FULL WAVE RECTIFICATION, NEGATIVE OUTPUT
FIG.
51
I I
NO
c%YT
+
CENTER-TAPPED
FULLWAVE
BRIDGE RECTIFIER
FIG.
52
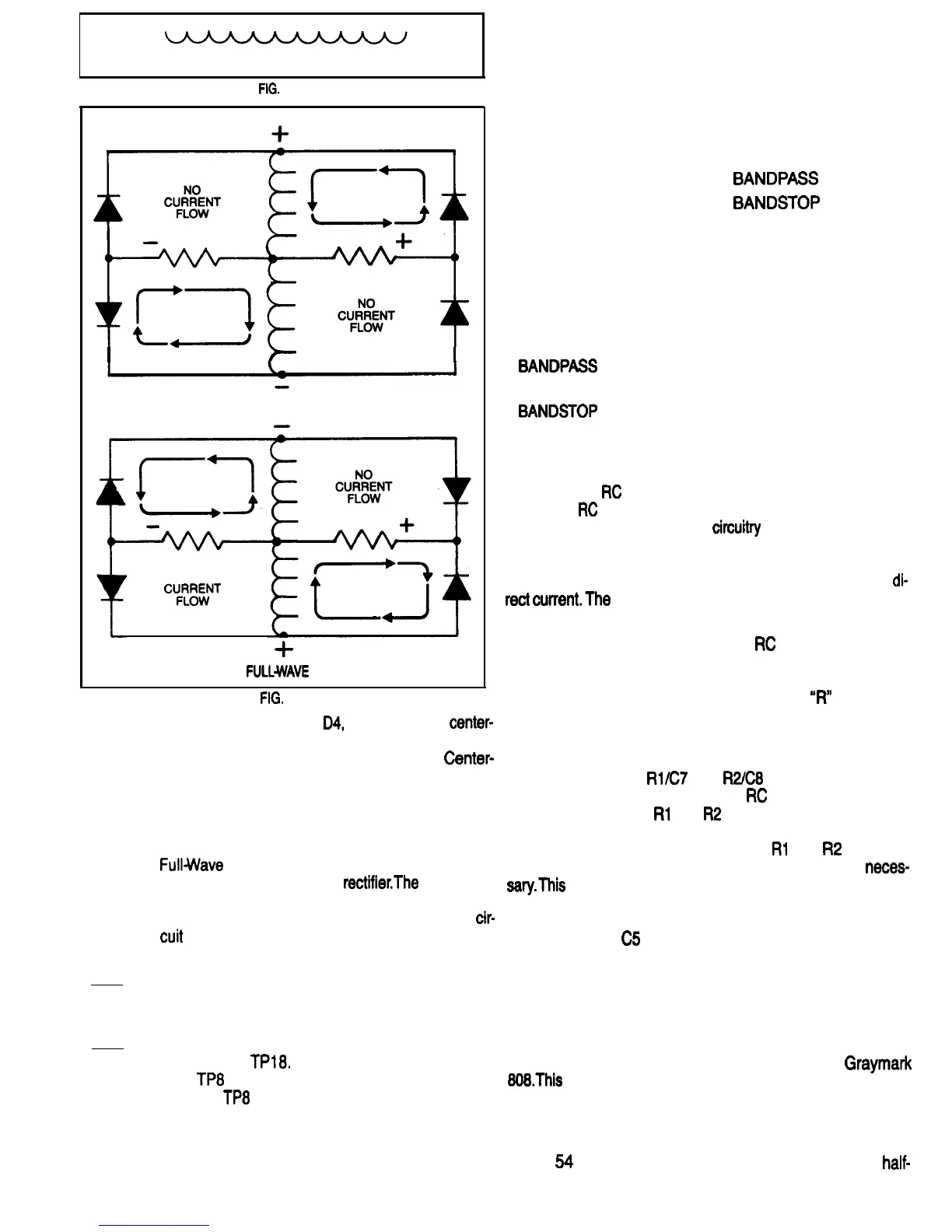
Fig. 51. Diodes D3 and
D4,
along with the
center-
tapped secondary winding that also is connected
to diodes Dl and D2, form a Full-Wave
Center-
Tapped Rectifier the output of which is negative
in respect to the transformer center-tap. These
two complimentary Full-Wave Center-Tapped
Rectifiers, sharing the same transformer wind-
ing, can also be correctly called a Center-Tapped
FuMVave
Bridge Rectifier. Figure 52 shows the
current flow in this type of
rectifier.The
transform-
er primary winding and core symbol have been
omitted so that the current flow in the rest of
cir-
cuit
can be shown clearly, but apart from that, it
is the same as Figs. 49A and 49B.
8. Turn the power switch Off and disconnect the
power plug from the outlet. Disconnect the scope
leads.
9. Unsolder and remove the green wire running
from TP6 to
TPl8.
Leave the red wire running
from
TP8
to TP17 and the diode connected to
TP3 and
TP8
in place, as you will be using them
later in another test.
-10
This completes the CENTER-TAPPED FULL
WAVE BRIDGE RECTIFIER EXPERIENCE.
Have your instructor initial your Progress Guide.
FILTER SECTION
DISCUSSION
In general, a filter is an electronic device used to pass a cer-
tain frequency or band of frequencies while rejecting or
blocking another frequency or band of frequencies.
There are four types of filters commonly used in
electronics:
LOW PASS
BANDPASS
HIGH PASS
BANDSTOP
A LOW PASS filter will pass all frequencies from DC to a
cutoff frequency. All frequencies above this cutoff are at-
tenuated. DC has a frequency of zero Hz; it is a straight line
on an oscilloscope.
A HIGH PASS filter will pass all frequencies above a cutoff
frequency, and attenuate all frequencies below that cutoff
frequency.
A
BANDPASS
filter will pass a band or group of frequen-
cies, and attenuate all frequencies outside that band.
A
BANDSTOP
filter will attenuate a particular band of fre-
quencies and will pass all other frequencies.
To remove the ripple from the output of the rectifier circuit,
most power supplies use a resistance/capacitance filter
(also called a
RC
filter) of the low pass type.The resistance
part of the
RC
filters in most DC power supplies is provided
by the resistance of the diode
circuitv
and the power trans-
former secondary winding, along with the reactance of the
power transformer. The term reactance applies to devices
operating on alternating current and varying (pulsating)
di-
rect
current.The
output of a rectifier circuit is an example
of pulsating direct current.
The resistance and reactance in a
RC
filter used in a DC
power supply serves to limit the peak current flowing
through the rectifier diodes to a value that the particular
diodes being used can handle safely. The
“R”
part of the
filter does not directly enter into the filter’s effectiveness.
Figure 53 shows part of the block diagram and schematic
of the 808 Power Supply, with the capacitive filters high-
lighted. Notice that
Rl/C7
and
R2/C8
are not highlighted.
These components appear to be
RC
low pass filters, but
are not. the resistors
Rl
and
R2
are current sensing resist-
ors used in the overcurrent detectors of the variable posi-
tive and negative power supplies. If
Rl
and
R2
were not
in the circuit, capacitors C7 and C8 would not be
neces-
sary.This
is due to the characteristics of the integrated cir-
cuit voltage regulators Ul and U2, And will be discussed
in the External Control and Protection Circuitry Section.
Capacitors C4,
C5
and C6 are also required because of
other characteristics of the voltage regulators. This will be
explained later in the section on voltage regulators.
CAPACITIVE FILTERS
DISCUSSION
NO half-wave rectifier circuits are used in the
Graymark
808This
experience included tests using a half-wave recti-
fier because, when done along with tests using a full wave
rectifier, they will help you to understand the operation of
capacitive filters.
Figure
!54
shows the circuit you built earlier for the
half-
wave rectifier test. The voltage waveform across resistor
28

 Loading...
Loading...