API Integration Manual for Daikin DKN Cloud Wi-Fi Adaptor
used by the service API to identify the application, and is also used to build authorization URLs that
are presented to users. The Client Secret is used to authenticate the identity of the application to
the service API when the application requests to access a user's account, and must be kept private
between the application and the API.
2.2 Oauth2 Authorization Code Grant Type
OAuth 2 defines four grant types, each of which is useful in different cases. The one used for the
Open API corresponds to the Authorization Code Grant Type. It’s the most commonly used
because it is optimized for server-side applications, where source code is not publicly exposed, and
Client Secret confidentiality can be maintained. This is a redirection-based flow, which means that
the application must be capable of interacting with the user-agent (i.e. the user's web browser) and
receiving API authorization codes that are routed through the user-agent. Nevertheless, it can also
be used with other server-side services which lack of web interface (programmatic interface).
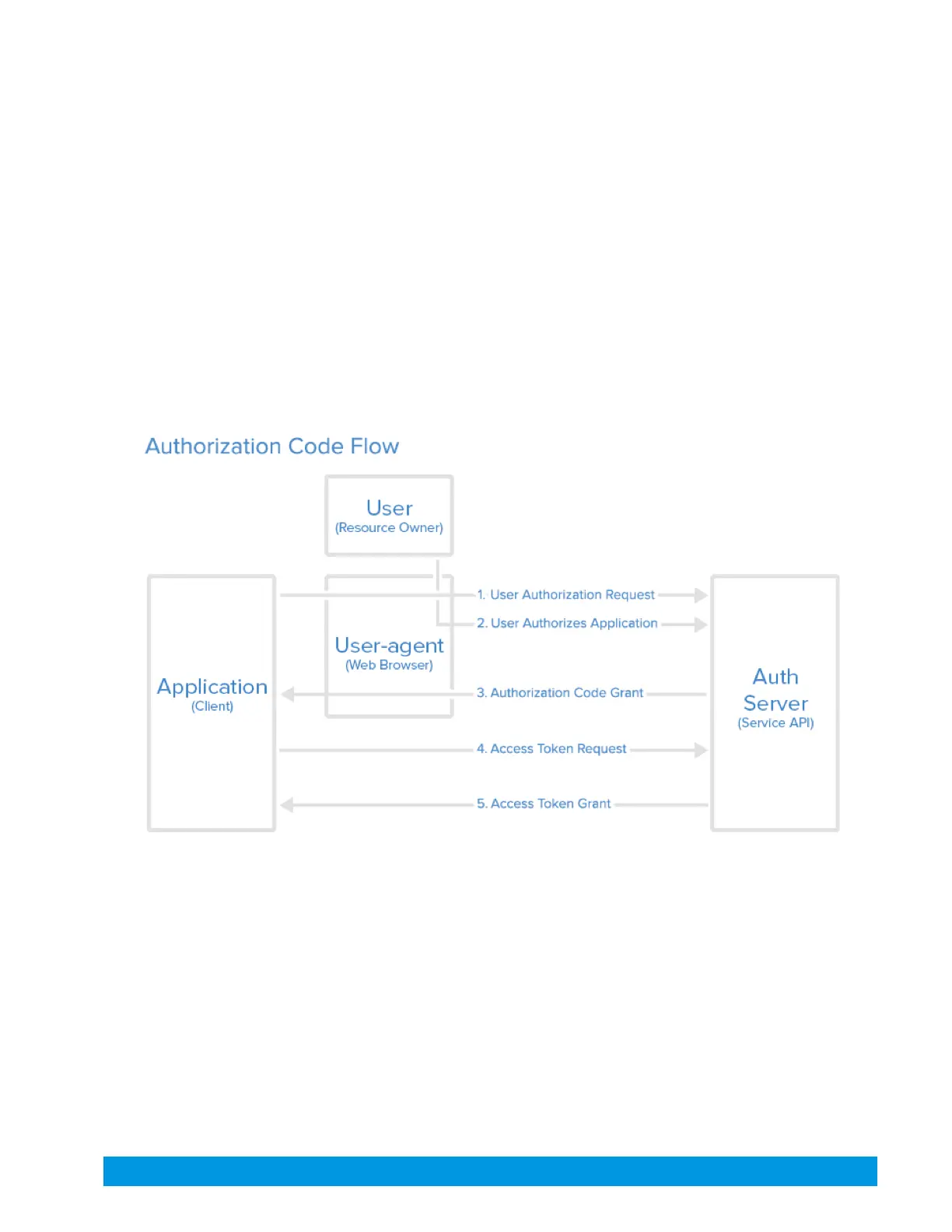
Here describes the authorization code flow:
The above diagram represents a typical authorization flow.
Here is a more detailed explanation of the steps in the diagram:
1. The application requests authorization to access service resources from the user
2. The user must log in to the Open API environment and authorize the request.
3. If the user authorized the request, the application receives an authorization grant (Code)
4. The application requests an access token from the authorization server (API) by presenting
authentication of its own identity (Client Secret and Client ID), and the authorization grant (Code).
5. If the application identity is authenticated (registered in the Open API environment) and the
authorization grant is valid (Code hasn’t expired or already been used), the authorization server (API)
issues a pair of access token/refresh token to the application. Authorization is complete.
 Loading...
Loading...