Application examples
4.3 Example 3: Path control
4−14
l
EDSVS9332P−EXT DE 2.0
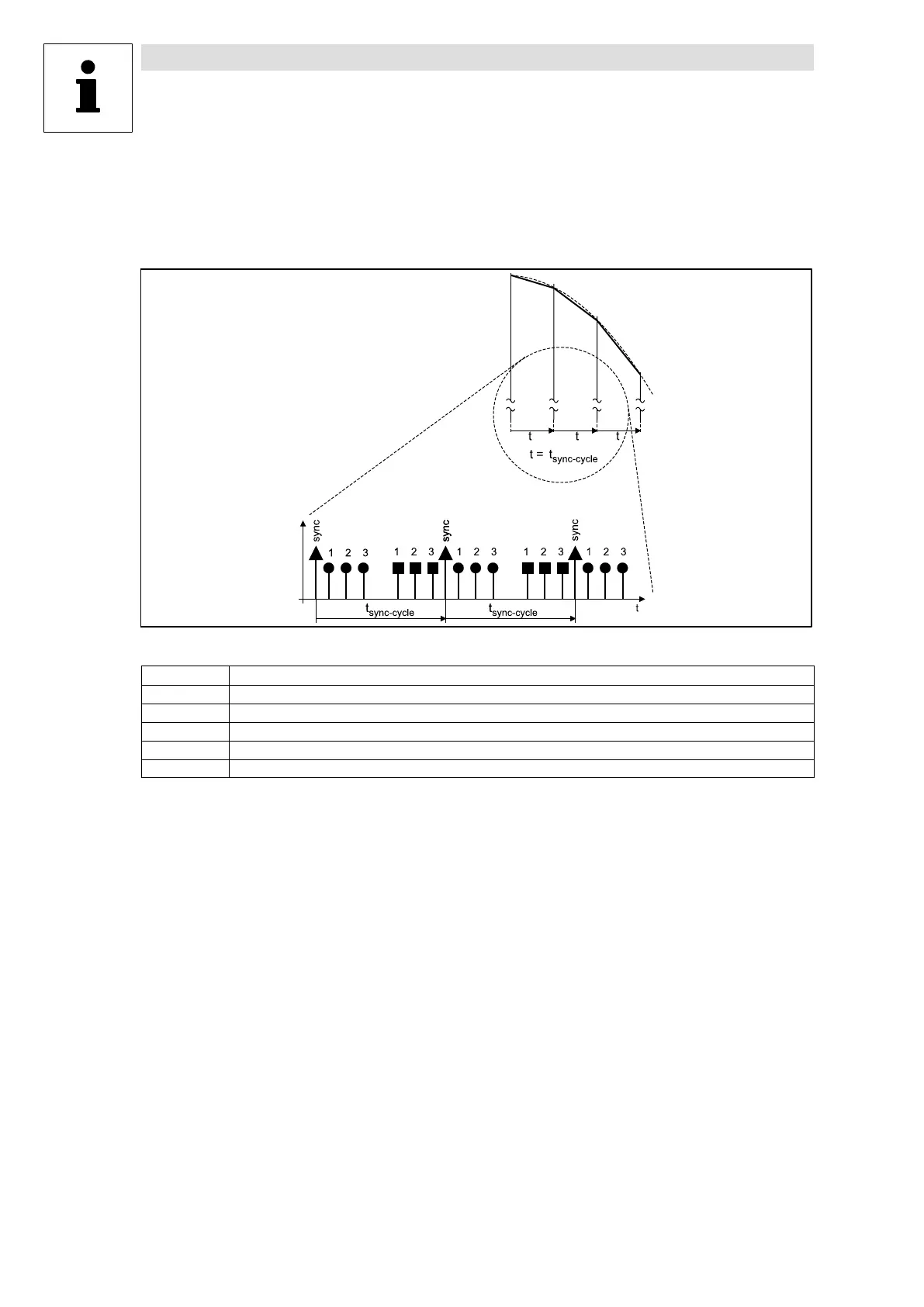
l Telegram sequence
– Send new position setpoint to slave 1, slave 2 and slave 3
– Send sync telegram
– All slaves reply with CAN−OUT1
Fig. 1 Sequence of communication between master and slaves
Character
Explanation
●
Response of the controller (CAN−IN1)
■
Send setpoint position (from the master) to the controller
1
Slave 1
2
Slave2
3
Slave 3
Input of the target position by an external control (here: PLC)
l The setpoint position is determined by cyclic set phase increments (t
sync−cycle
) in increments of
milliseconds ("150μs).
The input must be crystal−precise in the long term.
l The POS function block calculates the speed and the acceleration.
l Inputs in v
max
(C1240) and a
max
(C1250) have no effect.
l This means that speed profiles are possible in any form (e.g. cams).
l Activation by POSD−PSET−SWT = HIGH (e.g. FIXED1)
 Loading...
Loading...