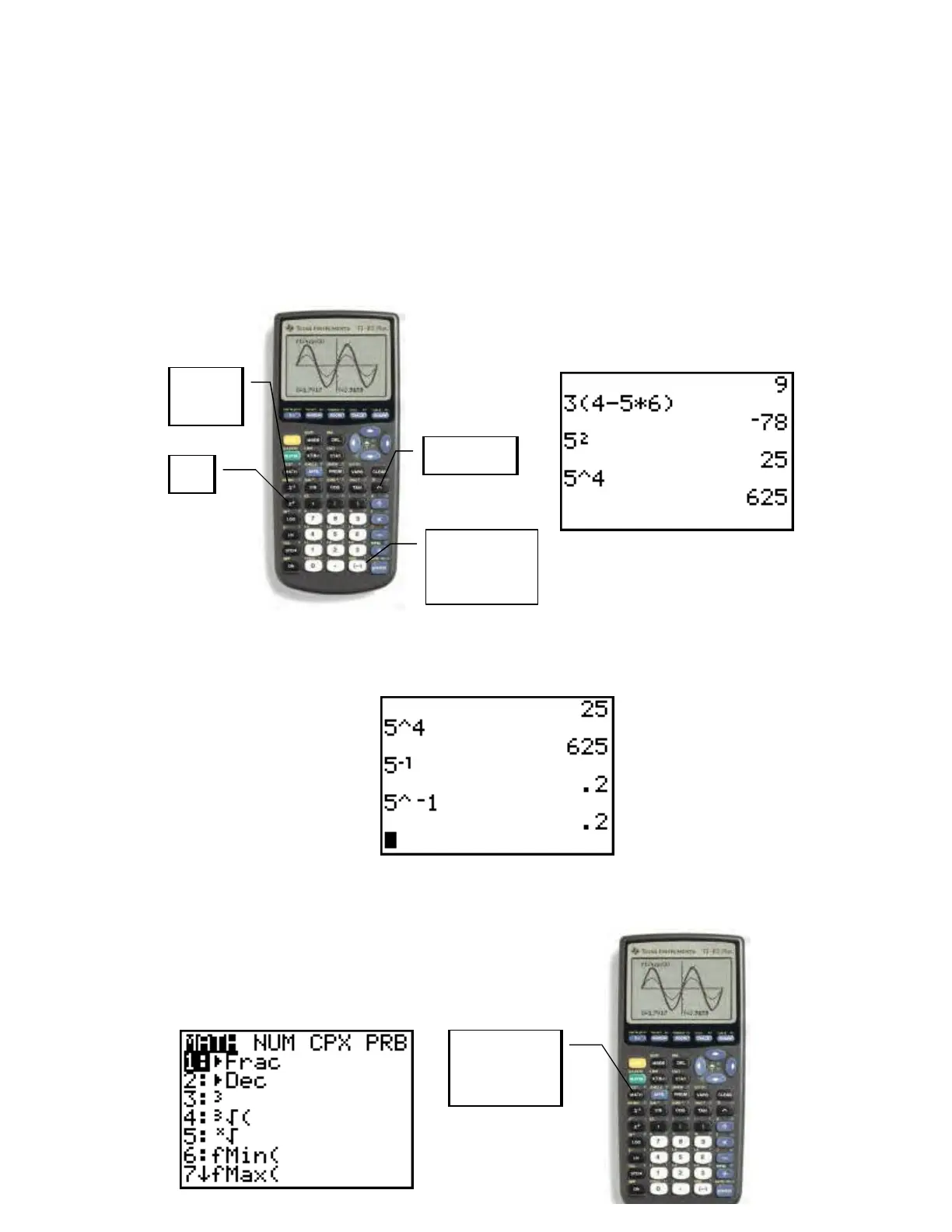
EXPONENTS
Exponents can be handled using either the
2
x button or the caret key (^). For example, to
evaluate
2
5 simply type 5 and then push the
2
x button and hit ENTER. To evaluate
4
5 ,
type 5 ^ 4 and hit ENTER. NOTE: The
2
x button may only be used to raise a
quantity to the 2
nd
power.
To compute the reciprocal of a number use the
1−
x button. For example to compute
1
5
−
,
type 5 and then push the
1−
x button. Alternatively, you could use the caret key with
the “negative” button.
Notice the TI-83 automatically puts the solution in decimal form. Should you want your
answer to be in a fraction, use the FRAC option under the MATH menu. For example, to
compute the reciprocal of 5 with the solution in fraction
form, type: 5 and then push the
1−
x button, but instead of
hitting ENTER, press the MATH button and you see the
following menu:
2
x
Caret (^)
1−
x
button
button
 Loading...
Loading...











