Hardware and physical integration guideline A1 PCR sensors
Page 24 of 30
© 2024 by Acconeer – All rights reserved 2024-02-07
4.3 Fresnel Zone Plate (FZP) lenses
The plano-convex and convex-planar type lenses are refracting type lenses. Another popular lens type
is the Fresnel zone plate lens which is based on diffraction instead of refraction [7]. Different types of
FZP lenses exists and here the phase correcting FZP lens is covered. The FZP lens structure is
composed of dielectric rings with different thickness for correcting the phase of the incident waves.
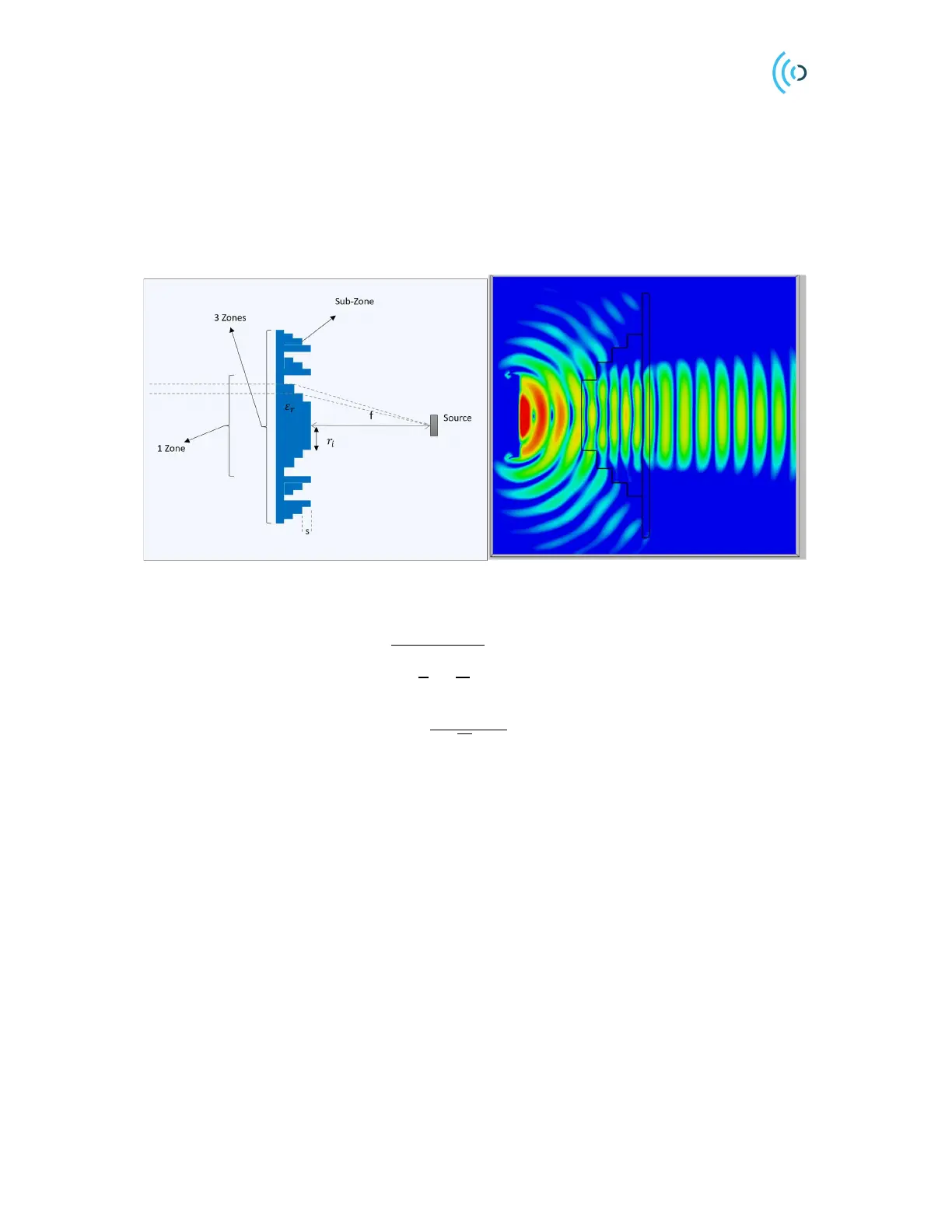
Figure 22 shows an example of FZP lens consist of 3 zones with the phase step of quarter of
wavelength.
Figure 22. FZP lens, collimating the beam originating from the source at distance f (focal length)
The radius r
i
of the rings and the step thickness s can be calculated from Eqs. (10) and (11)
(10)
(11)
Here F is the focal point, P is the number of sub-zones or steps, 𝜆 is the wavelength in free space (5
mm at 60 GHz), and 𝜀
is the relative dielectric constant. For small diameter lenses, we can choose
one zone and 4 or 8 steps. For larger diameter lenses, additional sub zones can be added for increased
gain. Notice that contrary to the refracting type lenses, the ring thickness and hence the lens total
thickness is independent of the lens radius. This allows us to construct large diameter lenses without
increasing the thickness.
4.3.1 Example FZP lens calculation
This is an example of a single zone FZP lens with a focal point F=10 mm and quarter of wavelength
steps or N=4. We assume a material permittivity of ε
r
= 2.6. Inserting this into Eq. (10) gives us the
lens radii as follows:
r
1
= 5.1 mm, r
2
= 7.46 mm, r
3
= 9.39 mm, r
4
= 11.12 mm
Eq. (11) gives us the step thickness of s= 2.02 mm. Total thickness of the lens is then 4*2.02 = 8.1
mm.
For further details regarding FZP lens design, see [7].
 Loading...
Loading...