26
G
RAPHING
T
ECHNOLOGY
G
UIDE
: TI-82
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Figure 2.71: Sequence mode
Of course, you could use the explicit formula for the n-th term of an arithmetic sequence, t
n
= a + (n – 1)d. First
enter values for the variables a, d, and n, then evaluate the formula by pressing ALPHA A + ( ALPHA N – 1 )
ALPHA D ENTER. For a geometric sequence whose n-th term is given by t
n
= a · r
n – 1
, enter values for the
variables a, r, and n, then evaluate the formula by pressing ALPHA A ALPHA R ^ (ALPHA N – 1 ) ENTER.
To use the explicit formula in Seq MODE, make u
n
= 7 + (n – 1) ·4 by pressing Y= and then 7 + (2nd n – 1 ) × 4.
Once more, calculate u
18
by pressing 2nd Y-
VARS
4 1 ( 18 ) ENTER.
There are more instructions for using sequence mode in the TI-82 manual.
2.7.3 Sums of Sequences: Calculate the sum
12
1
4(0.3)
n
n
=
∑
on the TI-82 by pressing 2nd LIST ► 5 2nd LIST 5 4 ×
.3 ^ ALPHA N , ALPHA N , 1 , 12 , 1) ENTER. You should get 1.714284803. The format of this command is
sum seq(expression, variable, begin, end, increment).
2.8 Parametric and Polar Graphs
2.8.1 Graphing Parametric Equations: The TI-82 plots up to six pairs of parametric equations as easily as it plots
functions. Just use the MODE menu (Figure 2.1), go to the fourth line from the top, and change the setting to Par.
Be sure, if the independent parameter is an angle measure, that MODE is set to whichever you need, Rad or Deg.
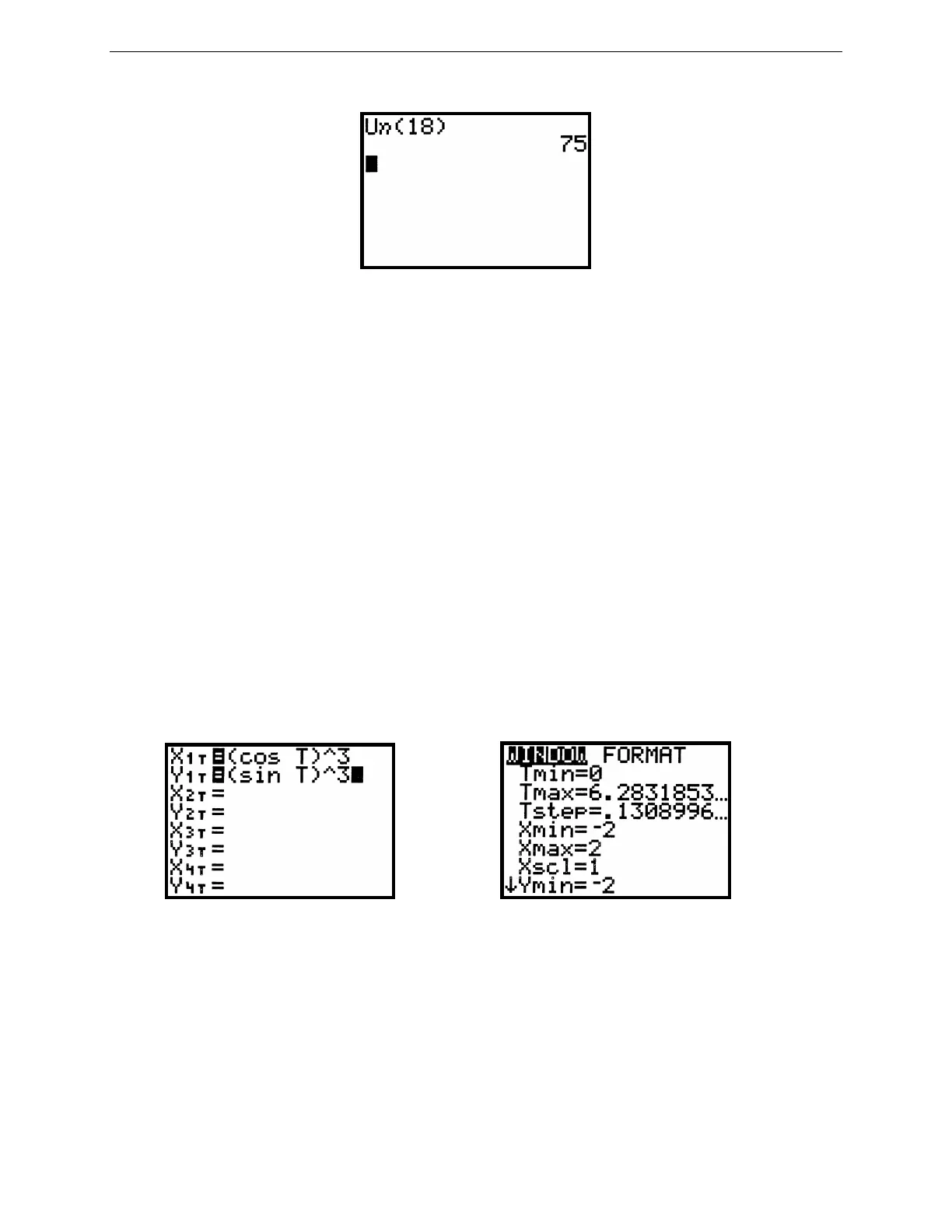
Figure 2.72: Parametric Y= menu Figure 2.73: Parametric WINDOW menu
For example, here are the keystrokes needed to graph the parametric equations x = cos
3
t and y = sin
3
t. First check
that angles are currently being measured in radians. Change to parametric mode and press Y= to examine the new
parametric equation menu (Figure 2.72). Enter the two parametric equations for X
1T
and Y
1T
by pressing ( COS
X,T,θ
) ^ 3 ENTER ( SIN
X,T,θ
) ^ 3 ENTER. Now, when you press the variable key
X,T,θ
, you get a T because the
calculator is in parametric mode.
 Loading...
Loading...











