3. INTERNATIONAL UNIT CONVERSION SYSTEM
(Based on MARKS' STANDARD HANDBOOK FOR MECHANICAL ENGINEERS)
Introduction
Although this manual uses the JIS unit system, if
you need SI unit, refer to the following international
system of units.
Given hereinafter is an excerpt of the units that
are related to this manual :
1. Etymology of SI Units
French:Le Systeme International d' Unites
English:lnternational System of Units
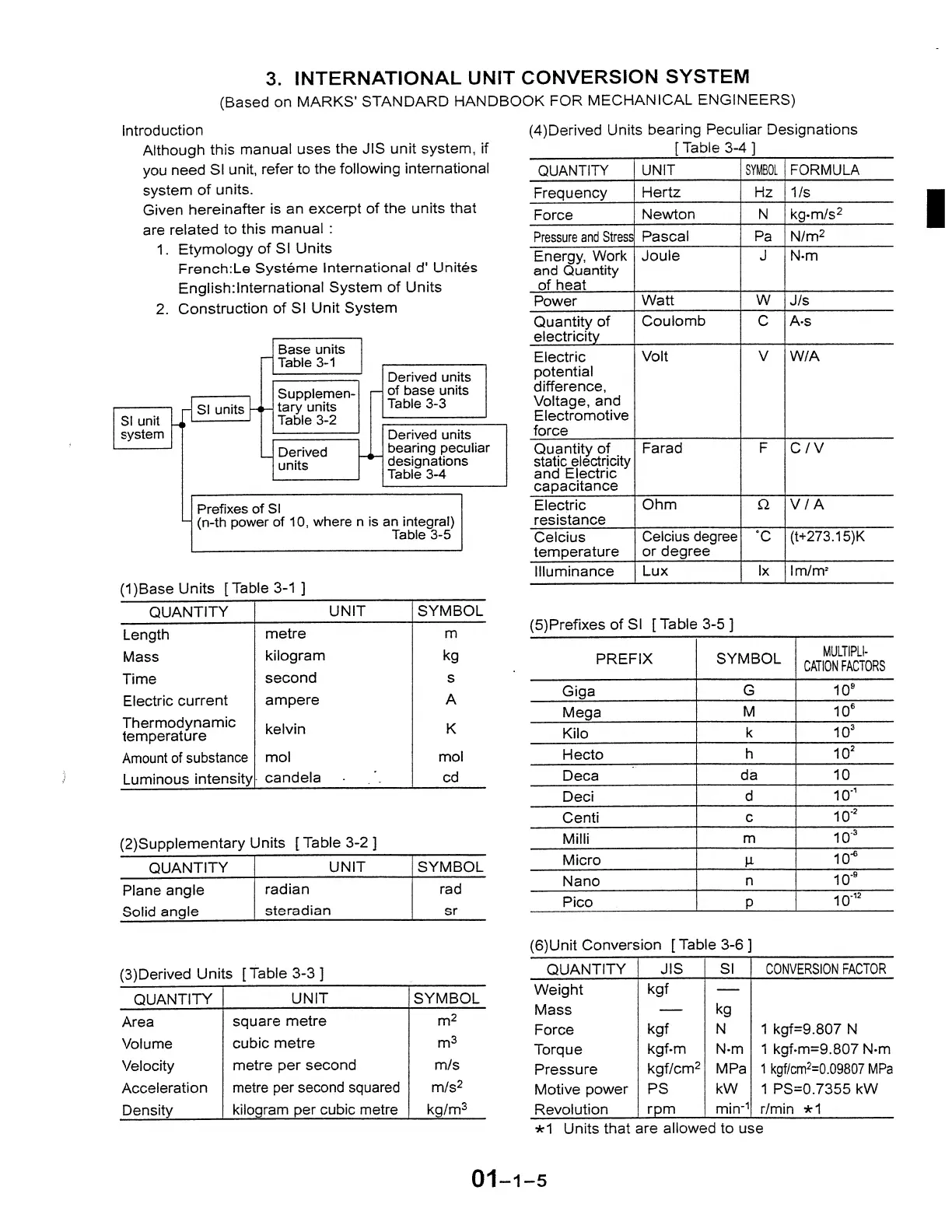
2. Construction of SI Unit System
SI unit
system
SI units
Base units
Table 3-1
Supplemen-
tary units
Table
3-2
Derived
units
Prefixes of SI
Derived units
of base units
Table 3-3
Derived units
bearing peculiar
designations
Table
3-4
(n-th power of
10,
where n is an integral)
Table
3-5
(1)Base Units [ Table 3-1 ]
QUANTITY
UNIT
Length
metre
Mass
kilogram
Time
second
Electric current
ampere
Thermodynamic
kelvin
temperature
Amount of substance
mol
Luminous intensity
. candela
(2)Supplementary Units [ Table 3-2 ]
QUANTITY UN IT
Plane angle
Solid angle
radian
steradian
(3)Derived Units [ Table 3-3 ]
QUANTITY UNIT
Area
Volume
Velocity
Acceleration
Density
square metre
cubic metre
metre per second
metre per second squared
kilogram per cubic metre
SYMBOL
m
kg
s
A
K
mol
cd
SYMBOL
rad
sr
SYMBOL
m2
m3
m/s
m/s
2
kg/m
3
(4)Derived Units bearing Peculiar Designations
[Table 3-4]
QUANTITY UNIT
SYMBOL
FORMULA
Frequency
Hertz Hz 1/s
Force
Newton N
kg-m/s
2
Pressure
and
Stresi
Pascal Pa
N/m
2
Energy, Work
Joule
J N-m
and Quantity
of heat
Power
Watt
w
J/s
Quantity of
Coulomb
C A-s
electricitv
Electric
Volt
V W/A
potential
difference,
Voltage, and
Electromotive
force
Quantity of
Farad
F C/V
static electricity
and Electric
capacitance
Electric
Ohm
n
V/A
resistance
Celcius
Celcius degree
·c
(t+273.15)K
temperature
or degree
llluminance
Lux Ix lm/m•
(5)Prefixes of SI [ Table 3-5]
PREFIX SYMBOL
MULTIPLI-
CATION FACTORS
Giga
G 10
9
Mega
M
10
6
Kilo
k 10
3
Hecto
h
10
2
..
Deca da
10
Deci d
10·1
Centi
C
10·2
Milli
m
10·3
Micro
µ
10~
Nano
n
10-9
Pico
p
10-12
(6)Unit Conversion [ Table 3-6]
QUANTITY JIS SI
CONVERSION FACTOR
Weight
kgf
-
Mass
-
kg
Force
kgf N
1 kgf=9.807 N
Torque
kgf-m
N-m
1 kgf-m=9.807 N-m
Pressure
kgf/cm
2
MPa
1 kgf/cm
2
=0.09807
MPa
Motive power PS kW
1 PS=0.7355 kW
Revolution
rom
min-
1
r/min *1
*1 Units that are allowed to use
01-1-5
I
 Loading...
Loading...