9
It is necessary to have a working knowledge of terms such as “frequency”, “carrier frequency”, “burst
frequency” and “premodulation” in order to understand Frequency Difference and Premodulated interfer-
ential currents.
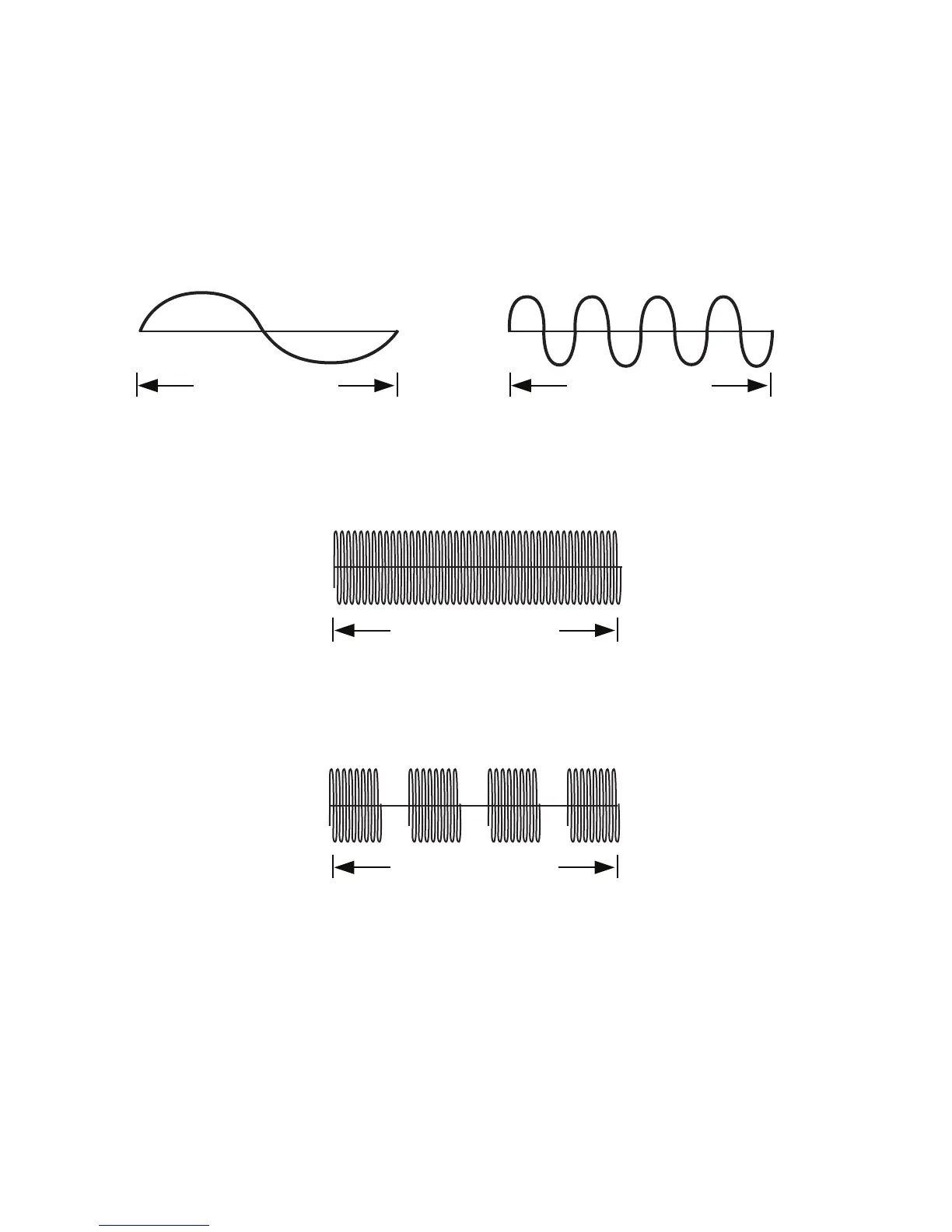
Frequency is synonymous with pulses per second, cycles per second and hertz. In an alternating
current (AC) there is both a positive and a negative component which together form one cycle. The number
of these cycles produced in one second therefore, determine the frequency (or hertz, or pulses per second
or cycles per second).
Carrier frequency is the number of cycles per second a generator produces. Most interferential units,
including the LSI System IV, operate at a carrier frequency of 4000Hz.
Burst frequency or Pre-modulation is the act of taking the carrier frequency and “bursting” it into a
predetermined number of bursts or packages per second without changing the carrier frequency.
In the above example, the carrier frequency of 4000Hz has been burst or pre-modulated into 4Hz with each
burst still containing the carrier frequency at the rate of 4000Hz. By maintaining the carrier of 4000Hz, the
advantage of reduced tissue resistance to the current is preserved.
It is necessary to have a working knowledge of terms such as “frequency”, “carrier frequency”, “burst
frequency” and “premodulation” in order to understand Frequency Difference and Premodulated
interferential currents.
Frequency is synonymous with pulses per second, cycles per second and hertz . In an alternating current
(AC) there is both a posititve and a negative component which together form one cycle. The number of
these cycles produced in one second therefore, determine the frequency (or hertz, or pulses per second or
cycles per second).
Carrier frequency is the number of cycles per second a generator produces. Most interferential units,
including the LSI System II, operate at a carrier frequency of 4000Hz.
Burst frequency or Pre-modulationis the act of taking the carrier frequency and “bursting” it into a
predetermined number of bursts or packages per second without changing the carrier frequency.
In the above example, the carrier frequency of 4000Hz has been burst or pre-modulated into 4Hz with
each burst still containing the carrier frequency at the rate of 4000Hz. By maintaining the carrier of
4000Hz, the advantage of reduced tissue resistance to the current is preserved.
2
1 sec. (1HZ)
1 sec. (4000HZ)
1 sec.
1 sec. (4HZ)
It is necessary to have a working knowledge of terms such as “frequency”, “carrier frequency”, “burst
frequency” and “premodulation” in order to understand Frequency Difference and Premodulated
interferential currents.
Frequency is synonymous with pulses per second, cycles per second and hertz . In an alternating current
(AC) there is both a posititve and a negative component which together form one cycle. The number of
these cycles produced in one second therefore, determine the frequency (or hertz, or pulses per second or
cycles per second).
Carrier frequency is the number of cycles per second a generator produces. Most interferential units,
including the LSI System II, operate at a carrier frequency of 4000Hz.
Burst frequency or Pre-modulationis the act of taking the carrier frequency and “bursting” it into a
predetermined number of bursts or packages per second without changing the carrier frequency.
In the above example, the carrier frequency of 4000Hz has been burst or pre-modulated into 4Hz with
each burst still containing the carrier frequency at the rate of 4000Hz. By maintaining the carrier of
4000Hz, the advantage of reduced tissue resistance to the current is preserved.
2
1 sec. (1HZ)
1 sec. (4000HZ)
1 sec.
1 sec. (4HZ)
It is necessary to have a working knowledge of terms such as “frequency”, “carrier frequency”, “burst
frequency” and “premodulation” in order to understand Frequency Difference and Premodulated
interferential currents.
Frequency is synonymous with pulses per second, cycles per second and hertz . In an alternating current
(AC) there is both a posititve and a negative component which together form one cycle. The number of
these cycles produced in one second therefore, determine the frequency (or hertz, or pulses per second or
cycles per second).
Carrier frequency is the number of cycles per second a generator produces. Most interferential units,
including the LSI System II, operate at a carrier frequency of 4000Hz.
Burst frequency or Pre-modulationis the act of taking the carrier frequency and “bursting” it into a
predetermined number of bursts or packages per second without changing the carrier frequency.
In the above example, the carrier frequency of 4000Hz has been burst or pre-modulated into 4Hz with
each burst still containing the carrier frequency at the rate of 4000Hz. By maintaining the carrier of
4000Hz, the advantage of reduced tissue resistance to the current is preserved.
2
1 sec. (1HZ)
1 sec. (4000HZ)
1 sec.
1 sec. (4HZ)
 Loading...
Loading...