Consequently, an objective lens is a piece of
optical equipment that is difficult to manufac-
ture and explains why refractors are the most
expensive form of telescope, aperture for
aperture. However, a refractor can deliver
exquisite images that are very well corrected
and extremly high in contrast, suitable for
observing fine lunar and planetary detail, or
for separating difficult double stars.
^ The catadioptric:
The goal of the telescope designer is to pro-
duce an optical system that delivers an image
as free from any aberrations (defects) as
possible in a package that is compact and
manageable. This has led to designs incorpo-
rating both reflecting and refracting elements
to produce an instrument that combines the
best attributes of both systems.
Thus, we now see many commercial tele-
scopes similar to the Maksutov-Cassegrain
system illustrated above that packs a long
focal length into a physically short tube, while
preserving the high-contrast imagery associ-
ated with refractors of the same aperture.
Catadioptric variations of the Newtonian tele-
scope are currently very much in vogue,
offering compact tube assemblies with conve-
nient viewing positions. Since these systems
often have optical windows sealing the end of
the tube (which would otherwise be open in a
conventional Newtonian), the internal optical
components are far better protected from the
elements and dust.
Remember that no particular design of tele-
scope is intrinsically better than another
– each is well suited to a wide variety of
observational subjects. The important consid-
eration is that the optics should be accurately
m a n u f a c t u red and be precisely collimated
(aligned).
3
Refractors are well suit-
ed for people on the
move since it is
e x t remely difficult for
the optical components
to come out of align-
ment. Also, the lenses
will not need to be
recoated in a lifetime's
use and maintenance is
minimal.
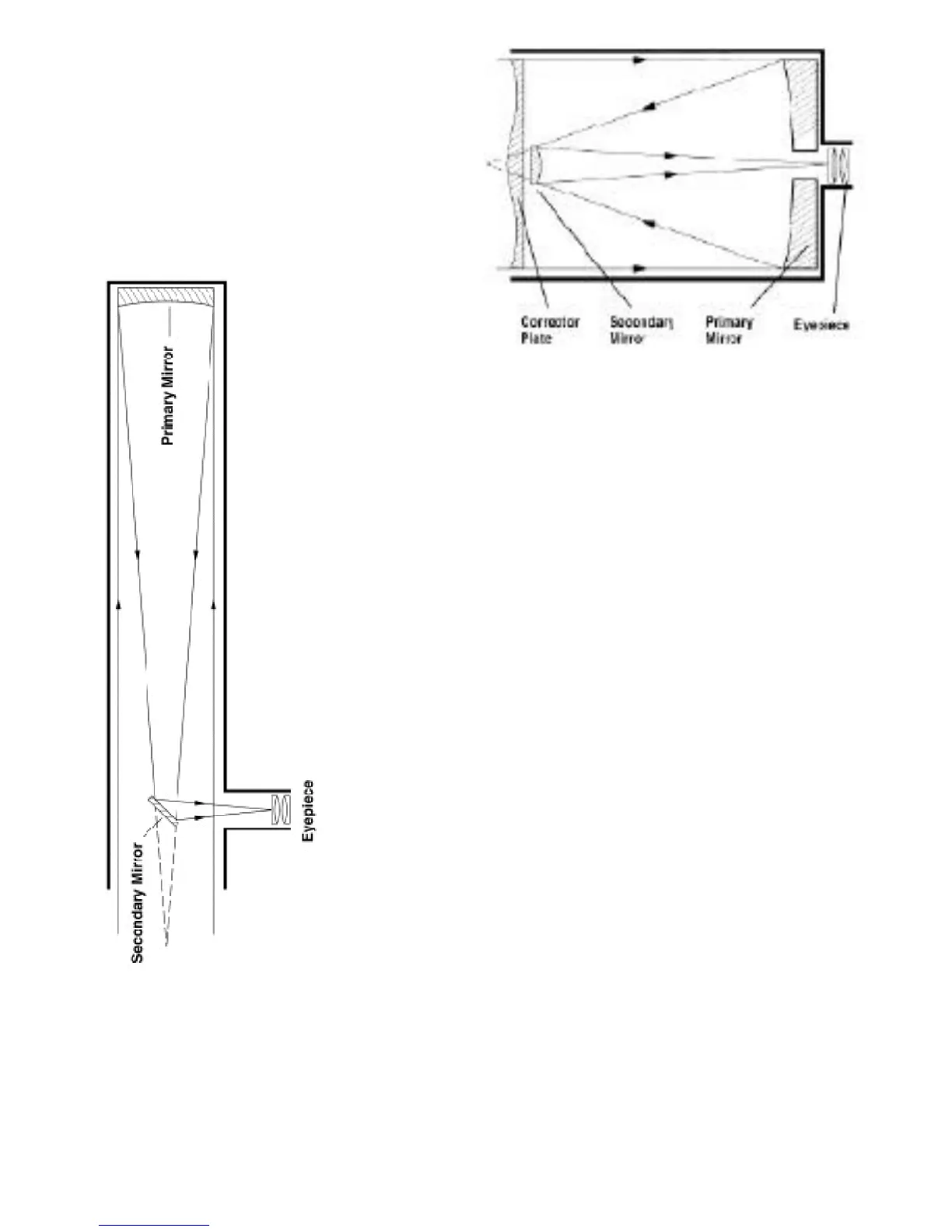
< The reflector: This
is the cheapest form of
telescope, aperture for
a p e rt u r e, that money
can buy. In the form
most encountered, the
Newtonian (after Isaac
Newton's design in
1668) uses a concave
mirror at the base of the
tube to gather
and focus the
light from the
object under
s c ru t i n y. The
light is interc e p t e d
b e f o re coming to a
focus near the mouth of
the tube by a small, flat
mirror inclined at 45° to
the optical axis which
relays the image out of
a hole in the side of the tube to a waiting
eyepiece that magnifies the image in the nor-
mal fashion. Since the light is not refracted in
any way, and a mirror reflects light of all
colours equally, there is no false colour from
a reflecting telescope.
 Loading...
Loading...