148 Cisco LAN Switching Configuration Handbook
weight m, where its capacity for active connections is m divided by the sum of
all server weights. SLB assigns new connections to the real server with the num-
ber of active connections farthest below its capacity.
■ With weighted least connections, SLB controls the access to a new real server, pro-
viding a slow start function. New connections are rate limited and allowed to
increase gradually to keep the server from becoming overloaded.
■ The virtual server can masquerade as the IP address for all TCP and UDP ports of the
real server farm. As well, the virtual server can appear as the IP address of a single
port or service of a server farm.
■ Sticky connections enable SLB to assign new connections from a client to the last
real server the client used.
■ SLB can detect a real server failure by monitoring failed TCP connections. SLB can
take the failed server out of service and return it to service when it is working again.
■ SLB can use server Network Address Translation (NAT) to translate between the
real and virtual server addresses if they reside on different Layer 3 subnets.
■ SLB can use client NAT to translate the source addresses of client requests into
addresses on the server side of the SLB device. This is used when several SLB devices
are operating so that return traffic can be sent to the correct SLB device.
■ SLB provides a control mechanism over incoming TCP SYN floods to the real
servers. This can prevent certain types of denial-of-service attacks.
■ SLB can coexist with Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) to provide a “stateless
backup.” If one SLB router fails, a redundant router can take over the SLB function.
However, existing SLB connections will be lost and will have to be reestablished
from the client side.
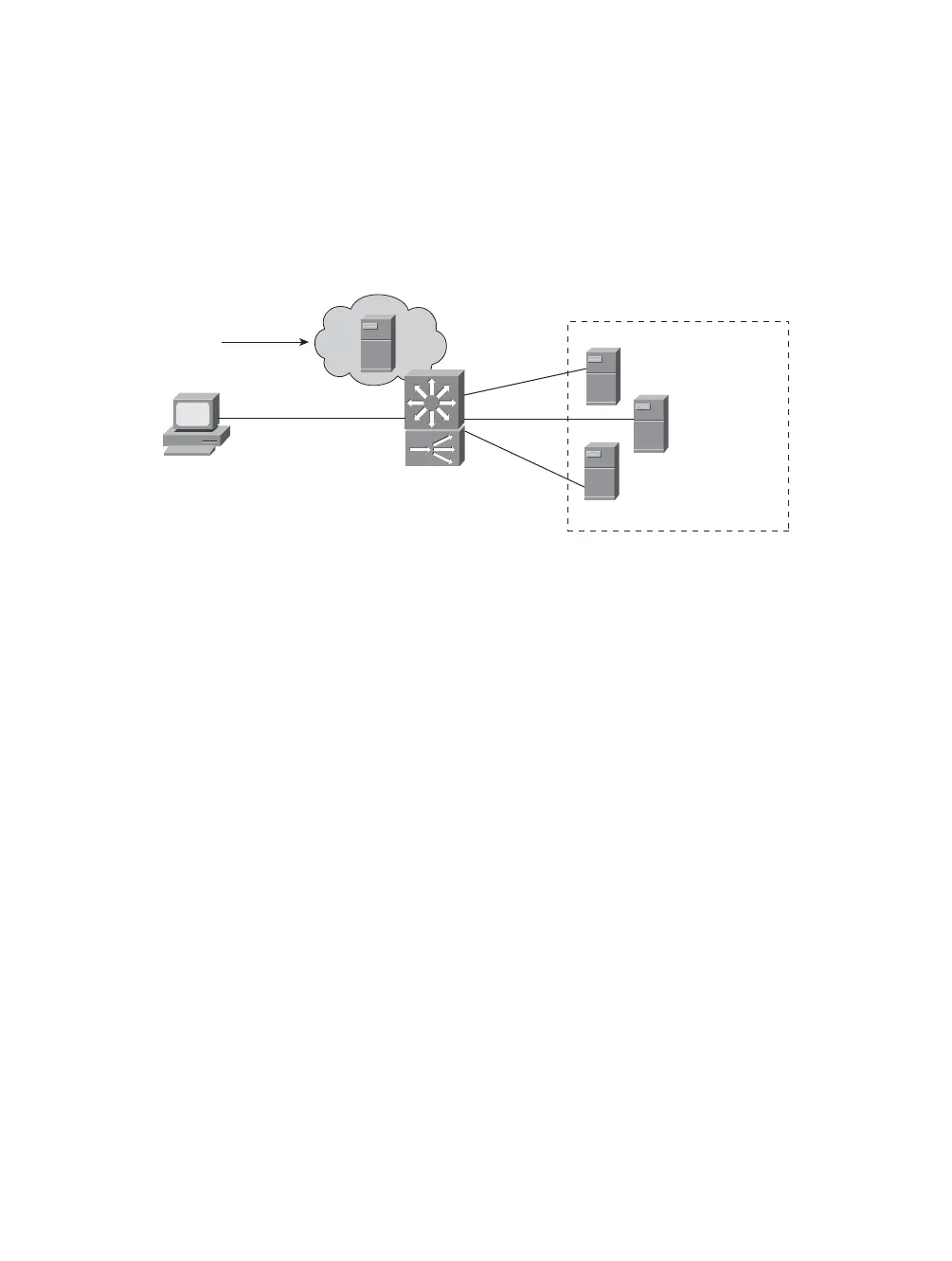
Virtual Server
Global IP Address
v.v.v.v
Client
Catalyst 6000
SLB
X.X.X.X
Y. Y. Y. Y
Z.Z.Z.Z
“Server_Farm”
Figure 10-1 SLB Concept
 Loading...
Loading...











