• 12 •
EEBC100A-Z
13. CALCULATING CHARGE TIMES
The Chart Method
Use the following table to more accurately determine the
time it will take to bring a battery to full charge.
First, identify where your battery ts into the chart.
• Small batteries – motorcycle, garden tractors, etc. –
are usually rated in Ampere Hours (AH). For example:
6, 12, 32 AH, etc.
• Batteries in cars and smaller trucks are usually rated
in Reserve Capacity (RC), Cold-Cranking Amps
(CCA), or both.
• Marine or deep-cycle batteries are usually rated in
Reserve Capacity (RC).
Find your battery’s rating on the chart below and note the
charge time given for each charger setting. The times given
are for batteries with a 50% charge prior to recharging.
Add more time for severely discharged batteries.
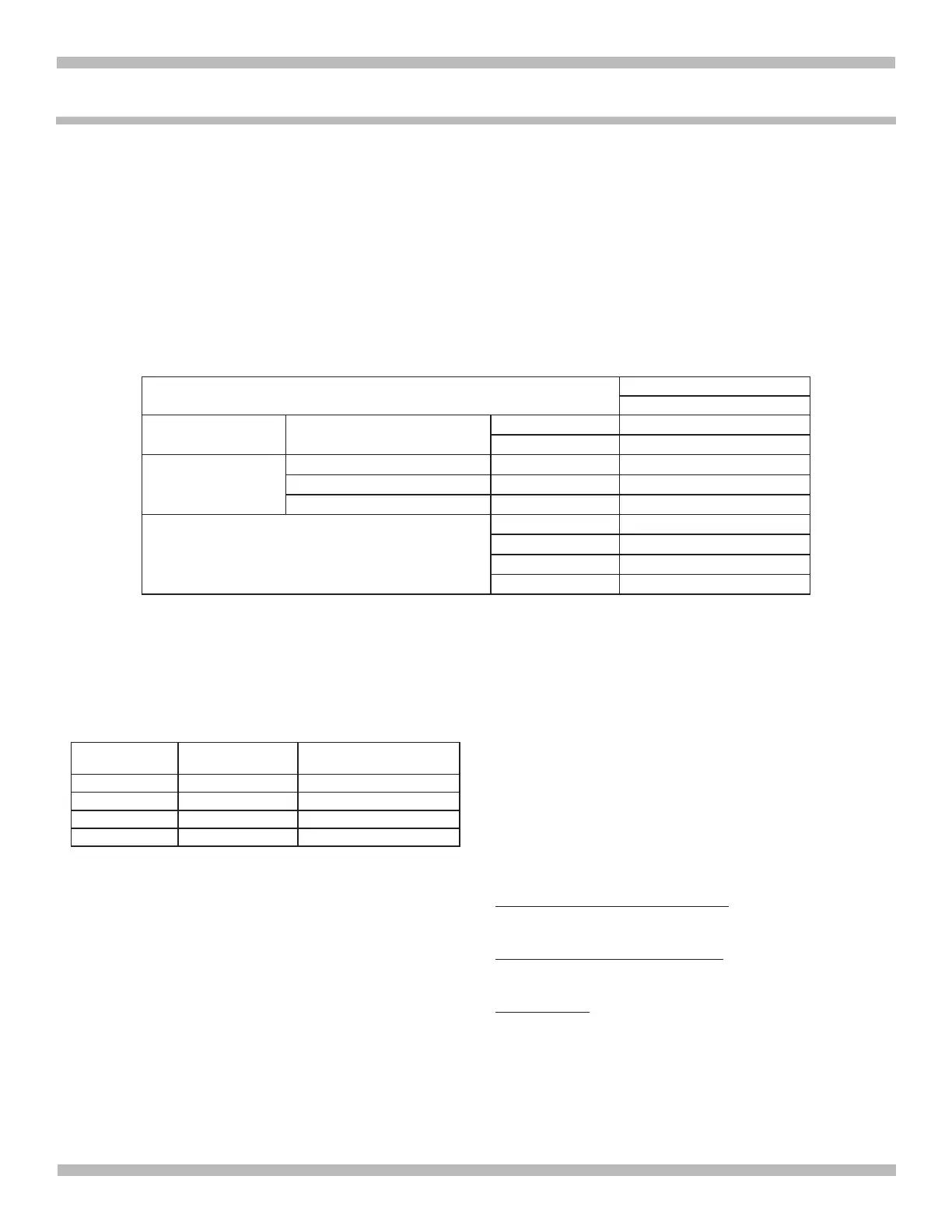
BATTERY SIZE/RATING
CHARGE RATE/TIME
6<>2 AMP
SMALL BATTERIES Motorcycle, garden tractor, etc.
6-12 AH 1½-2½ h
12-32 AH 2½-7 h
CARS/TRUCKS
200 - 315 CCA 40-60 RC 7½-9½ h
315 - 550 CCA 60-85 RC 9½-12 h
550 - 1000 CCA 85-190 RC MAINTAIN ONLY
MARINE/DEEP CYCLE
80 RC 12 h
140 RC MAINTAIN ONLY
160 RC MAINTAIN ONLY
180 RC MAINTAIN ONLY
The Hydrometer or Electronic Method
To nd the time needed to fully charge your battery,
determine the battery’s charge level with a hydrometer or
electronic Percent-of-Charge Tester. The following table
will help you convert hydrometer readings to percent of
charge values.
SPECIFIC
GRAVITY
PERCENT OF
CHARGE
PERCENT OF CHARGE
NEEDED
1.265 100% 0%
1.225 75% 25%
1.155 25% 75%
1.120 0% 100%
When you know the percent of charge and the Amp Hour
(AH) rating of your battery, you can calculate the approximate
time needed to bring your battery to a full charge.
To convert Reserve Capacity to Amp Hours,
multiply Reserve Capacity by 0.42:
Example:
Amp Hour Rating = Reserve Capacity x 0.42
NOTE: The Reserve Capacity can be obtained from the
battery specication sheet or the owner’s manual.
To calculate time needed for a charge:
• Find the percent of charge needed. (A battery at 50%
charge that will be charged to 100% needs another
50% [.50]).
• Multiply the Amp Hour rating by the charge needed (.50)
and divide by the charger setting (4, 15, or 60 amps).
• Multiply the results by 1.25 and you will have the
total time needed, in hours, to bring the battery to full
charge.
• Add one additional hour for a deep-cycle battery.
Example:
Amp Hour Rating x % of charge needed x 1.25 = hours of charge
Charger Setting
100 (AH Rating) x .50 (charge needed) x 1.25 = 3.125 hours
20 (Charger Setting)
100 x .50 x 1.25 = 3.125
20
You would need to charge your 100-Ampere Hour Battery
for a little more than three hours at the 20-Amp charge
rate, using the above example.

 Loading...
Loading...