Binomial Distribution calculations [in STAT] cont.
Example 2
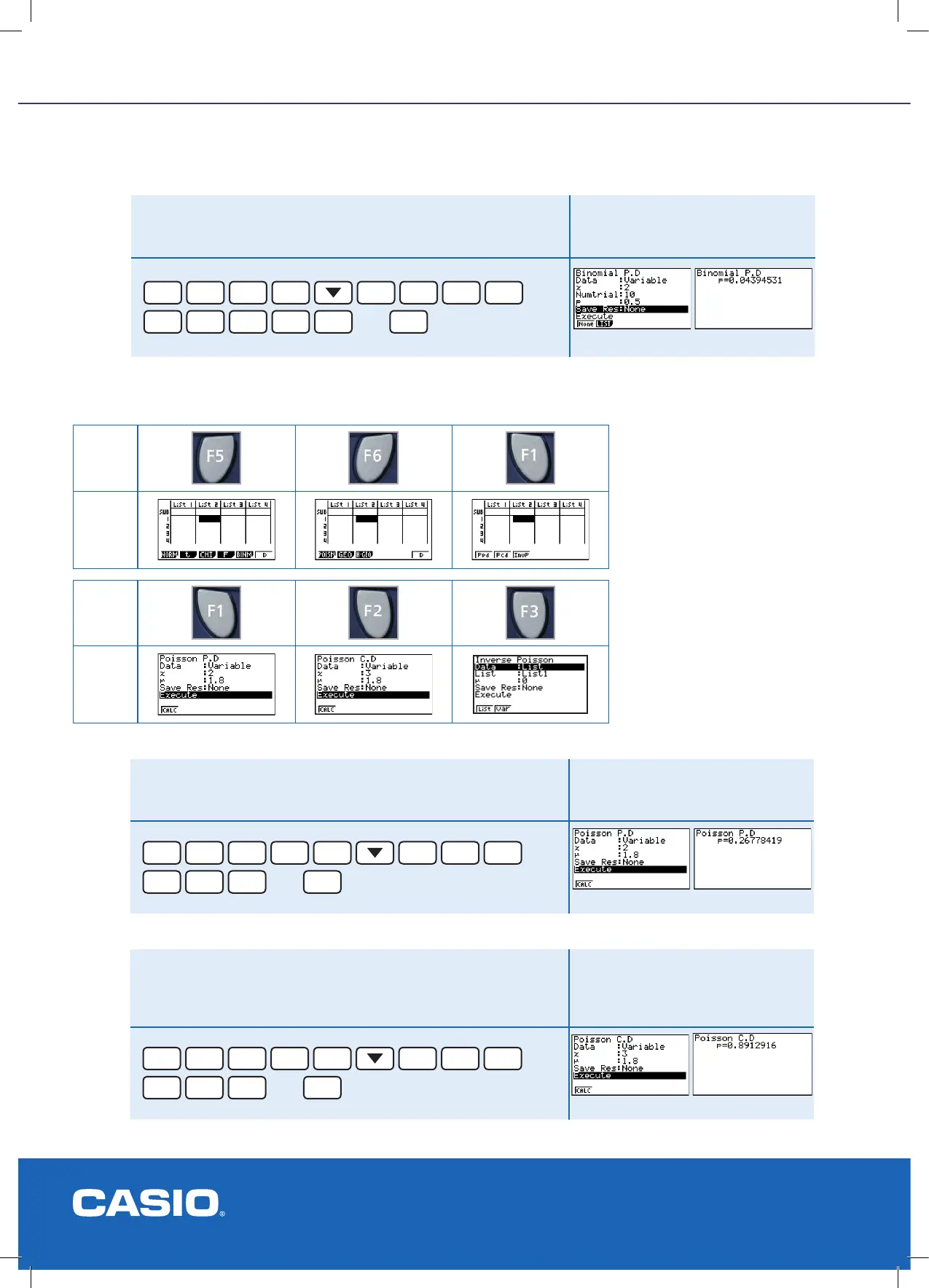
Calculate the probability that from 10 trials there are at most two
successful outcomes and the probability of a success is 0.5.
Here x < 4 or x ≤ 3, i.e. x = 0, 1, 2 or 3.
Result
F5
F5
F2
F2
3
EXE
1
0
EXE
0
.
5
EXE
then
EXE
Prob(x ≤ 3) = 0.0547 (4 d.p.).
Example
Calculate the probability that a carpet of size 1 square metre will
have 2 aws when the carpet generally has on average 1.8 aws
in it per square metre?
Result
F5
F6
F1
F1
F2
2
EXE
1
.
8
EXE
then
EXE
Probability = 0.2678 (4dp)
Example 2
Calculate the probability that from a carpet of size 1 square
metre will have at most three aws and the carpet generally has
on average 1.8 aws per square metre?
Here x < 4 or x ≤ 3, i.e. x = 0, 1, 2 or 3.
Result
F5
F6
F1
F2
F2
3
EXE
1
.
8
EXE
then
EXE
Probability = 0.8913 (4 d.p.)
Poisson Distribution calculations [in STAT]
The Poisson Distribution (P.D.) has only one parameter, λ, the mean.
Change the data as being
VARiable (you enter in the
data) from LIST - press
[F2] as illustrated with
Normal and Binomial
Distributions.
KEY
RESULT
KEY
RESULT
NORMAL, BINOMIAL AND POISSON DISTRIBUTIONS

 Loading...
Loading...