18
Chapter 2: Diagnostic GR8
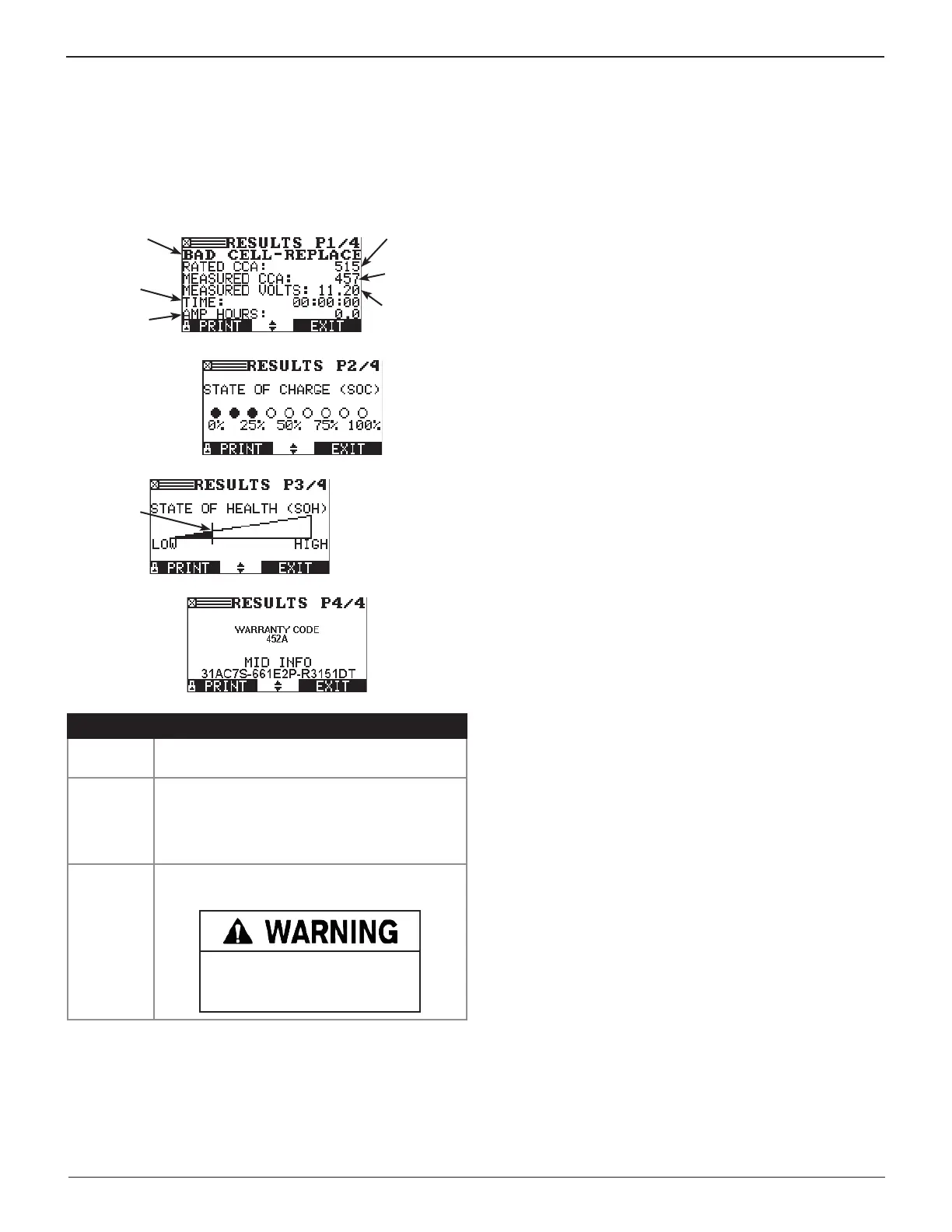
Diagnostic Charge Results
The charger displays one of three battery decisions and an
analysis, which includes the battery State-of-Charge (SOC) and
State-of-Health (SOH).
Use
or
to scroll to each screen. Press EXIT, to return to
the Main Menu. Press PRINT to print the test results.
Measured
Voltage
Measured
Capacity
Selected
Rating
Total Charging
Time
Decision
Replaced
Amp Hours
Filled circles
indicate
percentage SOC
Measurement
near line
suggests
a marginal
battery
Pass/Fail
Threshold
For REPLACE
decisions only
Decision Recommended Action
GOOD
BATTERY
Return the battery to service.
REPLACE
BATTERY
A REPLACE BATTERY result may also mean
a poor connection between the battery cables
and the battery. After disconnecting the battery
cables, retest the battery using the out-of-
vehicle test before replacing it.
BAD CELL–
REPLACE
Replace the battery. This decision indicates a
bad cell within the battery.
Risk of explosive gases
Charging a battery with a bad cell
my cause the battery to explode.
State-of-Charge (SOC)
The State-of-Charge (SOC) is one of several important factors
that aect the battery’s ability to crank an engine. It is a mea-
sure of the available capacity remaining of a battery expressed
as a percentage of its original rated capacity. During testing,
the charger accurately detects a battery’s State-of-Charge and
indicates this as part of the test results.
State-of-Health (SOH)
Another factor aecting a battery’s ability to crank an engine
is its actual condition or State-of-Health (SOH). It is a measure
of the battery’s condition relative to a fresh battery. Based on
cranking rating, open-circuit voltage, conductance (ability to
deliver current) and battery temperature, the charger will not
only qualify a battery as “good” or “bad” (should be replaced),
but can also identify a “marginal” battery.
Although a State-of-Health problem can be the result of
defects in construction, it is most often the result of normal
wear-out mechanisms, which are dependant on vehicle needs,
climate, and operating conditions. This results in irreversible
physical and chemical changes until eventually the battery
can no longer hold a charge and supply the power necessary
to start the car and provide auxiliary power to the electrical
system.
As the battery approaches end of life, its deterioration acceler-
ates, until it nally fails to start the vehicle. Before failing, the
battery may start the vehicle under normal conditions but may
not be able to operate in more extreme conditions. Extreme
heat or cold could expose a weak battery and cause it to fail.
The charger predicts a battery’s State-of-Health based on the
characterization of Toyota, Lexus, and Scion OEM batteries and
OEM replacement batteries.
 Loading...
Loading...











