2
Chapter 1: Introduction
ISO Class 5 Definition
Airborne particulate cleanliness inside any PCR Enclosure is
designated by ISO Class 5, which is equivalent to 3520 particles
0.5 µm or larger per cubic meter of air per ISO Standard 14644-1.
ISO Class 5 cleanliness is illustrated in the table to follow and is
equivalent to Class 100 air conditions as defined by Federal
Standard 209E. Class 100 is equal to 100 particles 0.5 µm or
larger per cubic foot of air.
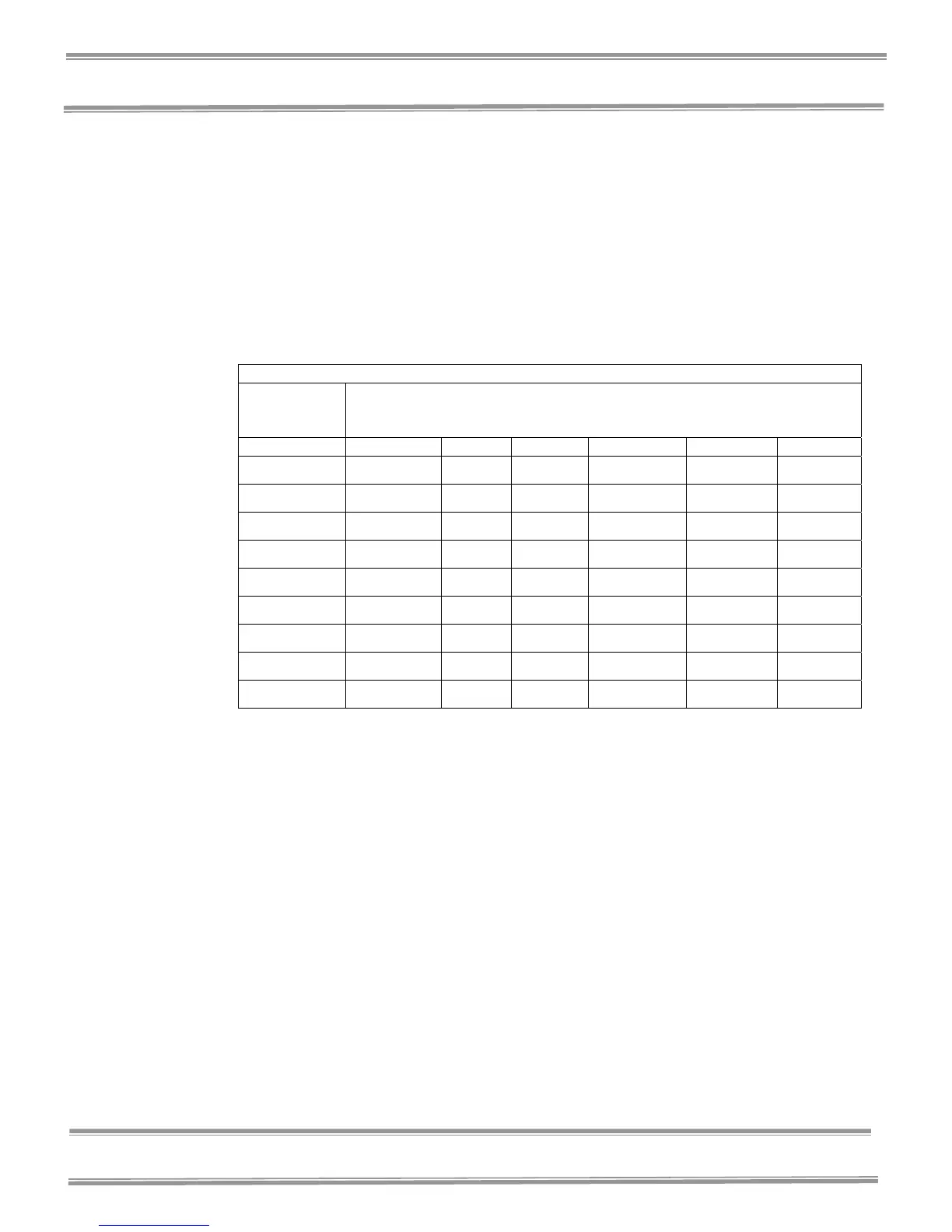
Table 1-1 Selected airborne particulate cleanliness classes for cleanrooms and clean zones.
ISO
classification
number (N)
Maximum concentration limits (particles/m3 of air) for particles equal to and
larger than the considered sizes shown below (concentration limits are
calculated in accordance with 3.2 of Standard 14644-1)
0.1 µm 0.2 µm 0.3 µm 0.5 µm 1 µm 5 µm
ISO Class 1 10 2
ISO Class 2 100 24 10 4
ISO Class 3 1 000 237 102 35 8
ISO Class 4 10 000 2 370 1 020 352 83
ISO Class 5 100 000 23 700 10 200 3 520 832 29
ISO Class 6 1 000 000 237 000 102 000 35 200 8 320 293
ISO Class 7 352 000 83 200 2 930
ISO Class 8 3 520 000 832 000 29 300
ISO Class 9 35 200 000 8 320 000 293 000
Table 1-1 ISO Classification Number (N)
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Definition (PCR)
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), is a laboratory process in
which a particular DNA segment from a mixture of DNA chains is
rapidly replicated, producing a large, readily analyzed sample of a
piece of DNA. In PCR, DNA is immersed in a solution containing
the enzyme DNA polymerase, unattached nucleotide bases (the
subunits that DNA is composed of), and “primers”, short
sequences of nucleotides designed to bind with an end of the
desired DNA segment. Two primers are used: one primer binds at
one end of the desired segment on one of the two paired DNA
strands and the other primer binds at the other end but on the other
strand. The solution is heated to break the bonds between the
strands of the DNA. When the solution cools, the primers bind to
the separated strands, and DNA polymerase quickly builds a new

 Loading...
Loading...