20 AC BOOST (AC BOOST)
AC BOOST is similar to FX BOOST, but is only active when the drive is accelerating. During acceleration,
the output voltage is increased according to the setting of AC BOOST, which increases motor torque. Refer
to the diagram below. AC BOOST, like FX BOOST, is used in applications with high-inertia loads.
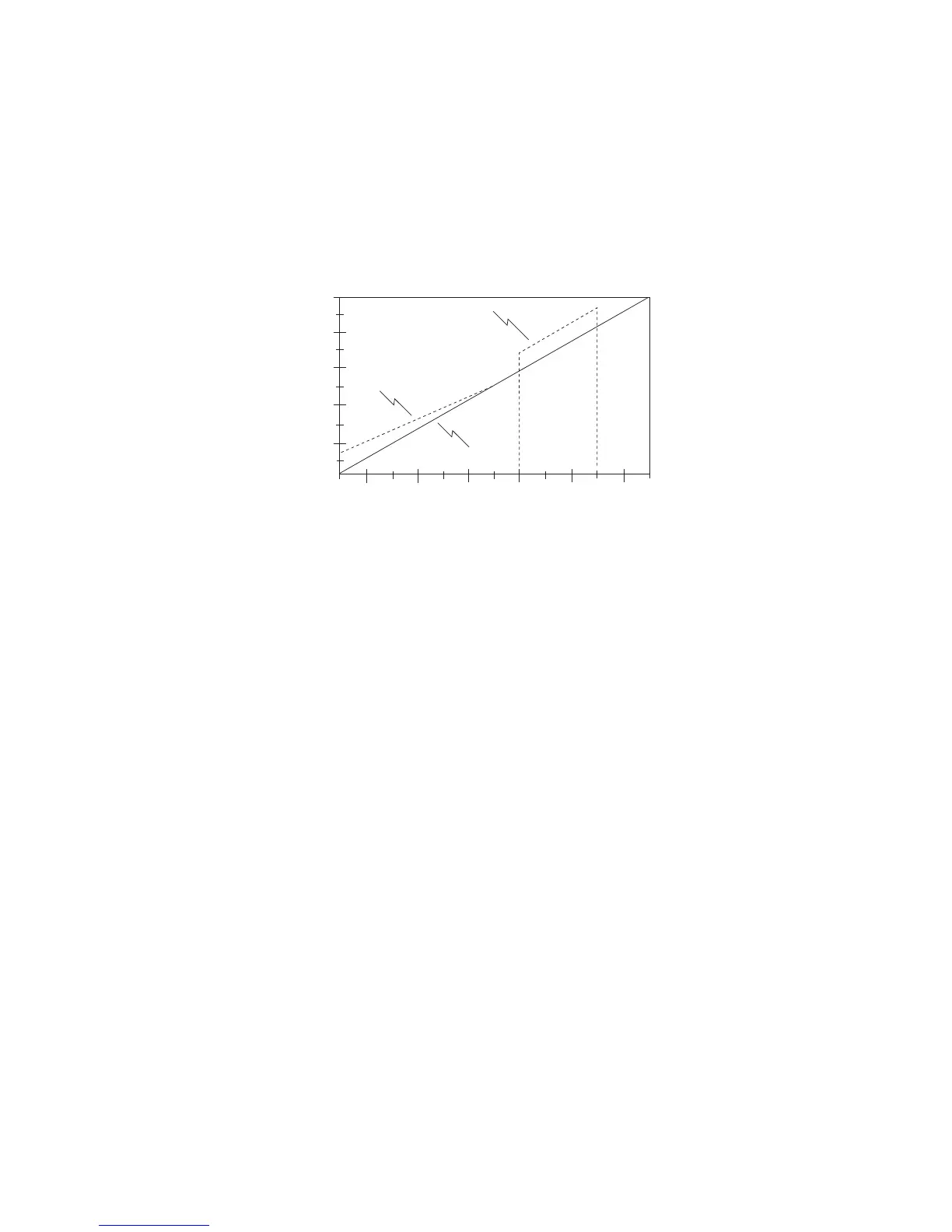
The above diagram illustrates how FX BOOST and AC BOOST alter the V/Hz ratio to increase motor
torque. FX BOOST sets the boost at 0 Hz (approximately 15% in the example above), and as the output
frequency approaches 30 Hz, the boost decreases to zero. AC BOOST only functions during acceleration.
In the diagram above, the drive is operating at 35 Hz and is then commanded to 50 Hz. The output voltage
is increased by the AC BOOST setting (approximately 15% in the example above) during acceleration to
the new speed setpoint. Once the new setpoint is reached, the output voltage returns to normal.
21 SLIP CMP (SLIP COMPENSATION)
SLIP COMPENSATION is used to compensate for changes in motor speed ("slip") which occur due to
changes in load. In a standard AC induction motor, as the load on the motor increases, the motor current
increases and the motor shaft speed decreases. By increasing the output frequency in response to the
increased motor current, SLIP COMPENSATION is able to counteract the reduction in motor sped due to
increased load. This parameter is useful in applications where precise speed regulation is needed, even under
changing load conditions. The use of SLIP COMPENSATION can result in speed regulation of less than
1% of base speed in most applications. SLIP COMPENSATION is often set to 3%, which is the standard
slip rating of most AC induction motors.
55

 Loading...
Loading...