Algebraic substitution – numeric [in RUN-MAT] cont.
Example
Calculate the value of the following when x = -2, 0, 2 and 4, in the expression
2x
2
+ 4x – 1.
Result
Enter the expression
SHIFT
VARS
F4
X,
θ
,T
SHIFT
VARS
F6
F5
2
X,
θ
,T
x
2
+
4
X,
θ
,T
-
1
then
EXE
A ‘?’ will display, this is the calculators way of saying, “Enter in a number.”
Enter in the number
-
2
then
EXE
the answer -1 is displayed, the calculator has done the calculation:
2×(-2)
2
+ 4×(-2) – 1 = -1
EXE
this brings up the ‘?’ again
0
then
EXE
Repeat the above sequence, calculating the expression of 2x
2
+ 4x – 1 for each
of the x-values required.
Note:
Differentiation d/dx and d
2
/dx
2
is via [SHIFT] [OPTN] [F4] for CALCulus.
Factorisation checking [in RUN-MAT]
Checking that you have factorised (put into brackets) or expanded (removed the brackets) correctly:
The ‘calculator’s logic’ will return a ‘0’ if incorrectly done or a ‘1’ if correctly done.
As this calculator is a ‘numerical manipulator’ and NOT a ‘symbolic manipulator’ the student MUST learn how to
factorise (put into brackets) or expand (remove from brackets).
cont. on next page
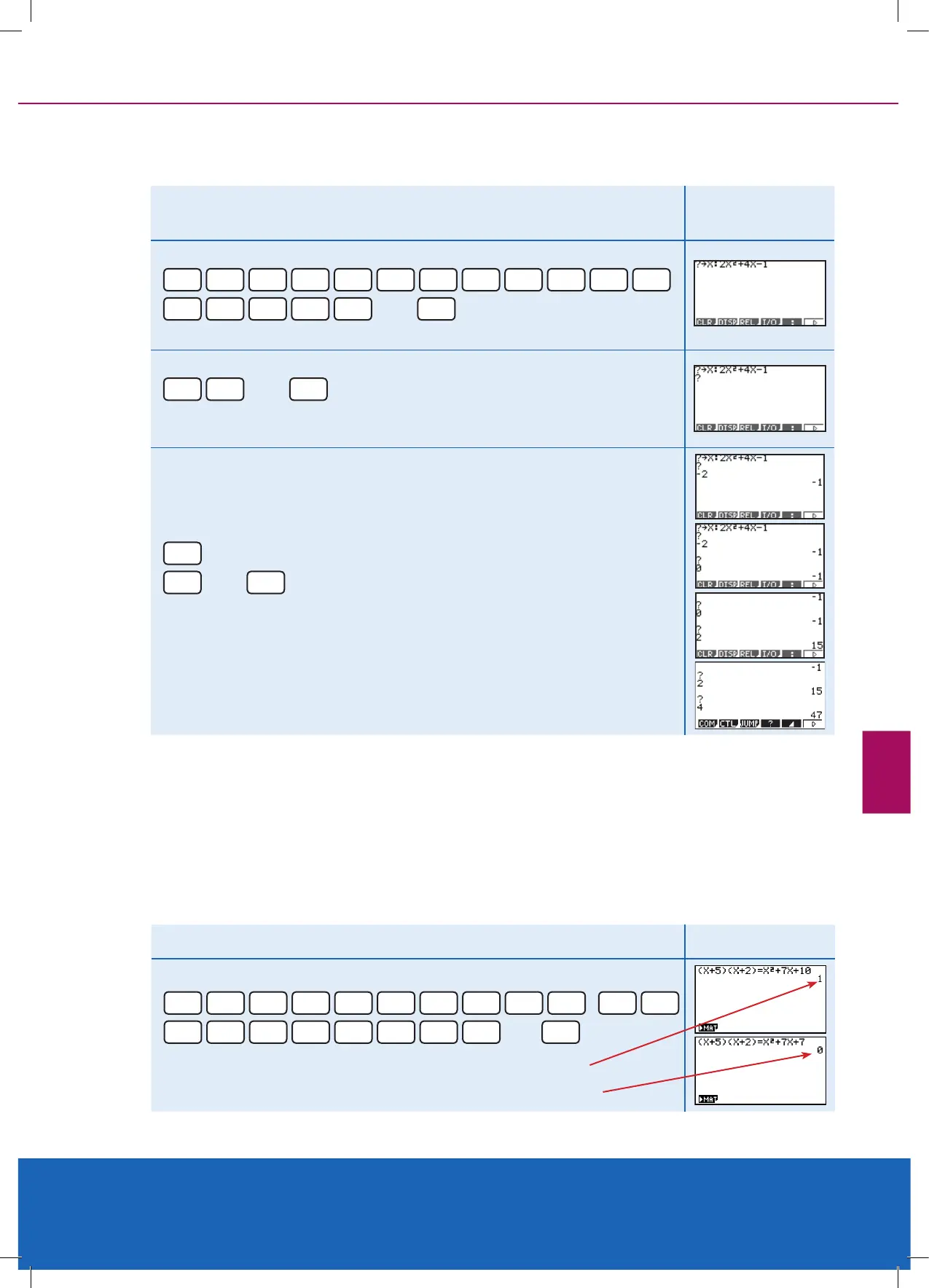
Example
Expand (x + 5)(x + 2) Result
Enter in the equation in bracketed and the expanded form
(
X,
θ
,T
+
5
)
(
X,
θ
,T
+
2
)
SHIFT
.
X,
θ
,T
x
2
+
7
X,
θ
,T
+
1
0
then
EXE
The result 1 indicates that it is correctly expanded.
The result 0 indicates that it is incorrectly expanded.
CHAPTER 7 | PG 59

 Loading...
Loading...