of the test solution with the
colour chart by looking sideways at the vial and
holding it approximately 1 cm (a finger‘s breadth)
in front of the white area of the colour chart.
After each test, rinse the test vial thoroughly with
tap water.
What action shall I take if...
...the iron content is too low?
Use Tetra plant fertiliser Tetra PlantaMin to
easily adjust the iron values in your aquarium.
l
Carbon dioxide (CO
2
)
Aquatic plants need CO
2
for nutrition and
growth. High concentrations of CO
2
, however,
can be dangerous to ornamental fish.
The optimum long-term concentration in
aquarium water is between 5 and 15 mg/l.
The test procedure
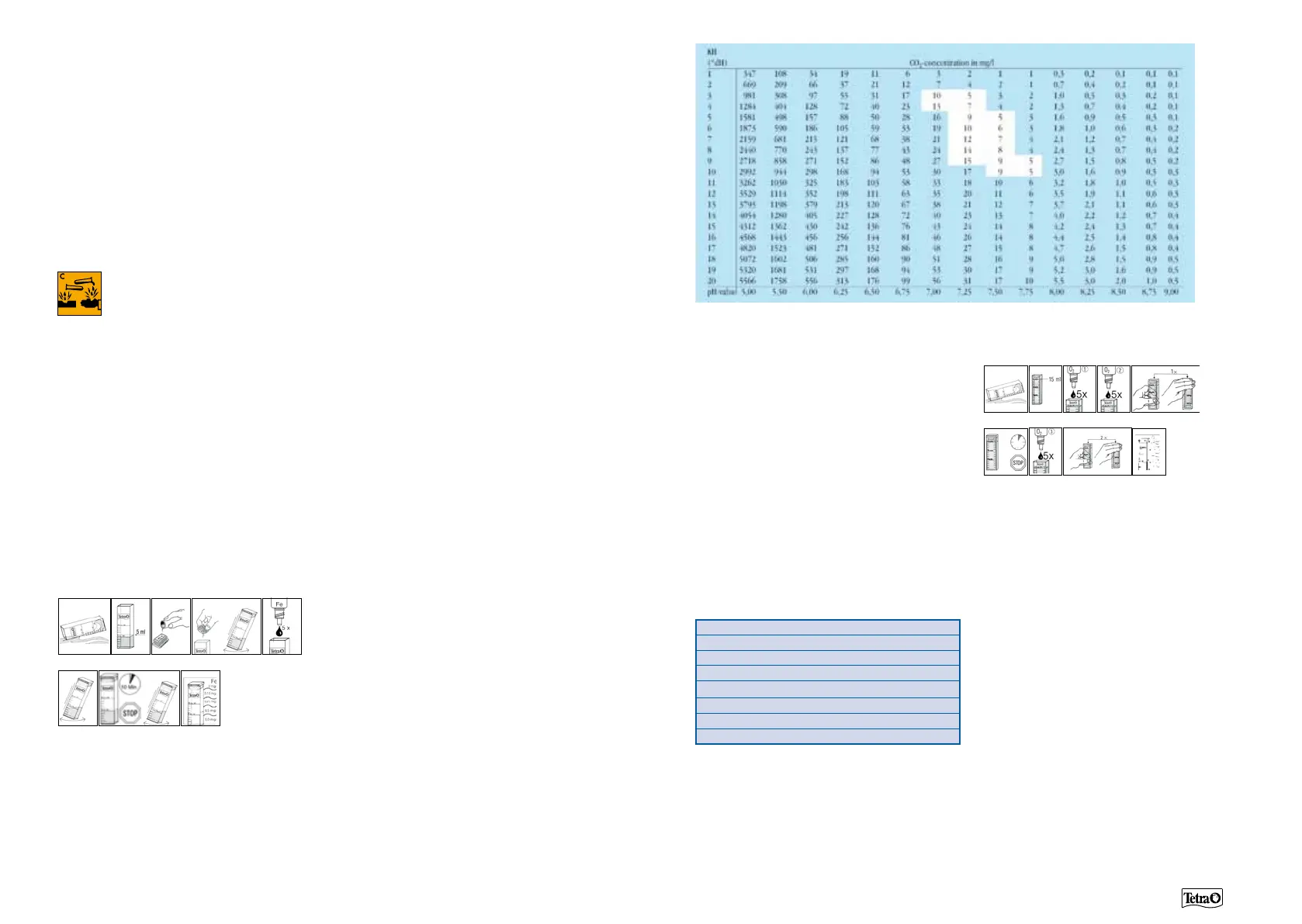
After having determined the pH value and the
carbonate hardness, you can read the CO2 content
of the aquarium water from the calculation
table. The values relate to a water temperature
of 25°C. With other water temperatures, the
values differ only slightly from those given in the
table. Recommended CO2, pH and KH values
can be found inside the area framed in white.
What action shall I take if...
...the CO
2
content is too high?
You can reduce excessive carbon dioxide
concentrations in the aquarium water by ventilating
the aquarium using an air stone and an air pump, e.g.
Tetra Air Pump.
...the CO
2
content is too low?
Use Tetra CO
2
-Optimaten to add carbon dioxide to
the water for an optimum value. CO
2
is also created
by adding Tetra EasyBalance on a weekly basis.
Causes burns. Keep locked up and out of the reach of children.
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. In case of contact with eyes, rinse
immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. In case
of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately
(show the label where possible). Contains sulphuric acid.
Corrosive
8
9

 Loading...
Loading...