Programming Techniques 13–23
File name 32sii-Manual-E-0424
Printed Date : 2003/4/24 Size : 17.7 x 25.2 cm
and line Y08 calls a different subroutine to compute
x
ˆ
after i has been
increased by 6:
&
&
!-
L
&
%1L2
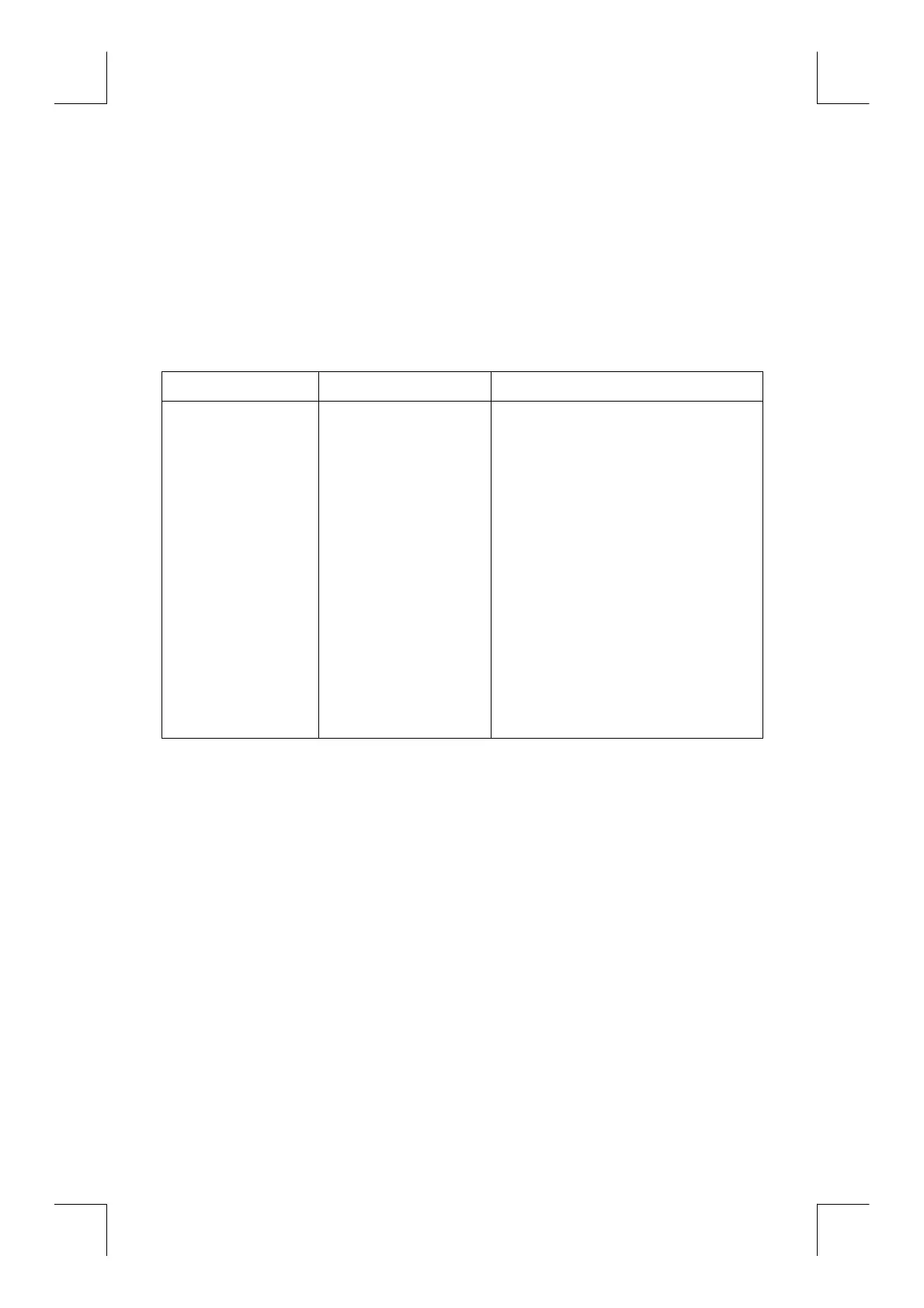
If i hold: Then XEQ(i) calls: To:
1 LBL A Compute
ˆ
for straight–line
model.
2 LBL B Compute
ˆ
for logarithmic
model.
3 LBL C Compute
ˆ
for exponential
model.
4 LBL D Compute
ˆ
for power model.
7 LBL G Compute
x
ˆ
for straight–line
model.
8 LBL H Compute
x
ˆ
for logarithmic
model.
9 LBL I Compute
x
ˆ
for exponential
model.
10 LBL J Compute
x
ˆ
for power model.
Example:
Loop Control With (i).
An index value in i is used by the program "Solutions of Simultaneous
Equations—Matrix Inversion Method" in chapter 15. This program uses the
looping instructions
L
and
L
in conjunction with the
indirect instructions
1L2
and
!1L2
to fill and manipulate a matrix .
The first part of this program is routine A, which stores the initial loop–control
number in i.
Program lines: Description:
The starting point for data input.
)
Loop–control number: loop from 1 to 12 in intervals of
1.

 Loading...
Loading...