5
CHAPTER 1 ● Ventilation for Healthy Living
3. Ventilation Method
3.1 Ventilation class and selection points
An appropriate ventilation method must be selected according to the purpose.
Ventilation is composed of “Supply air” and “Exhaust air” functions. These functions are classified according to natural flow or
mechanical ventilation using a fan (forced ventilation).
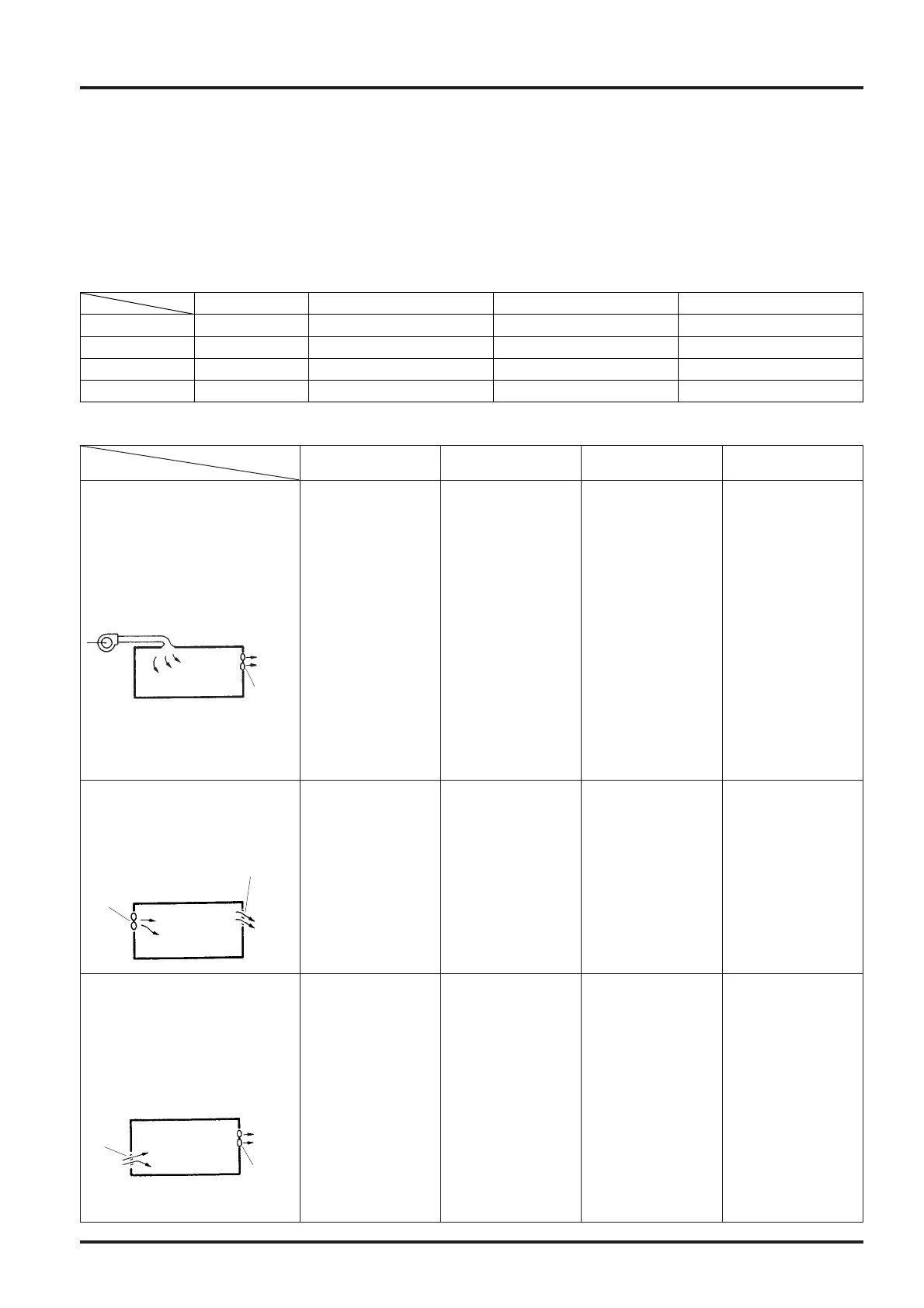
Classification of mechanical ventilation
Classification of ventilation (according to Building Standards Law)
1. Class 1 ventilation
Fresh outdoor air is mechanically
brought in and simultaneously the
stale air in the room is mechanically
discharged.
2. Class 2 ventilation
Fresh outdoor air is mechanically
brought in and the exhaust air is
discharged from the exhaust air
outlet (natural).
3. Class 3 ventilation
The stale air in the room is
mechanically discharged and
simultaneously fresh outdoor air is
mechanically introduced from the
supply air diffuser (natural).
Ex. of application
•Ventilation of air
conditioned rooms.
(buildings, hospitals,
etc.)
•Ventilation of room
not facing an outer
wall. (basement,
etc.)
•Ventilation of large
room. (office, large
conference room,
hall, etc.)
• Surgery theatre.
• Clean rooms.
• Foodstuff processing
factories.
• Local ventilation in
kitchens.
•Ventilation of hot
exhaust air from
machine room, etc.
•Ventilation of humid
exhaust air from
indoor pools, bath-
rooms, etc.
• General simple
ventilation.
System effect
By changing the
balance of the supply
fan and exhaust fan’s
air volumes, the
pressure in the room
can be balanced
freely, and the
interrelation with
neighboring spaces
can be set freely.
As the room is
pressurized, the flow
of odors and dust,
etc., from neighboring
areas can be
prevented.
The exhaust air is
removed from a local
position in the room,
and dispersion of the
stale air can be
prevented by applying
an entire negative
pressure.
Design and construction
properties
•
An ideal design in which
the supply air diffuser
and exhaust air outlet
position relation and air
volume, etc., can be set
freely is possible.
•A system which adjusts
the temperature and
humidity of the supply
air diffuser flow to the
room environment can
be incorporated.
•
The supply and
exhaust volume can be
set freely according to
the changes in
conditions.
• The position and
shape of the supply
air diffuser can be
set.
• The temperature and
humidity of the
supply air diffuser
flow can be set
accordingly, and
dust can be removed
as required.
•Effective exhausting
of dispersed stale air
generation sites is
possible from a local
exhaust air outlet.
•Ventilation in which
the air flow is not felt
is possible with the
supply air diffuser
setting method.
Selection points
• Accurate supply air
diffuser can be
maintained.
• The room pressure
balance can be
maintained.
• The supply air
diffuser temperature
and humidity can be
adjusted and dust
treatment is
possible.
• The pressure is
positive.
•
The supply air diffuser
temperature and
humidity can be
adjusted, and dust
treatment is possible.
•
The positional relation
of the exhaust air
outlet to the supply air
diffuser is important.
• The room pressure
is negative.
• Local exhaust is
possible.
•Ventilation without
dispersing stale air is
possible.
•Ventilation with
reduced air flow is
possible.
•
The positional relation
of the exhaust air
outlet to the supply air
diffuser is important.
Supply
air
diffuser
Exhaust
fan
Exhaust
air
outlet
Exhaust
fan
Exhaust
fan
Stale
air
Fresh
outdoor
air
Supply Exhaust Ventilation volume Room pressure
Class 1 Mechanical Mechanical Random (constant) Random
Class 2 Mechanical Natural Random (constant) Positive pressure
Class 3 Natural Mechanical Random (constant) Negative pressure
Class 4 Natural Mechanical & natural Limited (inconstant) Negative pressure

 Loading...
Loading...











