STARTER SOLENOID
Inrush current
Holding current
Pull in voltage
Voltage supply
STARTER
Type
Battery rates voltage
Locked torque
Current draw
Voltage
Maximum output
50-60 amps
8—10 amps
8
12
Paris-Rhone D10E59
12 volts
28
Nm
(20.6 ft./lb.)
540 amps
7 volts
130
KW
Voltage
Current draw
Torque
Minimum no load
Voltage
Maximum current draw
Mounting on motor
Clockwise running
Number of teeth
Diametral pitch
Spring tension
on new brushes
9.4 volts
260 amps
10 Nm (7.40 ft./lb.)
1300
rpm
4000 rpm
11.5
volts
60 amps
By flange (3 holes)
(pinion side)
9
2.116/1.814
About 15.5 Newtons
(3.3
lbs.) *
10%
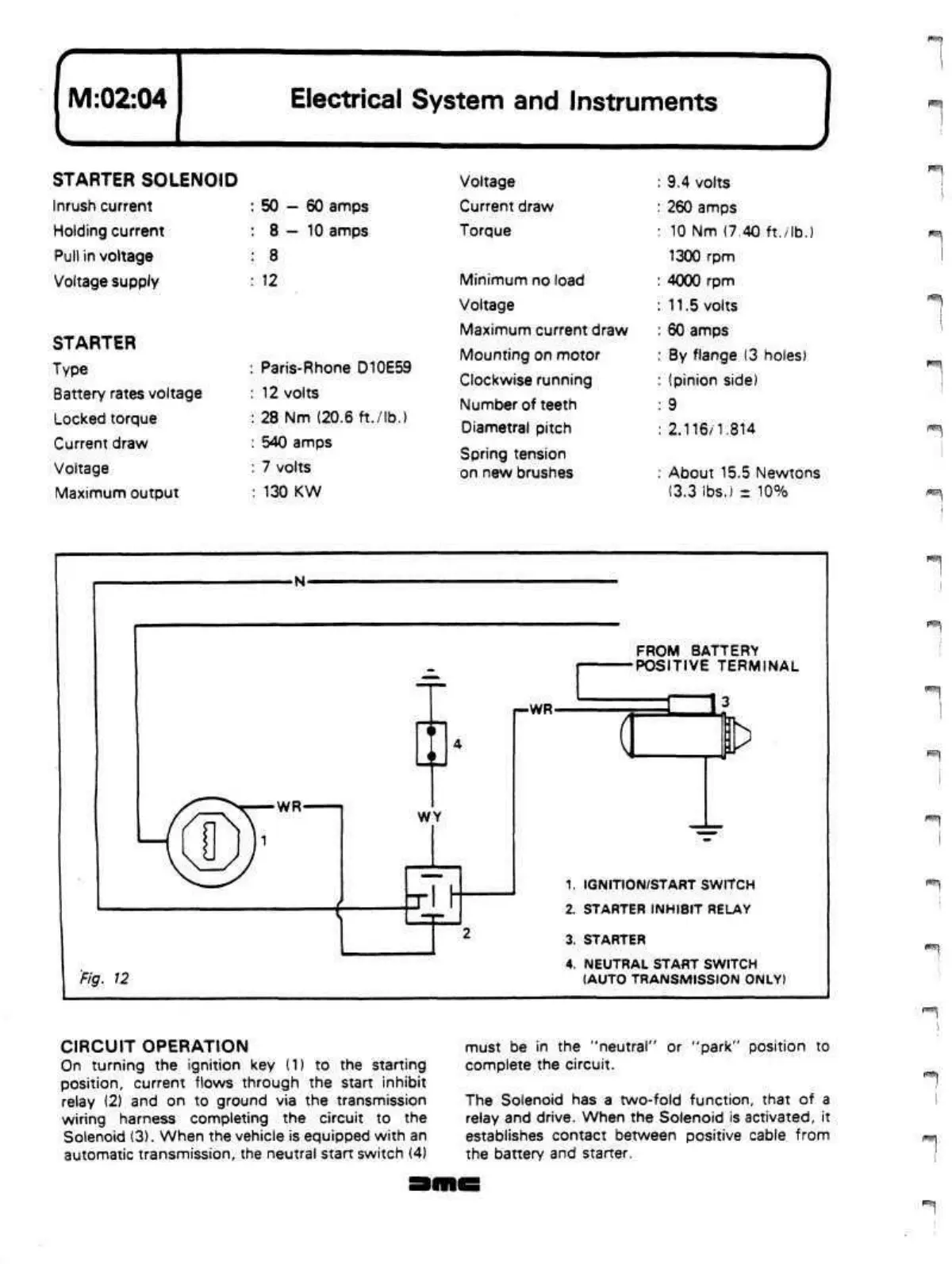
Fig. 12
•N-
WR-
IT
WY
r-WR-
FROM BATTERY
•POSITIVE TERMINAL
>
1.
IGNITION/START SWITCH
2.
STARTER INHIBIT RELAY
3. STARTER
4. NEUTRAL START SWITCH
(AUTO TRANSMISSION ONLY)
('-1
CIRCUIT OPERATION
On turning the ignition key (1) to the starting
position,
current flows through the start inhibit
relay (2) and on to ground via the transmission
wiring harness completing the circuit to the
Solenoid (3). When the vehicle is equipped with an
automatic transmission, the neutral start switch (4)
must be in the "neutral" or "park" position to
complete the circuit.
The Solenoid has a two-fold function, that of a
relay and drive. When the Solenoid is activated, it
establishes contact between positive cable from
the battery and starter.
 Loading...
Loading...