Choosing a Mode of Operation
VNET Switch Mode — Combined Net Types: Use a
configuration that combines VNETs and Traditional Nets only when
you expect little or no cross-VNET traffic.
System Bus
10BaseT
HUB 7
10BaseT
HUB 8
10BaseT
HUB 6
Net 3
Net 2
Net 5
LAN Driver
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
LAN Driver
Port 4
Port 3
Port 2
Port 1
Virtual Network Layer
10BaseT
HUB 4
10BaseT
HUB 2
Net 1
Net 1
Net 1
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
10BaseT
HUB 3
VNET
Switch
1
10BaseT
HUB 1
Router
10BaseT
HUB 5
Adapter 1
Adapter 2
ProtocolProtocol
Net 1
Net 4
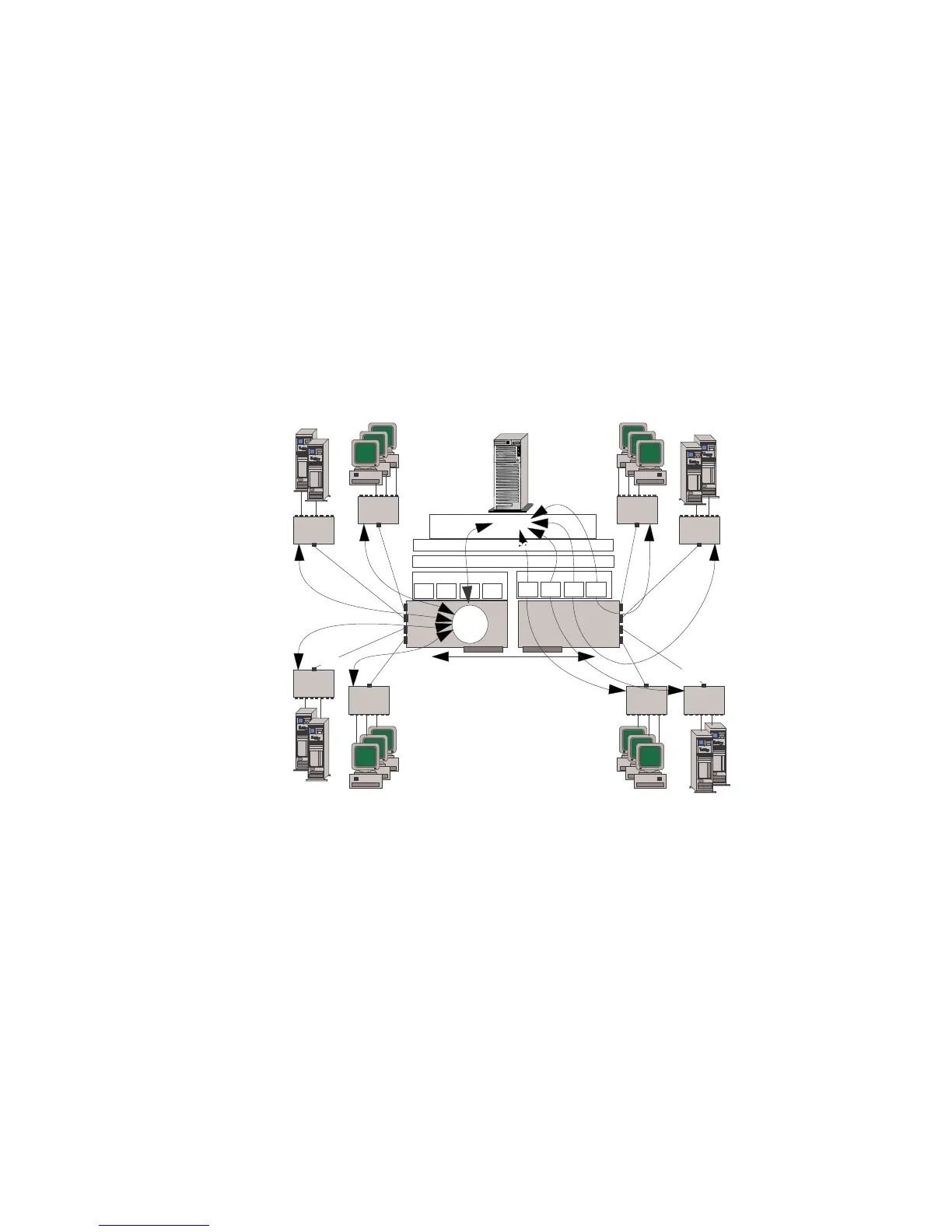
The illustration shows:
A 5-subnet network (Net 1, Net 2, Net 3, Net 4, and Net 5)
configured as one 4-segment VNET on adapter 1 and four
traditional subnet networks (Net 2, Net 3, Net 4, and Net 5) on
adapter 2. In this configuration, all traffic in Net 1 is
port-to-port. All traffic from Net 1 to any other Net is
peer-to-peer. Any traffic between Net 2, 3, 4 and 5 is
port-to-port.
Curved arrows that show the flow of peer-to-peer traffic
between subnet networks such as traffic between Net 1 and Net
2. This traffic is forwarded by the internal router of the server.
Curved arrows that indicate the flow of port-to-port traffic
within the VNET. This traffic is forwarded by the
microprocessor on the each PeerMaster adapter.
146 PC Server 520 User's Handbook for PCI/EISA
 Loading...
Loading...











