Using array-type memories
Lbl, 1, Z, A, [, Z, 1, ], A ,
Goto, 1
16 steps
The difference is readily apparent. When using the standard memories, the input
value is compared one by one with the value assigned to each memory (e.g. A = 1,
B=2,..).
With the array-type memories, the input value is immediately stored in the proper
memory determined by “ [ Z - 1]” . Formulas (Z - 1, A + 10, etc.) can even be used
for the subscript.
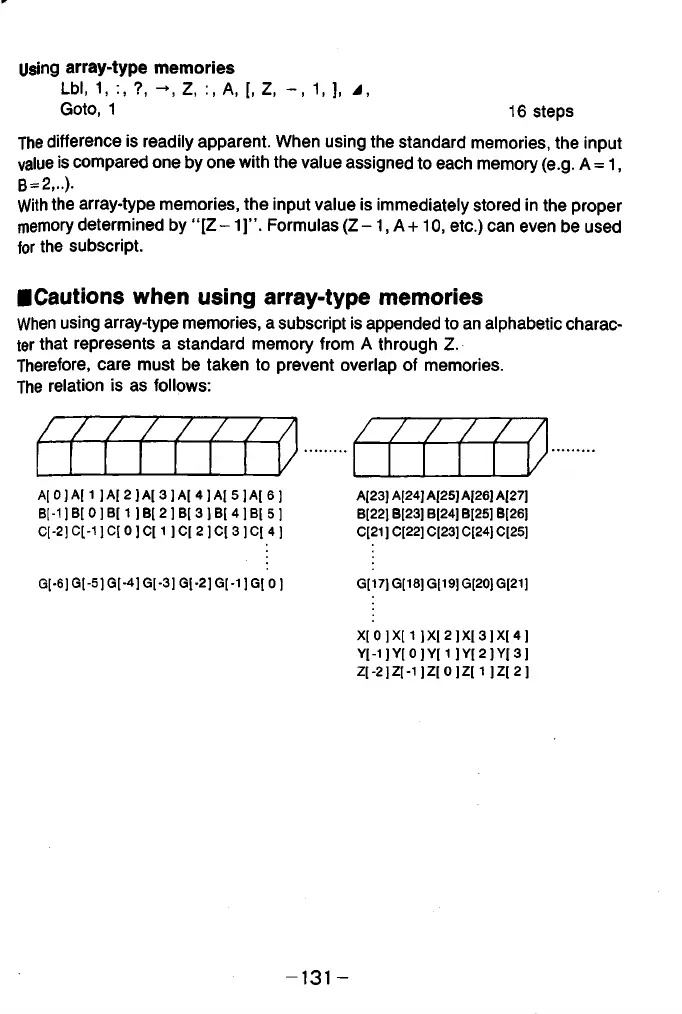
■Cautions when using array-type memories
When using array-type memories, a subscript is appended to an alphabetic charac
ter that represents a standard memory from A through Z.
Therefore, care must be taken to prevent overlap of memories.
The relation is as follows:
/ / '/- / /// A
A [0]A [ 1 ] A[ 2 ] A[ 3 ] A[ 4 ] A[ 5 ] A[ 6 ]
B[-1 ] B[ 0 ] B[ 1 ] B[ 2 ] B[ 3 ] B[ 4 ] B[ 5 ]
C[-2] C[-1 ] C[ 0 ] C[ 1 ] C[ 2 ] C[ 3 ]C [ 4 ]
G[-6] G[-5] G[-4] G[-3] G[-2] G[-1 ] G[ 0 ]
/ / / / / A
/ •
A[23] AI24] A[25] A[26] A(27)
B[22] B[23] B[24] B[25] B[26]
C[21 ] C[22] C[23] C[24] C[25]
G[17] G[18] G[19] G[20] G[21 ]
X [0 ]X [ 1 IX I 2 IX I 3 ] X[ 4 ]
YI-1JYJ0JY I 1 ] YI 2 ] Y( 3 I
Z[ -2 ] Z[ -1 ] ZI 0 ] Z[ 1 ] Z[ 2 I
131
 Loading...
Loading...