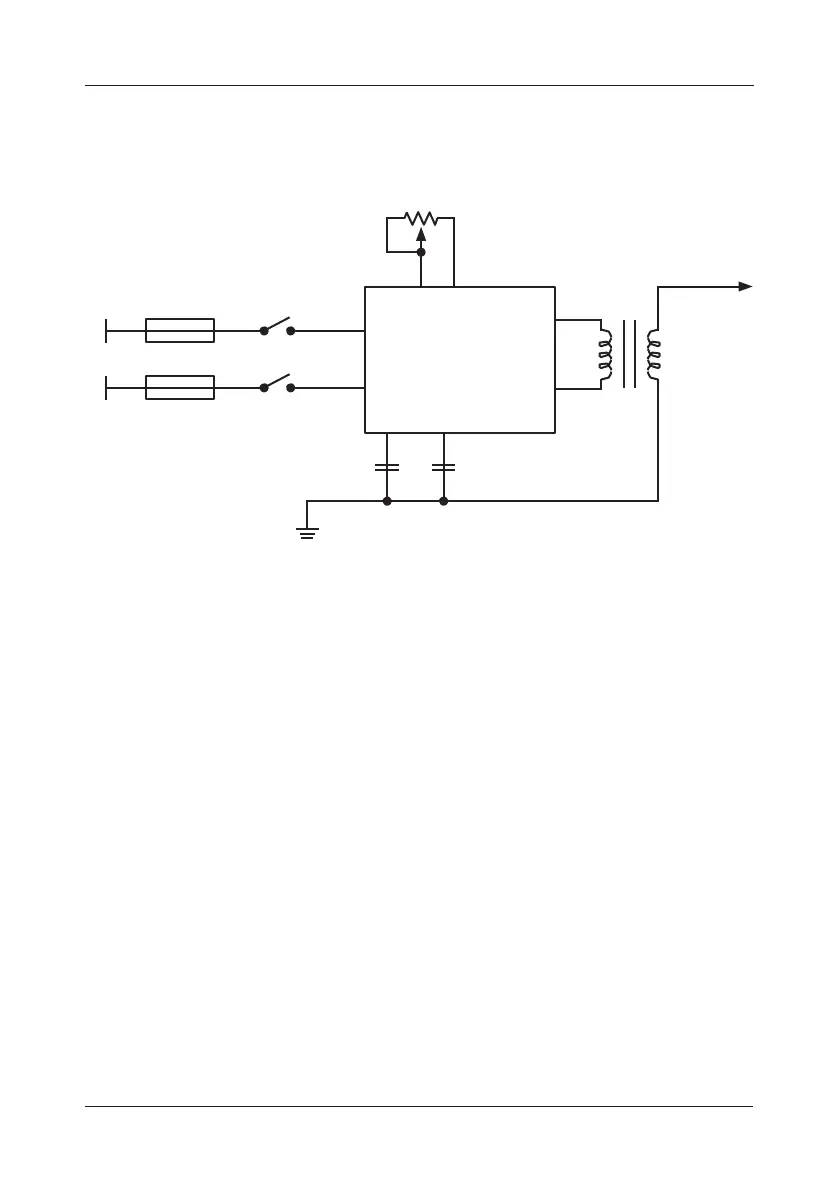
Below is a pictorial representation of the PST-100, detailing the functional
earth terminal arrangement.
Output adjustment pot
L fuse
L
Switch 1
Control
electronics
HT terminal
+
-
N
N fuse
Switch 2
-
+
Nose
cone
Y capacitors
PST-100 functional earth terminal arrangement
Calculating the test
voltage
The test voltage needs to be high enough to locate a fault but not
so
high as to cause one. With reference to BS EN 60052:2002, (measurement
of voltage with Sphere-Gaps) it can be seen that 32,000 volts will
jump a gap of 1cm between spheres of 5cm diameter, however the
same voltage will jump a gap of nearly 3cm between needles. This is
because the shape of the electrode affects the point at which corona
discharge starts. A spark or arc over, will occur when the voltage is high
enough such as to cause localised breakdown of the air between the
electrodes, a spark then forms, ionising the air drastically reducing its
electrical resistance.
For materials with a thickness in the range of 1mm to 30mm, the NACE
Standard SP-02-74 voltage calculation formula is normally used.
 Loading...
Loading...