127180 4-11 REV A
Test Example: PG/PL or PJ Pump
300 psi (21 bar) reading 7 gpm (26 l/min) (1st reading)
1100 psi (76 bar) reading 3 gpm (11 l/min) (2nd reading)
PG/PL or PJ
300 psi (21 bar) reading 7 gpm (26 l/min) (1st reading)
1100 psi (76 bar) reading
-3 gpm (11 l/min) (2nd reading)
4 gpm (15 l/min) (the difference)
Subtract the 1st reading from the 2nd.
(In this example, 4 gpm difference would indicate further pump examination).
Purging Procedures
Due to the effects air has on efficiency in hydrostatic drive
applications, it is critical that air is purged from the system.
These purge procedures should be implemented any time a
hydrostatic system has been opened to facilitate
maintenance or additional oil has been added to the system.
Air creates inefficiency because its compression and
expansion rates are higher than that of oil.
Entrained air in the oil may cause the following symptoms:
1. Noisy operation.
2. Lack of power or drive after short term operation.
3. High operation temperature and excessive expansion
of oil.
Before starting, make sure the reservoir is at the proper oil
level. If it is not, fill to the vehicle manufacturer’s
specifications.
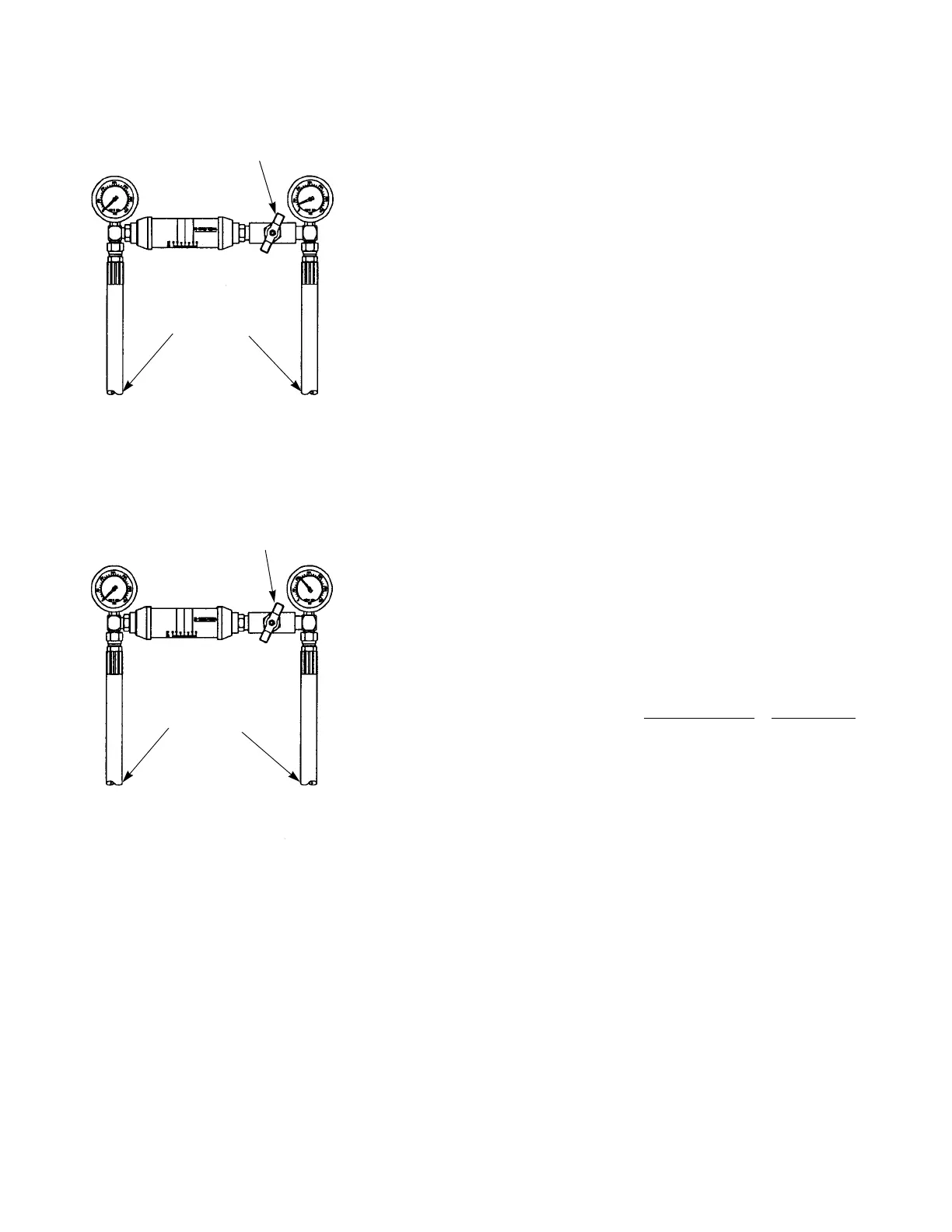
RESTRICTION VALVE
BI-DIRECTIONAL
FLOW METER
CONNECTIONS TO THE
FWD/RVS LINES DIS-
CONNECTED FROM
WHEEL MOTOR
CONNECTIONS TO THE
FWD/RVS LINES DIS-
CONNECTED FROM
WHEEL MOTOR
RESTRICTION VALVE
BI-DIRECTIONAL
FLOW METER
 Loading...
Loading...











