DSP Functions
Filters
14-12
PARAMETER RANGE OF VALUES
COARSE ADJUST ± 10800 cents
FINE ADJUST ± 100 cents
KEY TRACKING ± 250 cents per key
VELOCITY TRACKING ± 10800 cents
SOURCE 1 Control Source list
SOURCE 1 DEPTH ± 10800 cents
SOURCE 2 Control Source list
SOURCE 2 DEPTH CONTROL Control Source list
MINIMUM DEPTH, SOURCE 2 ± 10800 cents
MAXIMUM DEPTH, SOURCE 2 ± 10800 cents
Gated Lowpass Filter (LPGATE)
You may be familiar with gates as applied to effects like reverb, where the effect shuts off
abruptly after a specified time. The gated lowpass filter produces a somewhat similar effect in
terms of the sound’s amplitude. The filter’s cutoff frequency is controlled by the AMPENV.
When the AMPENV is at 100%, the cutoff frequency is high, so most of the partials are heard.
When the AMPENV decays or releases to 0%, the cutoff frequency is low, so only the lowest
partials are heard. You’ll hear the distinct effect of the filter closing as the amplitude envelope
releases.
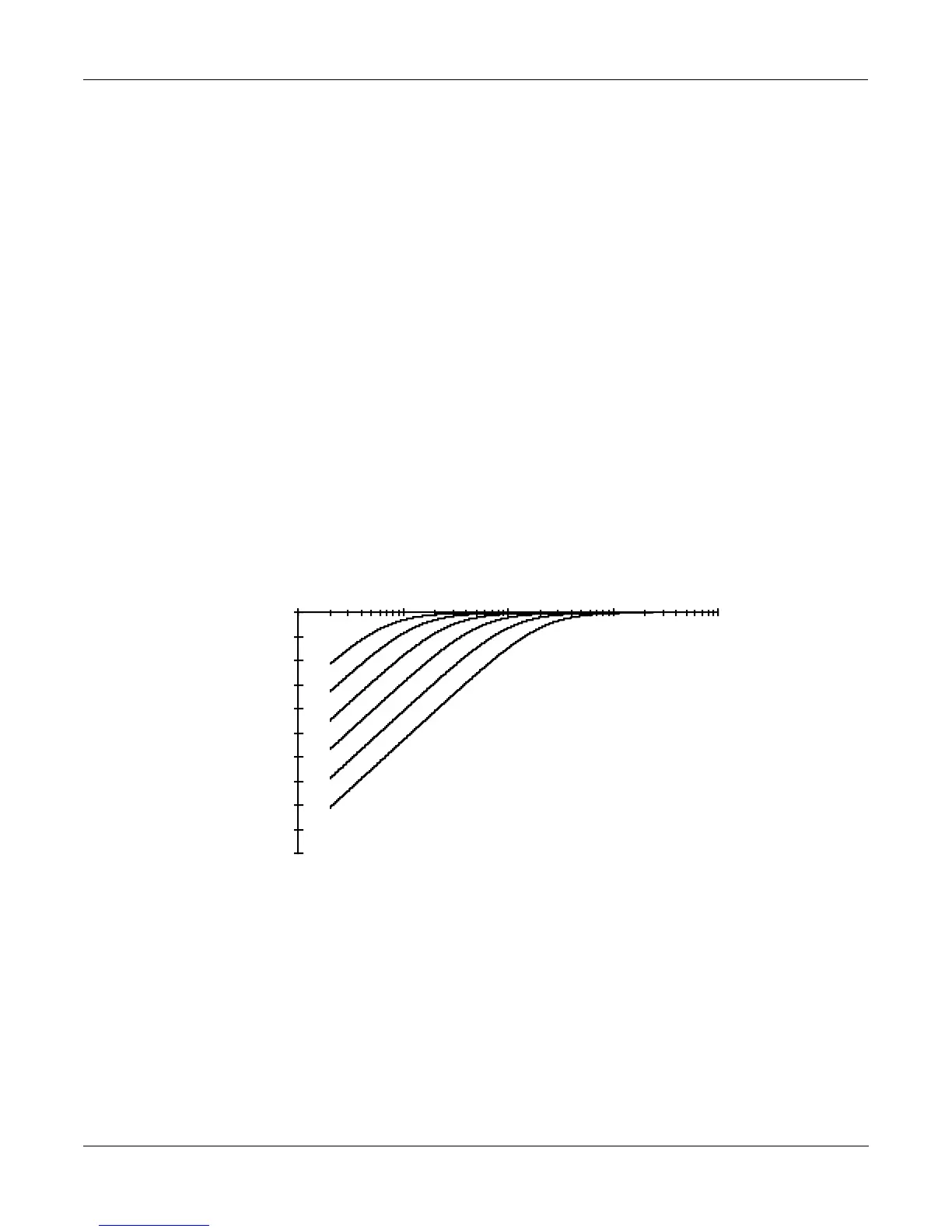
One-pole Highpass Filter (HIPASS)
High-frequency partials pass through this filter unaffected. At the cutoff frequency, the signal is
attenuated 3 dB. There’s a roll-off of 6 dB per octave below the cutoff frequency. The resonance
is fixed at -3dB. When the cutoff frequency is well above the the highest-frequency partials of a
sound, raising the cutoff further will not affect the timbre of the sound, but will merely
attenuate it further.
The Coarse Adjust parameter sets the cutoff frequency in terms of a key name. The remaining
parameters (except Pad) alter the cutoff frequency in increments of cents. Positive key tracking
values raise the cutoff frequency for high notes and lower it for low notes. More specifically, a
value of 100 cents per key on this page, when filtering a constant waveform like a sawtooth,
would result in waveforms of exactly the same shape for all pitches of the waveform. The cutoff
frequency moves in sync with the frequencies of the waveform’s partials as different pitches are
generated. Negative key tracking values will steepen the rolloff of highpass filters below the
-50
-45
-40
-35
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
10 100 1000 10000 100000
Frequency in Hertz
Amplitude in dB
Cutoff frequency
from C 2 to C 7
C 2 C 7

 Loading...
Loading...











